When it comes to choosing the right steel for your high-performance knives, the options can be overwhelming. Among the popular choices, 420HC and 7CR steels often come up in discussions, each boasting its own set of strengths and characteristics. But what truly sets them apart? Whether you’re a knife enthusiast or a seasoned professional, understanding the nuances between these two types of steel is crucial for making an informed decision.
In this article, we’ll delve into the chemical composition and properties of 420HC and 7CR, compare their hardness and wear resistance, and examine their corrosion resistance and maintenance needs. We’ll also consider their market availability, cost implications, and the environmental impact of their production. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of which steel might be better suited for your needs. So, is 420HC superior in performance, or does 7CR offer a better value? Let’s find out.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Chemical Composition
420HC Steel
420HC steel is a high-carbon stainless steel with specific alloying elements that enhance its properties. The chemical composition of 420HC steel includes:
- Carbon (C): 0.45%
- Chromium (Cr): 13%
- Manganese (Mn): 0.4%
- Silicon (Si): 0.4%
- Nickel (Ni): 0.5%
- Molybdenum (Mo): 0.6%
- Vanadium (V): Trace amounts
This composition makes 420HC a martensitic stainless steel, providing a good balance of hardness and corrosion resistance, suitable for various cutting applications.
7CR Steel
7Cr17MoV, commonly referred to as 7Cr steel, is another stainless steel variant known for its high carbon content and added alloying elements. The chemical composition of 7Cr steel includes:
- Carbon (C): 0.7%
- Chromium (Cr): 16-18.5%
- Vanadium (V): Present
- Molybdenum (Mo): Present
- Sulfur (S): Small amounts
- Phosphorus (P): Small amounts
The higher carbon and chromium content in 7Cr steel significantly enhance its hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and sharp edges.
Impact of Alloying Elements on Properties
Hardness and Edge Retention
420HC steel, with a carbon content of 0.45%, achieves a Rockwell hardness of 55-58 HRC, providing good wear resistance. In contrast, 7Cr steel, with a higher carbon content of 0.7%, can reach up to 60 HRC, offering better edge retention but potentially more brittleness.
Corrosion Resistance
The chromium content in 420HC (13%) and 7Cr (16-18.5%) enhances their corrosion resistance, making them suitable for various environments. This property is essential for maintaining the integrity of the steel in various conditions.
Toughness and Sharpening Ease
420HC is known for its toughness and ease of sharpening, ideal for field maintenance. 7Cr steel, while offering excellent edge retention, is harder and slightly more brittle, making it less forgiving in demanding applications.
Both 420HC and 7Cr steels are tailored for different needs: 420HC is versatile for various cutting tools, while 7Cr is better for demanding applications requiring durable, sharp edges.
Hardness, Wear Resistance, and Performance
Definition and Role of Hardness in Knife Making
Hardness is crucial in knife making as it determines how well a blade resists deformation and retains a sharp edge under use. Measured on the Rockwell Hardness Scale (HRC), higher hardness values indicate better edge retention and wear resistance but can also mean increased brittleness. The ideal hardness for a knife balances these factors to provide durability, sharpness, and ease of maintenance.
Comparative Hardness Levels of 420HC and 7CR
420HC Steel
420HC steel typically achieves a hardness of Rockwell C 54-58. This range makes 420HC relatively easy to sharpen and maintain, which benefits users needing frequent edge maintenance, though it may not hold its edge as long as harder steels.
7CR Steel
7CR steel reaches a higher hardness level, usually between Rockwell C 58-60. This increased hardness provides superior wear resistance and edge retention, making it ideal for tasks that demand prolonged sharpness. However, the trade-off is that 7CR steel can be more challenging to sharpen, requiring more effort and specialized tools to achieve a fine edge.
Wear Resistance Analysis
420HC Steel Wear Resistance
420HC steel’s wear resistance is suitable for general-purpose knives and tools, making it ideal for outdoor knives, hunting blades, and everyday carry (EDC) knives due to its balanced composition and ability to withstand moderate wear. The ease of sharpening 420HC compensates for its lower wear resistance, allowing users to quickly restore a sharp edge when needed.
7CR Steel Wear Resistance
7CR steel has excellent wear resistance thanks to its higher carbon and chromium content. This makes it a preferred choice for high-performance knives and tools used in demanding environments. The enhanced wear resistance ensures that 7CR blades retain their cutting edge longer, reducing the frequency of sharpening. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for professional chefs, hunters, and individuals who require a dependable blade in rigorous conditions.
Performance Considerations
420HC Steel Performance
420HC steel offers a good balance of performance for general applications. Its moderate hardness and wear resistance, coupled with excellent toughness, make it versatile for various cutting tasks. The ease of maintenance and sharpening makes 420HC a practical choice for users who value convenience and reliability.
7CR Steel Performance
7CR steel is designed for high-demand situations, offering exceptional edge retention and wear resistance where they matter most. Its higher hardness allows it to maintain a sharp edge longer, providing consistent cutting performance over extended use. However, the increased hardness can make the blade more susceptible to chipping under extreme conditions, highlighting the importance of proper use and maintenance.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Understanding Corrosion Resistance in Stainless Steels
Corrosion resistance is crucial for stainless steels, especially in environments where exposure to moisture and corrosive elements is common. The presence of chromium in stainless steel forms a passive oxide layer on the surface, which protects the underlying metal from corrosion.
Comparative Corrosion Resistance of 420HC and 7CR Steel
420HC Steel
420HC steel is recognized for its good corrosion resistance, primarily due to its 13% chromium content. This makes it suitable for environments where moisture is prevalent, such as marine gear, outdoor equipment, and everyday carry (EDC) knives. However, in highly corrosive conditions, such as exposure to saltwater or acidic substances, 420HC may require more frequent maintenance to prevent rust and pitting.
7CR Steel
7CR steel offers better corrosion resistance than 420HC because it contains more chromium, between 16% and 18.5%. This enhanced chromium level significantly improves its resistance to rust and corrosion, making 7CR steel an excellent choice for industrial applications and high-end knives used in demanding environments. The increased corrosion resistance reduces the need for constant maintenance, making it more reliable in harsh conditions.
Maintenance Guidelines for Optimal Performance
420HC Steel Maintenance
Despite its good corrosion resistance, 420HC steel requires regular maintenance. Clean the blade with mild soap and water after use, dry it thoroughly, and apply a light coat of oil to protect it from moisture. Regularly sharpen the blade and store it in a dry place.
7CR Steel Maintenance
7CR steel, with its higher hardness and superior corrosion resistance, requires less frequent maintenance but still benefits from regular care. Clean the blade after use, especially if it has been exposed to corrosive substances or environments. Due to its higher hardness, sharpening 7CR steel can be more challenging and may require specialized tools. However, it retains its edge longer, so it doesn’t need sharpening as often. Regularly lubricate the blade and store it in a dry environment to maximize its lifespan and performance.
Key Differences in Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
- Chromium Content: 420HC has 13% chromium, providing good corrosion resistance, while 7CR has 16-18.5%, offering superior protection.
- Maintenance Frequency: 420HC requires more frequent maintenance to prevent rust, whereas 7CR’s higher corrosion resistance reduces the need for constant upkeep.
- Sharpening Ease: 420HC is easier to sharpen but may lose its edge quicker, while 7CR holds its edge longer but is more difficult to sharpen.
Cost, Market Availability, and Economic Factors
Cost Comparison
When comparing 420HC steel and 7CR steel, cost is a significant factor.
420HC Steel
420HC steel is more affordable because it has lower hardness and a simpler composition. The reduced chromium content and straightforward heat treatment process contribute to its affordability. This makes 420HC an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers, particularly those seeking durable and cost-effective knives for everyday use.
7CR Steel
In contrast, 7CR steel is more expensive. Its higher hardness and enhanced corrosion resistance come from its higher carbon and chromium content, which require more advanced manufacturing processes. These premium properties make 7CR steel suitable for high-end applications where superior performance is necessary, justifying its higher price point.
Market Availability
The availability of these steels in the market also varies.
420HC Steel
420HC steel is widely available, especially in North America. It is commonly used by well-known brands such as Buck Knives and Leatherman. Its versatility and affordability make it popular for knives used by outdoor enthusiasts and general consumers. Its broad use in various products ensures a steady supply in the market.
7CR Steel
On the other hand, 7CR steel is more prevalent in specialized or high-end applications. It is less commonly found in mass-market products, as its use is often reserved for premium knives designed for specific tasks like hunting or high-performance cutting. This specialized focus can limit its availability in the general market but makes it a sought-after material in niche segments.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a crucial role in the production, demand, and distribution of 420HC and 7CR steel.
Production and Manufacturing
Producing 420HC steel is cheaper due to its simpler composition and easier heat treatment process. In contrast, 7CR steel requires more advanced manufacturing techniques to achieve its higher hardness and superior corrosion resistance. These additional processes increase production costs, making 7CR steel more expensive.
Demand and Market Trends
The demand for 420HC steel remains stable due to its affordability and versatility. It is widely used in various applications, ensuring consistent market demand. While demand for 7CR steel is more niche, it can be lucrative for manufacturers targeting premium markets that value superior performance.
Global Trade and Sourcing
Both steels are sourced globally, but there are differences in their distribution. 420HC steel tends to be more widely distributed due to its broad application in everyday products. It is sourced from multiple regions, ensuring a steady supply chain. Conversely, 7CR steel may be sourced more frequently from specialized suppliers catering to high-end markets, reflecting its targeted use in premium applications.
Comparison of Key Features
| Feature | 420HC Steel | 7CR Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | Generally 54-58 HRC | Range of 58-60 HRC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent but less than 7CR | Superior due to higher chromium content |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Applications | General knives, outdoor tools | High-end knives, specialty tools |
| Edge Retention | Easier to sharpen, less edge retention | More challenging to sharpen, but offers better edge retention |
Applications: Knives and Beyond
Best Uses for 420HC Steel in Knife Making and Other Tools
Outdoor and Survival Knives
420HC steel is a popular choice for outdoor and survival knives due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ease of sharpening. These attributes are crucial for tools that are frequently exposed to harsh environments and require regular maintenance. Brands like Buck Knives utilize 420HC for its ability to withstand the rigors of outdoor activities while remaining user-friendly for sharpening in the field.
Everyday Carry (EDC) Knives
The balanced hardness and toughness in 420HC steel make it ideal for everyday carry (EDC) knives. These knives benefit from the steel’s good edge retention and ability to be easily resharpened, ensuring they remain effective for daily tasks. The affordability of 420HC steel also contributes to its popularity among EDC knife enthusiasts.
Multi-tools and Utility Knives
420HC steel is frequently used in multi-tools and utility knives, where durability and low maintenance are key. The steel’s resistance to corrosion and wear, along with its affordability, makes it a preferred material for tools that need to perform reliably in various conditions.
Best Uses for 7CR Steel in Knife Making and Other Tools
7CR steel, known for its higher hardness and edge retention, is suited for more demanding applications where performance is paramount.
High-Performance and Professional Knives
7CR steel is favored for high-performance knives used by professionals like chefs and hunters. The superior edge retention and hardness allow these knives to maintain a sharp edge longer, which is essential for precision cutting tasks. However, the increased difficulty in sharpening 7CR steel means these knives are best suited for users who can provide the necessary maintenance.
Budget-Friendly Outdoor Knives
While 7CR steel offers high performance, it is also used in budget-friendly outdoor knives. These knives benefit from the steel’s hardness and edge retention while remaining affordable for a broader audience. This makes 7CR steel a popular choice for entry-level outdoor enthusiasts who need a reliable blade without a premium price tag.
General Purpose and Tactical Knives
The robust properties of 7CR steel make it suitable for general-purpose and tactical knives. These knives are often used in demanding situations where durability and edge retention are critical. The higher chromium content in 7CR steel also provides good corrosion resistance, adding to the steel’s suitability for tactical applications.
Industrial Tools
Beyond knives, both 420HC and 7CR steels are used in various industrial tools, each offering unique advantages.
420HC Steel in Industrial Tools
420HC steel’s toughness and corrosion resistance make it suitable for industrial tools that require frequent maintenance and exposure to harsh environments. These tools include cutting instruments, surgical tools, and certain types of blades used in manufacturing processes.
7CR Steel in Industrial Tools
7CR steel is used in industrial tools that demand high wear resistance and edge retention. Its application includes precision cutting tools, high-performance blades, and other tools that benefit from the steel’s superior hardness. The higher cost of 7CR steel is justified by its performance in critical industrial applications where tool longevity and reliability are essential.
Real-World Applications and User Experiences
Users of 420HC and 7CR steels report different experiences based on their specific needs and applications.
User Experiences with 420HC Steel
Users appreciate 420HC steel for its ease of maintenance and versatility. Outdoor enthusiasts, in particular, value the steel’s ability to resist corrosion and its ease of sharpening in the field. The steel’s affordability also makes it a go-to choice for everyday tools and multi-tools.
User Experiences with 7CR Steel
Users of 7CR steel often highlight its excellent edge retention and performance in demanding tasks. Professional chefs and hunters find the steel’s ability to maintain a sharp edge beneficial for their work. However, some users note the increased difficulty in sharpening, which requires more effort and specialized tools.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Production and Material Properties
420HC Steel Production
420HC steel is a high-carbon stainless steel known for its durability and excellent corrosion resistance. Its production process involves significant energy consumption due to heat treatment and alloying, which contributes to its carbon footprint. The precise conditions required for optimizing its properties further add to the energy demands.
7Cr17MoV Steel Production
7Cr17MoV steel, with a higher chromium content (16-18.5%), offers enhanced corrosion resistance. Its production process involves heat treatment, which may require fewer specialized procedures compared to 420HC, potentially reducing energy consumption.
Environmental Impact
Waste and Recycling
Both 420HC and 7Cr17MoV steels can be recycled, which helps reduce waste and the need for new production. However, the efficiency and frequency of recycling processes can differ between the two, impacting their overall environmental footprint.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
The high corrosion resistance of both steels contributes to their durability, reducing the necessity for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing waste generation. 420HC steel might have an edge in maintaining its properties over time due to its balanced composition, which could result in fewer replacements and less waste.
Energy Consumption
The heat treatment processes for both steels consume a lot of energy. However, 420HC steel requires more precise conditions, which might increase its energy footprint compared to 7Cr17MoV steel. This difference in energy consumption is a critical factor when considering the environmental impact of these materials.
Sustainability in Applications
420HC Steel Applications
420HC steel is often used in critical applications such as surgical instruments and marine equipment, where its corrosion resistance and durability are crucial. These applications demand high reliability, which reduces the risk of failure and ensures consistent performance under challenging conditions.
7Cr17MoV Steel Applications
7Cr17MoV steel is commonly used in mass-produced knives and outdoor tools due to its affordability and decent performance. While it offers good durability, it may not last as long as 420HC steel, potentially leading to more frequent replacements and increased waste. Its widespread use, however, makes it accessible for various applications, balancing cost-effectiveness with performance.
Key Comparisons
- Energy Consumption: 420HC steel’s production involves more precise heat treatment, increasing its energy footprint compared to 7Cr17MoV steel.
- Durability and Waste: 420HC steel’s balanced composition may result in better long-term durability, reducing the need for replacements and waste generation.
- Recyclability: Both steels are recyclable, but the efficiency of recycling processes can vary, impacting their environmental benefits.
Choosing between 420HC and 7Cr17MoV steel for sustainability involves considering specific application needs and the efficiency of recycling and production processes. Each steel offers distinct advantages that cater to different sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
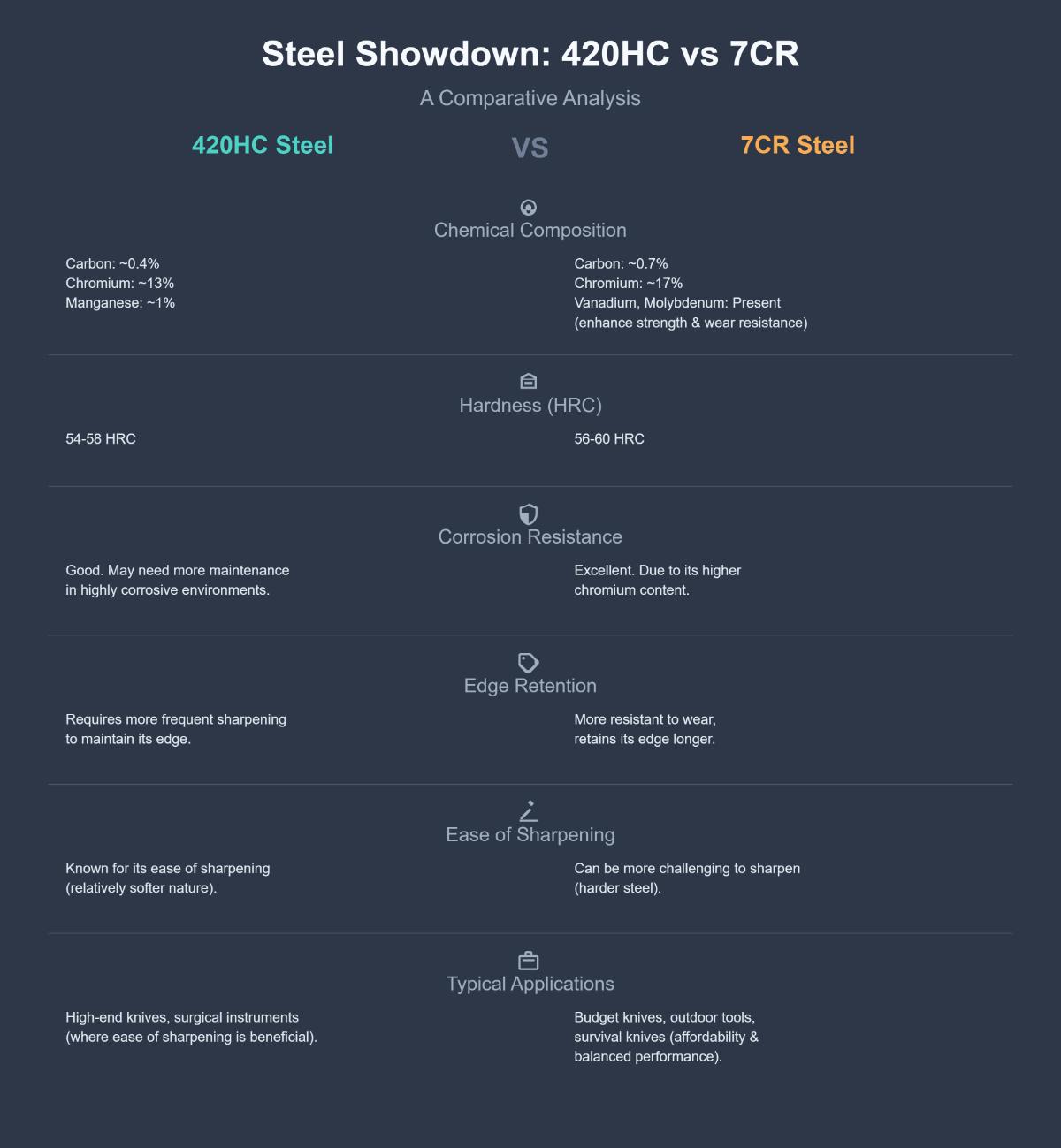
What are the key differences between 420HC and 7CR steel?
The key differences between 420HC and 7CR steel lie in their chemical composition, hardness, corrosion resistance, edge retention, and applications.
420HC steel contains approximately 0.4% carbon and 13% chromium, with 1% manganese. It is known for its ease of sharpening due to its relatively softer nature, with a hardness of about 54-58 HRC. However, it requires more frequent sharpening to maintain its edge. It offers good corrosion resistance, but may need more maintenance in highly corrosive environments.
On the other hand, 7CR steel, often referred to as 7Cr17MoV, has about 0.7% carbon, 17% chromium, and includes elements like vanadium and molybdenum. These additions provide enhanced strength and wear resistance. 7CR steel is harder, with a hardness range of 56-60 HRC, making it more resistant to wear and capable of retaining its edge longer, although it can be more challenging to sharpen. It also offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its higher chromium content.
In terms of applications, 420HC is suitable for high-end knives and surgical instruments where ease of sharpening is beneficial. 7CR is commonly used in budget knives, outdoor tools, and survival knives due to its affordability and balanced performance.
Which steel is better suited for high-performance knives?
For high-performance knives, 7CR steel is generally better suited compared to 420HC steel. This is primarily due to its higher carbon content (0.7% in 7CR vs. 0.4-0.5% in 420HC) and chromium content (17% in 7CR vs. 13% in 420HC), which enhance its hardness and wear resistance. 7CR steel typically achieves a hardness range of 58-60 HRC, providing superior edge retention and durability, making it ideal for applications that demand long-lasting sharpness, such as hunting or kitchen knives.
On the other hand, 420HC steel, with a hardness range of 54-58 HRC, is easier to sharpen and maintain, making it a good choice for everyday use or outdoor knives where ease of maintenance is crucial. While both steels offer good corrosion resistance, 7CR’s higher chromium content gives it a slight edge in this aspect as well.
How does the hardness of 420HC compare to 7CR steel?
When comparing the hardness of 420HC steel and 7CR steel, it’s important to consider their respective Rockwell hardness (HRC) levels. 420HC steel typically has a hardness range of HRC 54-58. This makes it relatively easier to sharpen and maintain, while still providing good edge retention and durability.
On the other hand, 7CR steel, also known as 7Cr, has a higher hardness range of HRC 58-60. This increased hardness contributes to better edge retention and wear resistance, making it more suitable for applications where maintaining a sharp edge for longer periods is crucial. However, the higher hardness also means that 7CR steel is more challenging to sharpen compared to 420HC steel.
How do 420HC and 7CR steels compare in terms of corrosion resistance?
When comparing 420HC and 7CR steels in terms of corrosion resistance, 7CR steel has a notable advantage. This is primarily due to its higher chromium content, around 17%, which enhances its ability to withstand moisture and salts, making it more suitable for use in harsh and humid environments. In contrast, 420HC steel contains approximately 13% chromium, providing good but comparatively lower corrosion resistance. While 420HC can resist moisture and oxidation well, it requires more frequent maintenance, such as cleaning and oiling, especially in challenging conditions. Therefore, for applications demanding superior corrosion resistance and durability, 7CR steel is the better choice. However, 420HC remains a cost-effective option for those needing reliable corrosion resistance without the higher expense associated with 7CR steel.
Are there significant cost differences between 420HC and 7CR steel?
Yes, there are significant cost differences between 420HC and 7CR steel. 420HC steel is generally less expensive due to its lower carbon and chromium content, which makes it easier to produce and more affordable. It is often favored for budget-friendly knives and tools that require good corrosion resistance and ease of sharpening. On the other hand, 7CR steel, specifically 7Cr17MoV, is more expensive because it contains higher levels of chromium and additional alloying elements like molybdenum and vanadium, which enhance its hardness, wear resistance, and overall performance.
What are the environmental impacts of producing 420HC and 7CR steel?
The environmental impacts of producing 420HC and 7CR steel are similar, as both are stainless steel alloys and share common production processes. Steel production is known for its significant environmental footprint, including high energy consumption, air and water pollution, and waste generation.
For 420HC steel, the inclusion of chromium in its composition necessitates energy-intensive processes for mining and refining, contributing to water pollution and soil degradation. However, 420HC is highly recyclable, which helps mitigate some of these environmental impacts.
7CR steel, which includes additional alloying elements like vanadium and molybdenum, also requires substantial energy for production, particularly in electric arc furnaces. The extraction of these elements further contributes to the environmental burden. Like 420HC, 7CR steel’s recyclability is a positive factor in reducing its
In summary, both 420HC and 7CR steel production have notable environmental impacts, primarily due to energy consumption and material extraction. However, their recyclability offers some environmental benefits by reducing the need for raw materials and associated energy use.
