When it comes to selecting the perfect steel for your cutting tools or structural components, the choice often narrows down to two popular options: 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV. But what sets these two materials apart? Whether you’re a knife enthusiast, a toolmaker, or simply curious about metallurgy, understanding the differences in corrosion resistance, hardness, and wear resistance between these two types of steel is crucial. 440 Stainless Steel is known for its exceptional hardness, while 8Cr13MoV is celebrated for its balanced performance and affordability. But which one is right for your specific needs? Dive in as we dissect their chemical compositions, physical properties, and ideal applications to help you make an informed decision. Could one of these steels be the perfect match for your next project? Let’s find out.
Introduction to 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV
Introduction to 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV
Overview of 440 Stainless Steel
440 Stainless Steel is a high-carbon, martensitic stainless steel renowned for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance. It is available in several grades, including 440A, 440B, 440C, and 440F, each with varying carbon content. This variation in carbon content primarily influences the steel’s hardness and machinability.
- Composition: The key elements in 440 Stainless Steel include chromium (16 – 18%), molybdenum (0.75% in 440A), and carbon (ranging from 0.6% to 1.2%). The chromium content provides the steel with its corrosion resistance, while the carbon content enhances hardness.
- Properties: 440 Stainless Steel can achieve a Rockwell hardness of up to 58, depending on the grade. Its high hardness ensures excellent edge retention and tensile strength, making it suitable for demanding applications.
- Applications: Common uses of 440 Stainless Steel include high – quality knife blades, surgical instruments, valve components, and bearings. Its high hardness and wear resistance make it ideal for cutting tools and other applications where durability is essential.
- Corrosion Resistance: While 440 Stainless Steel offers moderate corrosion resistance, it is less effective than austenitic grades such as 304 or 316 in harsh environments. It performs well in mild environments but may require additional protective measures in more corrosive settings.
Overview of 8Cr13MoV
8Cr13MoV is a high – carbon stainless steel developed by Chinese manufacturers, inspired by the Japanese VG – 10 steel and similar to the 440 series. It is widely used in budget – friendly knives and cutlery due to its balanced properties and affordability.
- Composition: The steel contains chromium (13 – 14%), molybdenum (1%), vanadium (0.1 – 0.3%), and carbon (0.6 – 0.8%). The addition of vanadium enhances the steel’s wear resistance and edge retention, making it a popular choice for cutting tools.
- Properties: 8Cr13MoV achieves a Rockwell hardness of around 56 – 58, which is comparable to 440C. It offers a good balance of hardness and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
- Applications: This steel is frequently used in knives, scissors, and cutting tools that need a balance of performance and cost. Its affordability makes it a popular choice for budget – friendly products.
- Corrosion Resistance: 8Cr13MoV provides good corrosion resistance, better than many martensitic stainless steels thanks to its balanced composition. However, it still falls short of the robustness offered by austenitic grades like 304.
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | 440 Stainless Steel | 8Cr13MoV |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Up to Rockwell 58, dependent on grade | Rockwell 56 – 58 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, less than austenitic grades | Better than many martensitic steels, good for knives |
| Cost | Generally more expensive than 8Cr13MoV | More affordable |
| Applications | High – end knives, surgical tools, bearings | Budget – friendly knives, cutlery, and cutting tools |
| Composition | High carbon, chromium content | Chromium, molybdenum, vanadium for enhanced properties |
| Machinability | Grades like 440F offer high machinability | Generally good machinability |
| Production Origin | Western countries, widely recognized | Chinese origin, similar performance at lower cost |
Chemical Composition Comparison
440 Stainless Steel is a high-carbon, martensitic stainless steel prized for its high hardness and excellent wear resistance, available in various grades including 440A, 440B, 440C, and 440F, each with different carbon content influencing hardness and machinability.
Chemical Composition of 440 Stainless Steel
440 Stainless Steel typically contains 0.6-1.2% Carbon, up to 1% Manganese, up to 1% Silicon, up to 0.04% Phosphorus, up to 0.03% Sulfur, 16-18% Chromium, and up to 0.75% Molybdenum.
Overview of 8Cr13MoV
8Cr13MoV is a high-carbon stainless steel developed in China, known for being cost-effective and offering a balanced set of properties suitable for tools and knives.
Chemical Composition of 8Cr13MoV
- Carbon (C): Approximately 0.8%
- Manganese (Mn): Around 1%
- Silicon (Si): Around 1%
- Phosphorus (P): Typically below 0.04%
- Sulfur (S): Typically below 0.03%
- Chromium (Cr): Approximately 13-14%
- Molybdenum (Mo): Around 0.2-0.3%
- Vanadium (V): Approximately 0.1-0.2%
Comparison and Analysis
Carbon Content
440 Stainless Steel, especially 440C, has a higher carbon content (0.95-1.20%) compared to 8Cr13MoV (around 0.8%), which contributes to its greater hardness and strength.
Chromium Content
The chromium content in 440 Stainless Steel (16-18%) is significantly higher than that in 8Cr13MoV (13-14%). Higher chromium content generally enhances corrosion resistance, making 440 Stainless Steel more resistant to oxidation and rust compared to 8Cr13MoV.
Molybdenum and Vanadium
440 Stainless Steel can contain up to 0.75% molybdenum, while 8Cr13MoV includes around 0.2-0.3% molybdenum and 0.1-0.2% vanadium. Molybdenum improves the steel’s strength and resistance to pitting, while vanadium in 8Cr13MoV contributes to wear resistance and toughness. The presence of vanadium gives 8Cr13MoV an edge in applications where these properties are crucial.
| Element | 440 Stainless Steel (e.g., 440C) | 8Cr13MoV |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.95-1.20% | ~0.8% |
| Manganese (Mn) | Up to 1% | ~1% |
| Silicon (Si) | Up to 1% | ~1% |
| Phosphorus (P) | Up to 0.04% |
Physical Properties Comparison
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a crucial factor when selecting materials for environments exposed to moisture and other corrosive elements.
440 Stainless Steel, with its higher chromium content (16-18%), offers moderate corrosion resistance. It performs well in mild conditions but can be susceptible to localized corrosion, such as small pits and crevices, in harsher environments. On the other hand, 8Cr13MoV, with a chromium content of around 13-14%, provides good corrosion resistance. It is effective in various environments, making it a popular choice for everyday cutlery and budget-friendly knives. While it does not match the corrosion resistance of higher-end stainless steels, it strikes a satisfactory balance for many practical applications.
Hardness
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation and wear, crucial for cutting tools and blades. The Rockwell Hardness Scale (HRC) is a commonly used scale to measure hardness.
440 Stainless Steel is known for its exceptional hardness, reaching up to 58 HRC, depending on the grade and heat treatment. This high hardness ensures excellent edge retention and durability, making it ideal for high-stress applications like knife blades and surgical instruments. Similarly, 8Cr13MoV achieves a respectable hardness, typically ranging from 56 to 58 HRC, depending on heat treatment. While its hardness is comparable to 440 Stainless Steel, it is often slightly lower, which can result in marginally less edge retention. However, this difference is generally minimal for most practical uses.
Wear Resistance
Wear resistance determines how well a material can withstand abrasion and maintain its integrity over time, which is essential for materials used in cutting and high-friction environments.
440 Stainless Steel excels in wear resistance due to its high carbon and chromium content. Its hardness significantly contributes to its ability to resist wear, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting sharpness and durability, such as high-quality knife blades and bearings. In contrast, 8Cr13MoV, while not as wear-resistant as 440 Stainless Steel, still offers good performance in this area. The addition of vanadium enhances its wear resistance, making it suitable for everyday knives and tools that require a balance between performance and cost. Its wear resistance is sufficient for most general-purpose applications, although it may not match the extreme durability of 440 Stainless Steel in high-stress scenarios.
| Property | 440 Stainless Steel | 8Cr13MoV |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Good |
| Hardness (HRC) | Up to 58 | 56-58 |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
Both 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV offer distinct advantages in terms of physical properties, making them suitable for different applications based on specific requirements such as hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Application Areas for Each Material
Blades and Cutting Tools
440 stainless steel is a preferred material for high-end blades and cutting tools due to its excellent hardness and wear resistance. Its high hardness and excellent wear resistance make it ideal for surgical instruments and high-performance bearings and fasteners in the aerospace industry, which require durability and strength under extreme conditions. High-quality kitchen knives often use 440 stainless steel because it maintains a sharp edge through extensive use.
While 8Cr13MoV may not match the extreme durability of 440 stainless steel in high-stress applications, it is a cost-effective choice for everyday household knives and scissors. For general cutting tasks around the house or in light-duty workshops, 8Cr13MoV provides a practical solution without sacrificing too much in terms of performance.
Structural Components
In the realm of structural components, 440 stainless steel is employed in critical applications. For example, in industrial machinery, pump shafts made of 440 can withstand high-speed rotation and heavy loads due to its high hardness and strength. In the medical field, it is used for parts of medical equipment that need to be corrosion-resistant and have high mechanical properties.
8Cr13MoV is typically found in general-purpose structural components, such as simple tools and instruments, where a balance of strength and cost is required. However, the variability in its quality means that it may not be suitable for applications where strict performance standards are necessary.
Understanding Martensitic Stainless Steel and High-Carbon Stainless Steel
Martensitic Stainless Steel
Martensitic stainless steel is known for its high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. These properties are achieved through the transformation of austenite into martensite during heat treatment, which significantly enhances the material’s mechanical performance.
Composition and Properties
- Composition: Martensitic stainless steel typically consists of 11 – 18% chromium, 0.08 – 1.20% carbon, and minimal nickel (below 2.5%). The high carbon content is crucial for achieving the desired hardness and strength.
- Heat Treatment: These steels can be hardened through heat treatment, which involves heating to a high temperature followed by rapid cooling (quenching) to form martensite, a hard and brittle microstructure.
- Magnetic Properties: Martensitic stainless steels are magnetic and can be attracted to magnets and magnetized.
- Corrosion Resistance: Offers moderate corrosion resistance, which is less than that of austenitic stainless steels but sufficient for many applications in mild environments.
Applications
Martensitic stainless steels are widely used in applications that require high strength and wear resistance. High – carbon martensitic grades like 440 are popular for knives and scissors due to their excellent edge retention. They are also used in medical instruments, where the high polishability and hygiene make them suitable for surgical tools. In the aerospace and automotive industries, components such as shafts and gears benefit from their strength and durability.
High – Carbon Stainless Steel
High – carbon stainless steels are a subset of stainless steels that contain higher carbon content, typically greater than 0.3%. This higher carbon content enhances the hardness and wear resistance of the steel.
Key Characteristics
- Hardness: The increased carbon content significantly enhances the hardness of the steel, making it ideal for applications requiring sharp edges and high wear resistance.
- Corrosion Resistance: While the corrosion resistance is generally lower than that of austenitic stainless steels, it is still adequate for many applications, especially in mild corrosive environments.
Common Grades
- 440 Stainless Steel: A high – carbon martensitic stainless steel known for its excellent hardness and wear resistance. It is used in high – end knives, surgical instruments, and other applications requiring durable, sharp edges.
Comparative Analysis
Both martensitic stainless steels and high – carbon stainless steels are known for their high strength and hardness, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Strength and Hardness
Martensitic stainless steels and high – carbon stainless steels both excel in strength and hardness, making them suitable for demanding applications. The high carbon content in both types of steel is a key factor in achieving these properties.
Wear Resistance
Both types of steel offer excellent wear resistance, with martensitic stainless steels having an edge in applications where extreme hardness is required. High – carbon stainless steels like 440 also provide outstanding wear resistance, making them ideal for cutting tools and other high – stress applications.
Corrosion Resistance
Martensitic stainless steels provide moderate corrosion resistance, which is generally adequate for many applications but lower than austenitic grades. High – carbon stainless steels have similar corrosion resistance, performing well in mild environments but potentially requiring additional protective measures in more corrosive settings.
Material Selection Criteria for Specific Projects
Hardness and Wear Resistance
For projects requiring high hardness and wear resistance, 440 Stainless Steel, especially the 440C grade, is an excellent choice. It achieves a Rockwell hardness of up to 58-60 HRC, making it ideal for high-quality knife blades, ball bearings, and surgical instruments that require sharp edges and durability.
In comparison, 8Cr13MoV offers a balanced hardness around 56-58 HRC. While slightly lower than 440C, it still provides adequate wear resistance for many practical uses, especially in everyday knives and cutting tools where extreme hardness is not as critical.
Corrosion Resistance
The environment where the material will be used is crucial in the selection process. 440 Stainless Steel, with its higher chromium content, offers moderate corrosion resistance, suitable for mild environments. This makes it a good choice for certain kitchen tools and mechanical components.
On the other hand, 8Cr13MoV, with its slightly lower chromium content, provides good corrosion resistance that can be advantageous in various environments. This makes it particularly suitable for budget-friendly knives and tools that may be exposed to moisture but do not require the high corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steels.
Cost and Availability
Budget constraints are a crucial factor in material selection. 8Cr13MoV is generally more affordable than 440 Stainless Steel, making it a cost-effective option for consumer products like knives and scissors. Its widespread availability and lower cost make it an attractive choice for manufacturers looking to balance performance and expense.
440 Stainless Steel, especially the high-carbon 440C variant, is more expensive. However, its superior hardness and wear resistance justify the higher cost in high-end cutlery and industrial components.
Machinability
Additionally, the ease of machining is a crucial factor to consider. 8Cr13MoV is generally easier to machine than hardened 440 Stainless Steel, making it more suitable for manufacturing processes that require extensive machining. This can reduce production costs and improve efficiency in producing complex shapes and fine details.
While 440 Stainless Steel can be machined effectively in its annealed state, it becomes challenging to work with once hardened. This may necessitate more advanced machining techniques and equipment, potentially increasing production costs.
Heat Resistance
Both materials offer good heat resistance, essential for applications subjected to high temperatures. However, 440 Stainless Steel is more sensitive to heat treatment and tempering conditions, requiring precise control to achieve the desired hardness and mechanical properties.
8Cr13MoV, while still providing good heat resistance, is generally more forgiving in terms of heat treatment, making it easier to work with in standard manufacturing settings. This can be advantageous in applications where consistent heat resistance is needed without the need for specialized heat treatment processes.
Specific Applications
For high-stress applications requiring maximum hardness and wear resistance, 440 Stainless Steel, especially the 440C grade, is the superior choice. It is ideal for high-end knives, surgical instruments, and components in aerospace and automotive industries where durability and strength are critical.
For more general-purpose applications where a balance of performance and cost is needed, 8Cr13MoV is highly suitable. It is commonly used in everyday knives, scissors, and cutting tools, offering a practical solution that meets performance requirements without excessive cost.
Real-World Examples and User Testimonials
Real-World Applications in Knife Making
440 Stainless Steel
In the high-end knife market, 440 stainless steel is a common choice for custom knife makers who often select 440C for premium hunting knives. These knives are designed to endure the rigors of outdoor use, such as skinning and cutting through tough animal hides. The high hardness and excellent wear resistance of 440C ensure that the blade maintains a sharp edge for extended periods, even when used on abrasive materials.
One user testimonial from a professional hunter states, “My 440C hunting knife has been my go-to tool for years. It can handle the toughest jobs in the field, and I only need to sharpen it once in a while. The edge retention is truly remarkable.”
8Cr13MoV
On the other hand, 8Cr13MoV is widely used in budget-friendly kitchen knives. Home cooks like these knives because they perform well and are affordable. For instance, a popular brand of kitchen knives uses 8Cr13MoV in its everyday knife sets. These knives can easily handle common kitchen tasks like chopping vegetables, slicing meats, and dicing fruits.
A home cook’s testimonial reads, “I bought a set of 8Cr13MoV kitchen knives, and I’m really satisfied. They are sharp enough for my daily cooking needs, and if they get dull, I can sharpen them easily at home. And the price was very reasonable.”
Applications in Industrial Tools
440 Stainless Steel
In the industrial sector, 440 stainless steel is used in high-precision cutting tools like surgical scalpels. Its high hardness and corrosion resistance make it suitable for medical applications where sterility and sharpness are critical.
A surgeon shares, “The 440 stainless steel scalpels we use in the operating room provide excellent precision. They are resistant to corrosion, which is crucial for maintaining a sterile environment, and their sharpness ensures clean cuts.”
8Cr13MoV
8Cr13MoV finds its place in general-purpose industrial cutting tools, like utility knives used in factories for cutting cardboard, plastic, and thin metals. These tools need to be affordable while still performing well.
An industrial worker comments, “Our factory uses 8Cr13MoV utility knives. They are durable enough for our daily cutting tasks, and we can replace them easily when they start to wear out, thanks to their affordable price.”
Applications in Structural Components
440 Stainless Steel
In the aerospace industry, 440 stainless steel is used in manufacturing small, high-stress components like bearings and fasteners. These parts must withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and heavy loads.
An aerospace engineer says, “440 stainless steel bearings in our aircraft have proven to be reliable. Their high strength and wear resistance ensure the smooth operation of critical systems, even under harsh conditions.”
8Cr13MoV
8Cr13MoV is used in simple structural components in machinery, such as small brackets and supports. These components do not require the extreme performance of 440 stainless steel but still need a certain level of strength and corrosion resistance.
A machinery technician notes, “The 8Cr13MoV brackets in our machines work well. They are strong enough to hold the parts in place, and their corrosion resistance is sufficient for the indoor environment of our workshop.”
Chemical Composition
| Element | 440 Stainless Steel | 8Cr13MoV |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.60-1.20% | 0.5-0.8% |
| Contributes to hardness and strength | Enhances edge retention and hardness | |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16-18% | 8-13% |
| Provides corrosion resistance | Increases wear resistance | |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Up to 0.75% | 0.2-0.3% |
| Improves hardness and toughness | Enhances strength and hardenability | |
| Vanadium (V) | – | 0.1-0.2% |
| Improves wear resistance and toughness | Increases strength and wear resistance |
Physical Properties
| Property | 440 Stainless Steel | 8Cr13MoV |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Martensitic | High Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Simple cubic structure | Similar to 440 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Moderate |
| Hardness (HRC) | Up to 58 | 55-57 |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate strength |
| Machinability | Difficult due to high carbon content | Easier than 440 |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 797°F (425°C) continuously | Less than 440 series |
Applications
| Application Area | 440 Stainless Steel | 8Cr13MoV |
|---|---|---|
| High-quality knife blades | Preferred due to superior properties | Suitable for mid-range knives, balancing performance and cost |
| Surgical instruments | Excellent due to hardness and corrosion resistance | Less common due to lower strength |
| Bearings and valve seats | Ideal for high-stress applications | Not typically used |
| Everyday cutlery | Used in high-end products | Common in budget-friendly products, offering good value for money |
Key Observations
440 Stainless Steel’s higher hardness and tensile strength make it ideal for demanding applications like surgical instruments and high-quality knife blades. In contrast, 8Cr13MoV, while still hard, is slightly less robust, suitable for mid-range knives and general cutlery.
Both materials provide moderate corrosion resistance, but 440 Stainless Steel is slightly superior due to its higher chromium content, making it more effective in mildly corrosive environments.
8Cr13MoV is easier to machine compared to 440 Stainless Steel, making it more practical for mass production and less demanding applications.
440 Stainless Steel can withstand higher continuous operating temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring excellent heat resistance.
8Cr13MoV is more affordable and widely used in budget-friendly products, while 440 Stainless Steel is preferred for high-end applications where performance is critical.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
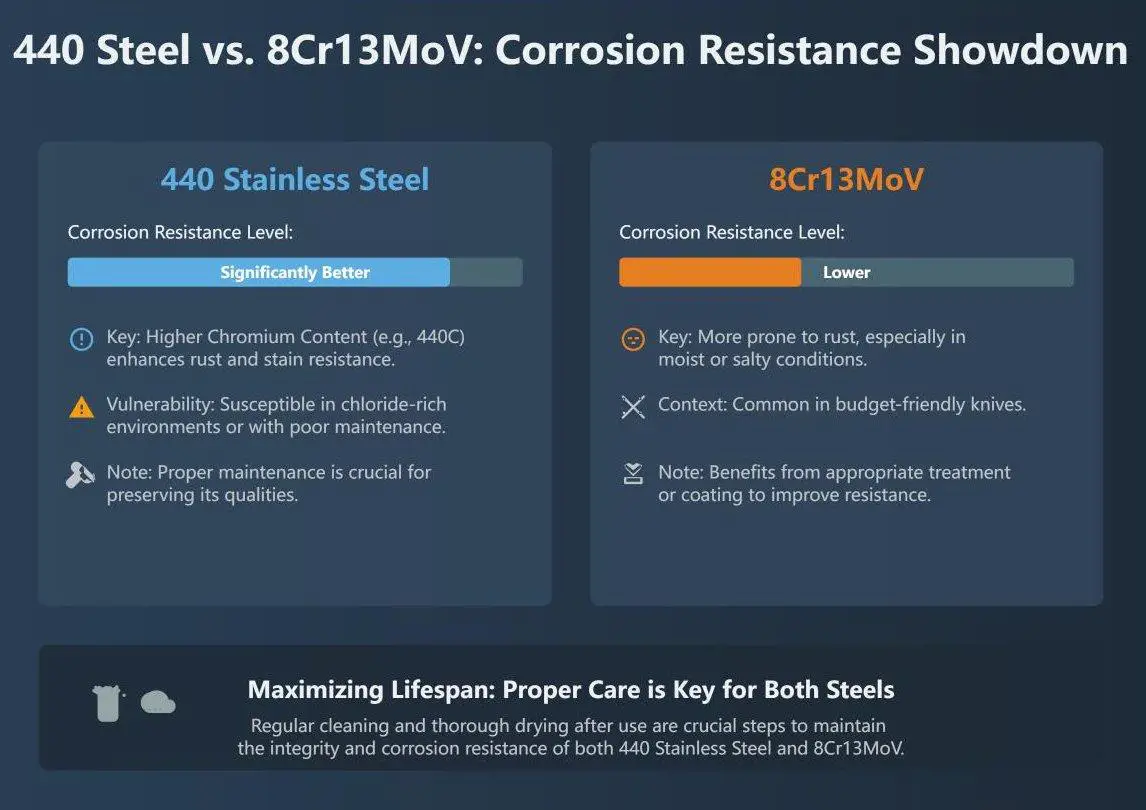
What are the differences in corrosion resistance between 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV?
440 Stainless Steel generally offers better corrosion resistance than 8Cr13MoV. The higher chromium content in 440 Stainless Steel, particularly in grades like 440C, contributes to its improved resistance to rust and staining. However, 440 Stainless Steel is still susceptible to corrosion in chloride-rich environments or if not properly maintained. In contrast, 8Cr13MoV, which is often used in budget-friendly knives, has a lower corrosion resistance. This alloy is more prone to rust, especially in moist or salty environments, unless treated or coated appropriately. Both materials require proper care, such as regular cleaning and drying, to maximize their corrosion resistance.
How do the hardness and wear resistance of 440 Stainless Steel compare to 8Cr13MoV?
The hardness and wear resistance of 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV differ significantly, primarily due to their composition and intended applications. 440 Stainless Steel, especially the 440C variant, is known for its high hardness, reaching up to Rockwell C 60 after proper heat treatment. This high hardness translates to excellent wear resistance, making 440C ideal for high-performance applications such as precision bearings, surgical instruments, and high-quality knives.
In contrast, 8Cr13MoV typically achieves a hardness of around Rockwell C 56-58. While this is slightly lower than 440C, it still provides sufficient hardness for many practical applications, particularly in the knife industry. 8Cr13MoV offers a balanced combination of hardness, corrosion resistance, and affordability, making it popular for budget-friendly knives and everyday use cutlery.
What applications are most suitable for 440 Stainless Steel versus 8Cr13MoV?
440 Stainless Steel is most suitable for applications that demand high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance. These characteristics make it ideal for high-end knives, surgical instruments, bearings, valve components, and aerospace parts. The high carbon content and the ability to achieve a Rockwell hardness of 58 HRC after heat treatment contribute to its superior edge retention and durability, which are critical in professional and demanding environments.
On the other hand, 8Cr13MoV is well-suited for mid-range knives and cutting tools where a balance between performance and affordability is essential. While it offers good hardness and corrosion resistance, it is not as wear-resistant as 440 Stainless Steel, making it less ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, its lower cost makes it a popular choice for everyday use knives and general-purpose cutting tools, providing satisfactory performance without the premium price tag.
Are there any significant cost differences between the two materials?
When comparing 440 stainless steel and 8Cr13MoV, there are significant cost differences. Generally, 8Cr13MoV is more affordable and budget-friendly compared to 440 stainless steel, especially higher-end grades like 440C. This cost difference impacts the accessibility and pricing of products made from these materials.
8Cr13MoV is often used in budget-friendly knives, offering a good balance between performance and cost, making it accessible to a wider range of consumers. In contrast, 440 stainless steel, particularly 440C, is considered a mid-to-high-end material due to its superior hardness, edge retention, and corrosion resistance, justifying its higher cost. This makes 440C more suitable for premium products that target professionals and enthusiasts who prioritize performance over price.
How do the maintenance requirements differ between 440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV?
440 Stainless Steel and 8Cr13MoV have distinct maintenance requirements. 440 Stainless Steel, with high hardness and wear – resistance, is more challenging to sharpen, often requiring specialized tools. Regular cleaning with mild detergents, drying, and oiling are essential to prevent corrosion, especially in moist environments. It’s also crucial to avoid harsh chemicals and saltwater. In contrast, 8Cr13MoV is easier to sharpen due to its slightly lower hardness. It needs similar cleaning but may not perform as well as 440 Stainless Steel in highly corrosive environments.
Can 8Cr13MoV be used as a direct substitute for 440 Stainless Steel in all applications?
8Cr13MoV cannot be used as a direct substitute for 440 Stainless Steel in all applications. While both materials are martensitic stainless steels with good hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, they have distinct differences that affect their suitability for specific uses.
440 Stainless Steel, particularly in its 440C variant, has a higher carbon content (~1%) and chromium content (~17.5%) compared to 8Cr13MoV, which contains about 0.8% carbon and 13% chromium. This higher carbon and chromium content in 440C results in superior edge retention and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty applications, such as professional knives and industrial tools.
On the other hand, 8Cr13MoV, with its slightly lower hardness and chromium content, offers better toughness and ease of sharpening, which makes it more suitable for budget-friendly knives, everyday carry (EDC) tools, and applications where cost and maintenance are significant considerations.
Therefore, while 8Cr13MoV is a viable alternative for less demanding applications, it cannot match the performance of 440 Stainless Steel in scenarios requiring the highest levels of edge retention and wear resistance. The choice between these steels should be based on the specific requirements of the project, including performance needs, budget, and maintenance preferences.
