In the realm of stainless steel, the choice between 420HC and 440C can significantly impact the performance of various products. For intermediate-level enthusiasts and professionals, understanding their differences is crucial. 420HC and 440C vary notably in key aspects like hardness and corrosion resistance. While one might offer better durability for knife blades, the other could excel in surgical tool applications. So, which steel is truly the better option for your specific needs? Let’s dive deeper into the details.
Introduction to Stainless Steel
Understanding Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a widely used material renowned for its corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. These qualities make it popular in many industries such as construction, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products. Two notable grades of stainless steel are 420HC and 440C, each offering distinct properties suitable for specific applications.
Properties of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel’s defining characteristic is its ability to resist corrosion, which is achieved through the addition of chromium. Chromium (at least 10.5%) creates a protective chromium oxide layer on the steel surface, which prevents further rusting. Besides corrosion resistance, stainless steel is valued for its:
- Strength: Stainless steel exhibits high tensile strength, making it suitable for load-bearing applications.
- Durability: Its resistance to wear and impact ensures long-lasting performance.
- Versatility: Stainless steel can be alloyed with other metals to enhance specific properties such as hardness and machinability.
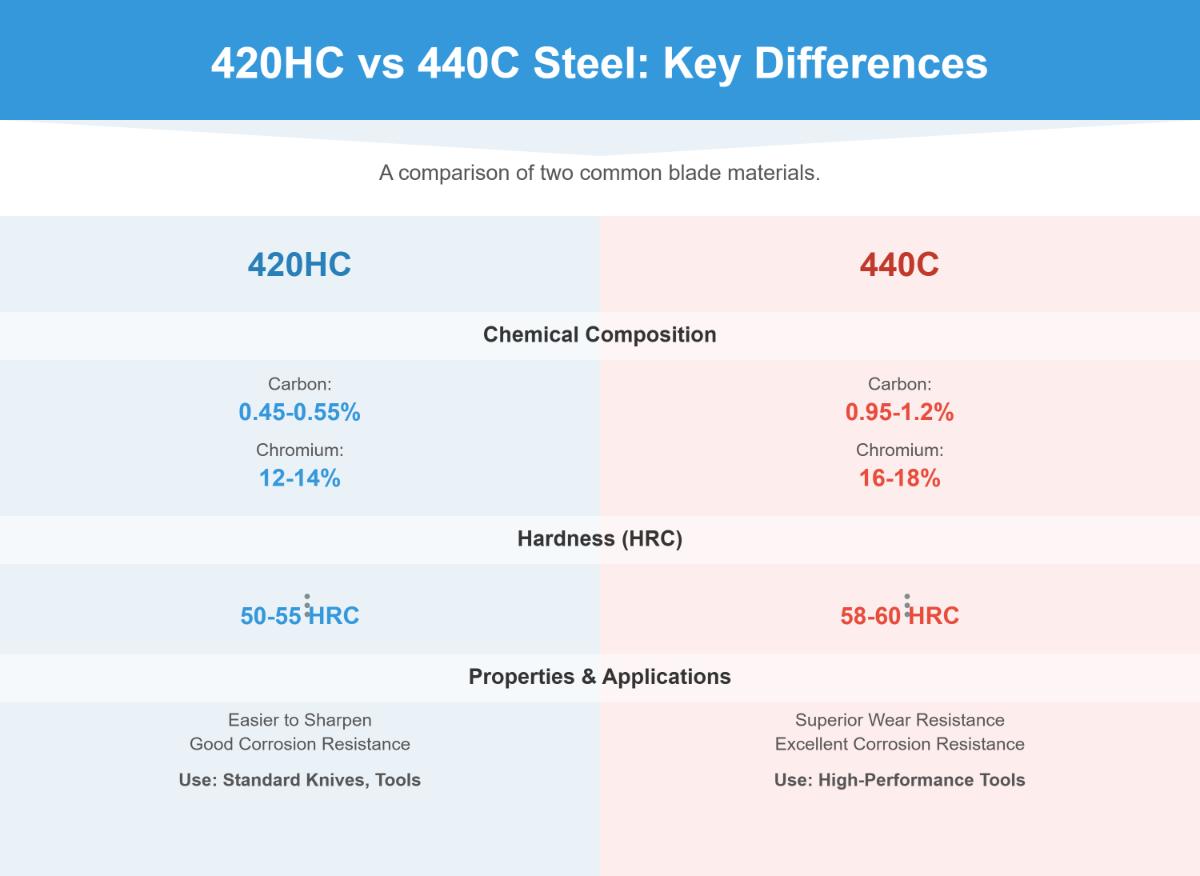
Composition and Grades: 420HC vs 440C
The chemical composition of stainless steel determines its properties and performance in various applications.
420HC Stainless Steel
- Chromium Content: 12-14%
- Carbon Content: 0.45-0.55%
- Additional Elements: Includes small amounts of silicon, manganese, and molybdenum for improved performance.
440C Stainless Steel
- Chromium Content: 16-18%
- Carbon Content: 0.95-1.20%
- Additional Elements: Contains higher levels of carbon and chromium, plus trace amounts of silicon and manganese.
Comparative Analysis
Hardness
Hardness is essential for applications needing wear resistance and edge retention.
- 420HC: Achieves a Rockwell Hardness (HRC) of approximately 50-55.
- 440C: Can reach an HRC of 58-60, making it one of the hardest stainless steels available.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is vital for applications exposed to moisture, chemicals, and varying environmental conditions.
- 420HC: Offers good corrosion resistance, suitable for mild environments.
- 440C: Exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to its higher chromium content.
Wear Resistance
Wear resistance determines how well a material can withstand abrasion and repeated use.
- 420HC: Provides adequate wear resistance for everyday tools and applications.
- 440C: Delivers excellent wear resistance, ideal for high-performance tools and components.
Applications of 420HC and 440C
Both 420HC and 440C stainless steels are used in specific applications based on their properties:
- 420HC: Commonly found in cutlery, surgical instruments, and industrial applications where ease of sharpening is essential.
- 440C: Preferred for precision knife blades, ball bearings, and surgical instruments requiring superior wear resistance and hardness.
Knowing the differences between 420HC and 440C helps manufacturers and engineers choose the right material, ensuring better performance and durability.
420HC Steel: An Overview
Chemical Composition of 420HC Steel
420HC steel, part of the martensitic stainless steel family, is known for its high carbon content and well-balanced alloy composition. This combination allows the steel to be heat-treated to achieve excellent properties.
420HC steel contains approximately 0.45% carbon, 13% chromium, up to 0.4% manganese, up to 0.4% silicon, around 0.5% nickel, about 0.6% molybdenum, and roughly 0.3% vanadium. The presence of these elements contributes to the steel’s overall balance of hardness, corrosion resistance, and toughness.
Key Properties and Characteristics
Hardness
One of the standout features of 420HC steel is its ability to achieve significant hardness through proper heat treatment. With a Rockwell Hardness (HRC) rating of about 55 – 58, it strikes a good balance between hardness and ease of sharpening, making it ideal for applications where a sharp edge is crucial.
Corrosion Resistance
420HC steel’s high chromium content provides excellent corrosion resistance. This makes it suitable for use in environments with moderate moisture and humidity exposure. The protective chromium oxide layer formed on the surface of the steel helps prevent rust and degradation, ensuring longevity and reliability in various applications.
Edge Retention and Sharpening
Although 420HC steel may not hold its edge as long as some higher – end steels, it offers respectable edge retention for its class. Additionally, it is relatively easy to sharpen, which is a major advantage for users who need to maintain a sharp edge frequently.
Toughness
420HC steel exhibits good toughness, meaning it can withstand impacts and daily use without chipping or breaking easily. This toughness is essential for tools and knives that are subjected to rough handling and demanding conditions.
Applications of 420HC Steel
Thanks to its balanced properties, 420HC steel is widely used in cutlery and general – purpose knives. Its moderate hardness and ease of sharpening make it a popular choice for kitchen knives, outdoor knives, and utility blades, while its corrosion resistance ensures durability even in humid environments.
In the medical field, 420HC steel is used to manufacture surgical tools. The steel’s ability to achieve a sharp edge, coupled with its corrosion resistance, makes it suitable for precision instruments that require frequent sterilization. Its toughness ensures that the tools can withstand repeated use and autoclaving without compromising their performance.
420HC steel is also utilized in various industrial applications where moderate hardness and corrosion resistance are required. This includes the production of scissors, hand tools, and other equipment that benefit from the steel’s balance of durability and ease of maintenance. Its ability to be easily sharpened and its resistance to wear make it a popular choice for items that undergo frequent use and require a reliable cutting edge.
440C Steel: An Overview
Chemical Composition
440C is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel. It has a carbon content of 0.95 – 1.20% and a chromium content of 16 – 18%, contributing significantly to its robust mechanical properties. In contrast, 420HC steel has a lower carbon content of 0.45 – 0.55% and a chromium content of 12 – 14%. The higher carbon and chromium levels in 440C steel are key to its enhanced performance characteristics.
Key Properties and Characteristics
Hardness
440C steel can achieve a Rockwell C hardness of up to 60 through heat treatment, making it one of the hardest stainless steels. This is notably higher than the up-to-HRC 55 hardness of 420HC steel. The high hardness of 440C provides excellent edge retention and wear resistance, which is crucial for applications requiring a sharp and long-lasting edge.
Corrosion Resistance
Thanks to its higher chromium content, 440C offers better corrosion resistance than 420HC. Chromium forms a protective oxide layer on the steel’s surface, preventing rust and degradation. While 420HC has good corrosion resistance suitable for mild environments, 440C can better withstand more corrosive conditions.
Machinability
The higher carbon content in 440C makes it harder and more brittle, leading to potential issues like tool wear and chipping during machining. In contrast, 420HC is relatively easier to machine and shape, making it more suitable for general-purpose manufacturing processes.
Applications
440C is widely used in high-performance tools, ideal for high-quality knife blades due to its hardness and excellent edge retention. In the medical field, it is used to manufacture surgical instruments that require precision and durability. Additionally, it is employed in bearings and valve components due to its excellent wear resistance. On the other hand, 420HC is more commonly found in budget-friendly knives, general tools, and applications where ease of maintenance is a priority.
Comparative Evaluation of 420HC and 440C Steel
Hardness
Hardness Measurement Techniques
Hardness in steels is commonly measured using the Rockwell scale. The Rockwell hardness test involves pressing an indenter into the material under a specific load and measuring the depth of the indentation. For both 420HC and 440C steels, the Rockwell C (HRC) scale is often used, providing a numerical value that indicates the steel’s resistance to indentation.
Comparative Hardness Analysis
420HC steel typically achieves a Rockwell hardness rating in the range of 56 – 59 HRC. This level of hardness is suitable for general-purpose knives and tools, offering a good balance between hardness and toughness. For instance, it is often used in hunting knives, where a durable yet relatively easy-to-sharpen blade is essential. In contrast, 440C steel can reach a Rockwell hardness rating of 58 – 62 HRC. The higher hardness of 440C results in superior edge retention, making it ideal for high-performance knives used in professional kitchens and precision cutting tools used in industrial applications.
Corrosion Resistance
Factors Influencing Corrosion Resistance
The primary factor influencing the corrosion resistance of stainless steels like 420HC and 440C is the chromium content. Chromium forms a protective layer of chromium oxide on the steel’s surface, which acts as a barrier against rust and corrosion. Other factors include the presence of additional alloying elements, the heat treatment process, and the environment in which the steel is used.
Comparative Corrosion Resistance Analysis
Both 420HC and 440C are stainless steels and offer good corrosion resistance. However, 440C has a higher chromium content (16 – 18%) compared to 420HC (12 – 14%). This higher chromium content allows 440C to form a more robust and continuous chromium oxide layer, enhancing its resistance to rust and corrosion, especially in harsh environments like marine settings or during prolonged exposure to moisture.
Wear Resistance
Definition and Importance of Wear Resistance
Wear resistance refers to a material’s ability to withstand abrasion, friction, and other forms of wear during use. In applications such as knife blades, bearings, and cutting tools, wear resistance is crucial as it determines the lifespan and performance of the component. A material with high wear resistance will maintain its shape and functionality longer, reducing the need for frequent replacement and ensuring consistent performance.
Comparative Wear Resistance Analysis
420HC steel provides adequate wear resistance for everyday tools and general-purpose applications. However, due to its relatively lower hardness, it may experience more wear over time compared to 440C. With its higher hardness and more wear-resistant alloy composition, 440C offers excellent wear resistance. This makes it well-suited for high-performance applications where the material is subjected to heavy use and abrasive conditions, such as in tactical knives, surgical instruments, and high-precision industrial tools.
Heat Treatment Processes
Overview of Heat Treatment in Steel Production
Heat treatment is essential in steel production for changing the physical and chemical properties of steel. It involves heating and cooling steel in a controlled manner, which modifies its internal structure and significantly enhances performance.
Heat Treatment Specifics for 420HC
Process
The heat treatment process for 420HC steel is relatively straightforward. It typically starts with austenitizing, where the steel is heated to a specific temperature range to transform its structure into austenite. This is followed by quenching, a rapid cooling process that hardens the steel.
Achieved Properties
After heat treatment, 420HC steel offers good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for mild environments. It is also relatively easy to sharpen, which is a valuable property for tools and knives. Additionally, it has decent toughness, allowing it to withstand normal use without excessive chipping or breaking.
Heat Treatment Specifics for 440C
Process
440C steel requires a more meticulous heat treatment process to reach its full potential. It involves heating the steel to a high temperature, typically around 1010 – 1065°C, to form austenite. Then, it is rapidly cooled, often in oil or air, through quenching. Subsequently, tempering is carried out at a temperature usually between 150 – 370°C. This process results in a Rockwell hardness rating of 58 – 60 HRC.
Achieved Properties
The heat-treated 440C steel exhibits exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention. These properties make it ideal for high-performance applications such as high-end knife blades and precision components that are subjected to heavy use and abrasive conditions.
Impact of Heat Treatment on Both Steels
Hardness
Heat treatment greatly impacts the hardness of both steels. 440C, with its more complex heat treatment, achieves a higher hardness compared to 420HC. The higher carbon content in 440C also contributes to its ability to attain greater hardness, which is crucial for applications requiring long-lasting sharp edges.
Corrosion Resistance
Both steels resist corrosion, but 440C, with its higher chromium content and proper heat treatment, offers superior resistance. The heat treatment helps in forming a more stable and continuous chromium oxide layer on the surface of 440C, protecting it from rust and corrosion better than 420HC, especially in harsh environments.
Wear Resistance
Heat treatment enhances the wear resistance of both steels, but 440C shows excellent wear resistance due to its high hardness and optimized microstructure after heat treatment. In contrast, 420HC has moderate wear resistance, which is sufficient for general-purpose tools.
Machinability
The heat-treated hardness of the steels also impacts their machinability. 420HC, with its moderate hardness, is easier to machine compared to 440C, which is more challenging to cut, shape, and finish due to its higher hardness.
Industrial Applications
Cutlery and Knife Production
Comparison of 420HC and 440C in Knife Making
In the knife production industry, choosing between 420HC and 440C steel depends on the balance desired between edge retention, hardness, and maintenance ease.
420HC Steel is favored for its ease of sharpening and moderate hardness, providing a Rockwell hardness (HRC) of approximately 56-59. This makes it suitable for general-purpose knives and kitchen cutlery, as the lower hardness allows for easier and more frequent sharpening. On the other hand, 440C Steel offers superior edge retention and higher hardness, reaching up to 58-62 HRC. This makes it ideal for high-end, professional-grade knives where long-lasting sharpness is critical, though it can be more challenging to sharpen.
Pros and Cons in Cutlery Use
- 420HC Steel:
- Pros: Easier to sharpen, cost-effective, good corrosion resistance.
- Cons: Lower edge retention, moderate wear resistance.
- 440C Steel:
- Pros: Excellent edge retention, superior wear resistance, higher corrosion resistance.
- Cons: More difficult to sharpen, generally higher cost.
Surgical Tools Manufacturing
Requirements for Surgical Tool Materials
Surgical tools need materials that are precise, durable, and can endure frequent sterilization. The steel used must provide excellent corrosion resistance to prevent degradation from sterilizing agents and bodily fluids.
Performance of 420HC and 440C in Surgical Tools
420HC Steel is commonly used for surgical instruments due to its good corrosion resistance and moderate hardness. It provides a reliable balance between ease of maintenance and performance, making it suitable for instruments that require frequent sharpening.
440C Steel is often preferred for high-precision surgical tools that need superior hardness and wear resistance. Its higher chromium content ensures better corrosion resistance, making it ideal for instruments that must maintain their integrity under harsh sterilization conditions.
Bearings
Importance of Material Choice in Bearings
Bearings are crucial in many mechanical systems, needing materials that can handle high loads and provide excellent wear resistance. The choice of material impacts the bearing’s lifespan and performance, especially during continuous operation.
Suitability of 420HC and 440C for Bearings
420HC Steel is less commonly used for bearings due to its lower wear resistance and hardness. However, it can be utilized in applications where the bearings are subject to moderate loads and require frequent maintenance.
440C Steel is highly suitable for bearing applications due to its superior hardness and wear resistance. It is capable of withstanding high loads and offers excellent longevity, making it the preferred choice for high-performance bearings in demanding environments.
Other Industrial Applications
420HC Steel is commonly used in industrial chains, fasteners, and tools, where its moderate hardness and corrosion resistance are adequate. Its ease of machining and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for general-purpose industrial components.
440C Steel is utilized in high-performance environments, including valve components, pump parts, molds, and dies. Its superior hardness and wear resistance are critical for applications where durability and long-lasting performance are essential.
Market Considerations
Overview of 420HC and 440C Steels
420HC Steel
420HC steel is known for being affordable and practical for budget-friendly uses. It contains a lower carbon content (0.45% to 0.55%), which contributes to its moderate hardness and ease of sharpening. These traits make 420HC ideal for users who value easy maintenance and cost-effectiveness, offering good corrosion resistance and toughness despite not retaining an edge as well as higher-end steels.
440C Steel
In contrast, 440C steel has a higher carbon content (0.95% to 1.2%), providing superior hardness and edge retention. This makes it ideal for high-performance knives and applications requiring long-lasting sharpness. The extra chromium in 440C improves its corrosion resistance, making it great for tough environments. However, it is more challenging to machine and generally more expensive.
Market Applications
General Use and Budget Knives
420HC steel is commonly used in budget knives and multi-tools. Its ease of sharpening and good corrosion resistance make it an attractive option for general-purpose tools. Consumers who need reliable yet affordable knives often prefer 420HC for its balance of performance and cost.
High-Performance Knives
When it comes to high-performance knives, 440C is often the top choice. Its superior hardness and edge retention make it suitable for professional-grade knives, including those used in demanding environments. The enhanced corrosion resistance of 440C ensures durability even under harsh conditions.
Key Differences
| Feature | 420HC Steel | 440C Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content | Lower (0.45% to 0.55%) | Higher (0.95% to 1.2%) |
| Hardness (HRC) | Moderate (50-55) | High (58-60) |
| Edge Retention | Fair; doesn’t hold an edge as well as 440C | Excellent; maintains sharpness over time |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good; suitable for most environmental conditions | Superior; higher chromium content enhances resistance to corrosion |
| Sharpening Ease | Easy to sharpen | Relatively easier to sharpen than very hard steels, but more challenging than 420HC |
| Machinability | Easier to machine | More difficult to machine due to higher hardness |
| Price and Availability | Generally less expensive and widely available | More expensive; popular in high-end applications due to its superior properties |
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
While there’s a growing demand for the durability of 440C steel, 420HC remains popular among budget-conscious consumers for its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance.
The knife steel market is continually evolving, with new materials offering enhanced performance. However, 420HC and 440C remain staples due to their well-understood properties and cost-effectiveness. Both steels have carved out specific niches in the market, balancing performance with affordability and maintenance ease.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Buck Knives and 420HC Steel
Buck Knives is a notable example of a company that has effectively utilized 420HC steel in their products. Known for their high – quality yet affordable knives, Buck uses a special heat – treatment process that significantly enhances the performance of 420HC steel. This process increases the steel’s hardness and edge retention while maintaining its ease of sharpening. Buck’s use of 420HC steel demonstrates its suitability for general – purpose knives that require a good balance of durability, corrosion resistance, and maintenance ease. These knives are popular among outdoor enthusiasts and everyday users who value reliability and cost – effectiveness.
High – Performance Knives and 440C Steel
In contrast, high – performance knife manufacturers often opt for 440C steel due to its superior hardness and edge retention. Brands such as Benchmade and Spyderco incorporate 440C into their premium knife models. These models are designed for demanding environments. The high carbon and chromium content in 440C steel provide excellent wear and corrosion resistance, making these knives ideal for professional chefs, tactical uses, and outdoor survival scenarios. These high – end knives are favored for their ability to maintain a sharp edge over extended use, reducing the need for frequent sharpening.
Surgical Instruments and 440C Steel
The medical industry also benefits from the superior properties of 440C steel. Surgical instruments made from 440C are prized for their precision, hardness, and corrosion resistance. The high hardness of 440C steel allows cutting tools like scalpels and surgical scissors to stay sharp through many procedures. Additionally, the excellent corrosion resistance of 440C steel is crucial for withstanding the harsh sterilization processes involving chemicals and high temperatures. This makes 440C a preferred material for surgical tools that require both durability and precision.
Industrial Bearings and 440C Steel
In the realm of industrial applications, 440C steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of high – performance bearings. 440C steel bearings can handle high loads and have excellent wear resistance, which is essential for maintaining performance in demanding environments. The hardness and robustness of 440C steel reduce the wear and tear on bearings, extending their operational lifespan and reliability. This makes them ideal for use in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery industries where durability and precision are paramount.
General – Purpose Tools and 420HC Steel
420HC steel finds extensive use in the production of general – purpose tools due to its balanced properties. Scissors, hand tools, and various industrial components benefit from the moderate hardness and good corrosion resistance of 420HC steel. Its ease of machining and cost – effectiveness make it a practical choice for manufacturers producing tools that need to be both durable and easy to maintain. The toughness of 420HC steel means these tools can handle regular use with little wear.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the key differences between 420HC and 440C steel?
The key differences between 420HC and 440C steel primarily revolve around their chemical composition, hardness, corrosion resistance, and typical applications.
420HC steel has a lower carbon content (0.45% to 0.55%), making it relatively softer with a Rockwell hardness (HRC) of 50-55. This lower hardness makes 420HC easier to sharpen and maintain, suitable for applications requiring frequent resharpening, such as standard knives and hand tools. Its chromium content (12-14%) provides good corrosion resistance in regular environments.
On the other hand, 440C steel contains a higher carbon content (0.95% to 1.2%), resulting in a significantly higher hardness, typically reaching 58-60 HRC. This high hardness grants 440C superior wear resistance, ideal for high-performance tools that demand durability and edge retention. Additionally, its higher chromium content (16-18%) offers excellent corrosion resistance, even in more aggressive environments.
Which steel is better for knife blades?
The choice between 420HC and 440C steel for knife blades depends on specific needs. 420HC offers good corrosion resistance, is easy to sharpen, and has decent toughness, making it ideal for general – purpose and budget knives. It has a Rockwell hardness of 56–59 HRC. On the other hand, 440C provides superior hardness, edge retention, and wear resistance (58–62 HRC), but is more difficult to sharpen. It is better suited for high – end knives and demanding applications. So, for general use and cost – effectiveness, 420HC is better, while for high – performance requirements, 440C is the preferred choice.
How do 420HC and 440C steel compare in terms of corrosion resistance?
420HC and 440C steels both offer good corrosion resistance due to their chromium content, but there are significant differences. 440C steel, with a chromium content of 16-18%, provides superior corrosion resistance compared to 420HC steel, which contains 12-14% chromium. This higher chromium content in 440C forms a more stable chromium oxide layer, offering better protection against corrosive elements. Additionally, 440C includes other alloying elements like molybdenum and vanadium, further enhancing its resistance in harsh environments such as fresh water, mild alkalies, and some acids. In contrast, 420HC is more suitable for milder conditions, though it still offers good resistance. Proper heat treatment and surface finishing, like passivation, are essential for maximizing the corrosion resistance of both steels.
What are the effects of heat treatment on the properties of 420HC and 440C steel?
Heat treatment significantly affects the properties of 420HC and 440C steel. For 420HC, with a carbon content of 0.4 – 0.5%, its less complex heat treatment involves hardening to balance hardness and toughness. After treatment, it reaches a Rockwell hardness of 56 – 59, maintains good corrosion resistance, and is easier to sharpen, making it suitable for general – purpose knives and tools.
On the other hand, 440C, with 0.95 – 1.20% carbon, requires meticulous heat treatment including high – temperature heating, quenching, and tempering. This allows it to achieve a Rockwell hardness of 58 – 62, offering superior edge retention and wear resistance. However, it’s more brittle and challenging to sharpen, making it ideal for high – performance applications like quality knife blades and surgical instruments.
Are 420HC and 440C steel suitable for bearings?
Both 420HC and 440C steels have their merits and can be used for bearings, but their suitability depends on the specific application requirements.
440C steel is highly suitable for bearing applications due to its superior hardness (58-60 HRC) and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-performance and high-stress environments. Its higher chromium content (16-18%) also provides excellent corrosion resistance, which is beneficial in demanding conditions such as those found in aerospace and food processing industries. However, 440C’s higher hardness can lead to increased brittleness and higher manufacturing costs.
On the other hand, 420HC steel, with lower carbon content (0.4-0.5%) and chromium content (12-14%), offers good corrosion resistance and is easier to machine. While it is less hard and wear-resistant than 440C, it can be used in mild environments where cost and ease of maintenance are more critical.
How do the costs of 420HC and 440C steel compare?
When comparing the costs of 420HC and 440C steel, 420HC is generally the more affordable option. This cost-effectiveness is due to its lower carbon content and simpler manufacturing process, which reduce production expenses. Conversely, 440C steel is typically more expensive, attributed to its higher carbon content and the additional manufacturing steps required to achieve its superior hardness and wear resistance. The increased complexity in production and the enhanced material properties make 440C a premium choice for high-end applications. Therefore, while 440C offers better performance in terms of hardness and corrosion resistance, 420HC remains a cost-effective solution for general-purpose uses.
