When it comes to selecting the right aluminium alloy for your project, understanding the subtle differences between Aluminium 5083 and 5754 can be crucial. Both alloys are popular in industries ranging from automotive to marine engineering, yet they each bring unique properties to the table. Aluminium 5083 is known for its exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion, making it a preferred choice for high-stress applications. On the other hand, Aluminium 5754 offers excellent weldability and moderate strength, often making it ideal for structural applications.
In this comprehensive comparison, we will delve into the chemical compositions, material properties, and industrial applications of both alloys. You’ll discover how their distinct characteristics impact their performance and suitability for various uses. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to determine which aluminium alloy best meets the demands of your specific project. So, which one will it be – the robust Aluminium 5083 or the versatile Aluminium 5754? Let’s find out.
Understanding Aluminum – Magnesium Alloys
Definition and Overview of Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys
Aluminum-magnesium alloys, often referred to as Al-Mg alloys, are a significant group within the aluminum alloy family. These alloys are mainly composed of aluminum with 2.5% to 5.5% magnesium, which is their key alloying element. This combination results in alloys that exhibit a unique balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and workability, making them highly desirable for a wide range of industrial applications.
General Properties and Significance in Manufacturing
Strength and Durability
A major advantage of aluminum-magnesium alloys is their improved strength-to-weight ratio. The addition of magnesium increases the material’s tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and workability, making it highly suitable for applications in the aerospace, automotive, and marine industries where lightweight and durability are critical factors.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum-magnesium alloys are well-known for their excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments. Magnesium helps form a protective oxide layer on the alloy’s surface, preventing further oxidation and damage. This property makes Al-Mg alloys ideal for use in shipbuilding, offshore structures, and other applications exposed to harsh, corrosive conditions.
Weldability and Formability
These alloys also offer superior weldability and formability, which are crucial for manufacturing processes. They can be easily welded with standard methods like MIG and TIG welding, without losing much of their mechanical properties. Additionally, their high formability allows them to be easily shaped into complex geometries, which is advantageous for producing intricate components and assemblies.
Comparative Analysis of Aluminum 5083 and 5754 Alloys
Chemical Composition
- 5083 Alloy: Typically contains about 4.5% magnesium, along with small amounts of manganese and chromium. This composition provides high strength and excellent resistance to seawater corrosion.
- 5754 Alloy: Contains between 2.6% and 3.6% magnesium, with lower levels of other alloying elements. This results in medium strength but with enhanced formability and weldability.
Mechanical Properties
- Strength: The 5083 alloy generally offers higher tensile strength and hardness compared to the 5754 alloy, making it more suitable for applications requiring robust structural integrity.
- Ductility: The 5754 alloy, with its lower magnesium content, provides better ductility and formability. This makes it easier to work with in manufacturing processes that involve bending and shaping.
Corrosion Resistance
Both 5083 and 5754 alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, but the 5083 alloy is particularly noted for its performance in marine environments due to its higher magnesium content. The 5754 alloy, while still highly resistant to corrosion, is often preferred for applications where formability is more critical.
Applications
- 5083 Alloy: Commonly used in shipbuilding, pressure vessels, and cryogenic applications due to its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance.
- 5754 Alloy: Frequently utilized in automotive manufacturing for body panels, fuel tanks, and other components where a balance of strength, formability, and corrosion resistance is required.
Knowing the differences and general properties of aluminum 5083 and 5754 alloys is essential for choosing the right material for specific industrial uses. The choice of alloy depends on the specific requirements of the project, including strength, corrosion resistance, formability, and cost considerations.
Introduction to Aluminium 5083
Aluminium 5083 is an alloy mainly composed of aluminium, with magnesium as the key element that enhances its properties. This alloy also contains small amounts of manganese and chromium, which contribute to its unique characteristics.
- Aluminium (Al): 92.4 – 95.6%
- Magnesium (Mg): 4.0 – 4.9%
- Manganese (Mn): ≤ 1.0%
- Silicon (Si): ≤ 0.40%
- Iron (Fe): ≤ 0.40%
- Chromium (Cr): ≤ 0.25%
- Zinc (Zn): ≤ 0.25%
- Titanium (Ti): ≤ 0.15%
Aluminium 5083 is known for its exceptional performance in extreme environments. This non-heat treatable alloy gains its strength from alloying elements and cold working, rather than heat treatment. Here are some of its notable characteristics:
- High Strength: With an ultimate tensile strength of 290 MPa and a tensile yield strength of 145 MPa, Aluminium 5083 is one of the stronger non-heat treatable alloys.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Particularly resistant to seawater and industrial chemicals, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications.
- Good Weldability: Can be easily welded using conventional methods such as MIG and TIG welding without significant loss of strength.
Understanding the physical and mechanical properties of Aluminium 5083 is essential for its use in various industries. Key properties include a density of 2650 kg/m³, melting point of 591-638°C, and ultimate tensile strength of 290 MPa. These properties make Aluminium 5083 suitable for applications where high strength, durability, and resistance to harsh environments are required.
Aluminium 5083 adheres to industry standards, ensuring reliability and suitability for critical applications. It meets specifications from ASTM and ISO, such as ASTM B209 for sheets and plates, and ISO 6361 for wrought aluminium products.
Aluminium 5083 is widely used where high strength and corrosion resistance are crucial. Common applications include shipbuilding, rail cars, vehicle bodies, pressure vessels, and aerospace components, thanks to its durability and performance in harsh conditions.
Introduction to Aluminium 5754
Chemical Composition
Aluminium 5754 is an alloy primarily composed of aluminum, with specific elements contributing to its unique properties. The typical chemical composition is as follows:
- Aluminum (Al): 94.2 – 97.4%
- Magnesium (Mg): 2.6 – 3.6%
- Manganese (Mn): ≤ 0.50%
- Chromium (Cr): ≤ 0.30%
- Iron (Fe): ≤ 0.40%
- Silicon (Si): ≤ 0.40%
- Zinc (Zn): ≤ 0.20%
General Characteristics
Aluminium 5754 is renowned for its balanced combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and formability. Here are some of its key characteristics:
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminium 5754 excels in resisting corrosion, especially in marine and industrial environments. For instance, in chemical plants where exposure to corrosive substances is common, such as in the storage and handling of acidic or alkaline materials, Aluminium 5754 proves invaluable due to its durability and resistance to degradation.
Mechanical Strength
This alloy offers a good balance between strength and weight. With tensile strength ranging from 200 to 330 MPa, it provides higher structural integrity compared to some other aluminum alloys like 5052, making it suitable for applications that demand both robustness and lightness.
Formability
While Aluminium 5754 may not be as formable as some other alloys in the 5000 series, such as 5083 or 5052, it still offers good versatility. It can be used in deep-drawing and machining processes, making it practical for creating complex shapes and designs.
Weldability
The excellent weldability of Aluminium 5754 allows it to be easily welded using conventional methods like MIG and TIG welding. This characteristic ensures that the alloy maintains its mechanical properties after welding, which is crucial for applications that require strong, reliable joints.
Industry Standards Compliance
Aluminium 5754 complies with several industry standards, ensuring its reliability and suitability for various applications. Key standards include:
- ASTM B209: Standard Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Sheet and Plate, ensuring material consistency and quality.
- ISO 6361: Wrought Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy Sheets, Strips, and Plates, guaranteeing the material meets international quality and performance benchmarks.
Applications of Aluminium 5754
Marine Industry
In the marine industry, Aluminium 5754 is an ideal choice for constructing boat hulls, superstructures, and fittings. Its excellent resistance to seawater corrosion ensures long-lasting performance in harsh marine environments.
Automotive Industry
Aluminium 5754 is highly valued in the automotive industry for body panels and other exterior components. Its combination of formability, strength, and corrosion resistance makes it perfect for producing durable and lightweight automotive parts.
Construction and Architecture
For construction and architectural applications, Aluminium 5754 is used in building facades and decorative elements. Its aesthetic appeal, along with its resistance to corrosion, makes it a popular choice for both functional and decorative applications.
Industrial Equipment
Aluminium 5754 is well-suited for various types of industrial equipment and storage tanks. Its strength and resistance to harsh environments ensure reliable, long-lasting performance in demanding industrial settings.
Comparison of Material Properties
Strength and Corrosion Resistance
Quantitative Comparison of Strength Metrics
Aluminium 5083 and 5754 exhibit distinct differences in their strength properties. Aluminium 5083 (H111) has a yield strength of 145 MPa and a tensile strength of 310 MPa, whereas Aluminium 5754 (H22) boasts a yield strength of 190 MPa and a tensile strength of 285 MPa. In terms of hardness, Aluminium 5083 has a value of 75 HB, and Aluminium 5754 has 78 HB. While 5083 has higher tensile strength, 5754 provides a higher yield strength and slightly more hardness.
Analysis of Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Aluminium 5083 is renowned for its excellent resistance to seawater and industrial chemicals, making it highly suitable for marine and shipbuilding applications where exposure to harsh, corrosive environments is common. On the other hand, Aluminium 5754 also offers excellent corrosion resistance in marine environments, but it is slightly less resistant compared to 5083.
Weldability
Welding Techniques Suitable for Each Alloy
Both Aluminium 5083 and 5754 can be welded using conventional methods such as MIG and TIG welding. These techniques are widely used in the industry due to their effectiveness in joining aluminium alloys.
Comparison of Welding Performance
Aluminium 5083 is highly weldable and retains good strength after welding. However, it has a limitation in high-temperature applications; it should not be used at temperatures above 65°C. Aluminium 5754 is also highly weldable and has good formability, making it versatile for various fabrication processes and manufacturing applications.
Industrial Applications
Shipbuilding
In shipbuilding, both Aluminium 5083 and 5754 are extensively used, each serving different purposes within the industry. Aluminium 5083 is favored for its high strength and exceptional seawater corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in the construction of hulls and other load-bearing structures, where durability against harsh marine environments and the ability to withstand heavy stresses are crucial, providing the necessary structural integrity for long-term operation in rough seas.
On the other hand, Aluminium 5754 is often used for superstructures and fittings. Its good formability allows for the creation of complex shapes, which is useful for aesthetic and functional design elements. Additionally, its excellent weldability and corrosion resistance make it suitable for joining and withstanding the marine environment, though it may not offer the same level of strength as 5083 in high-stress areas.
Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, Aluminium 5083 and 5754 have distinct applications. Aluminium 5083 is used in parts that require high strength and resistance to corrosion, such as certain structural components in heavy-duty vehicles. Its ability to maintain strength at low temperatures also makes it suitable for vehicles operating in cold climates.
Aluminium 5754, known for its strength, formability, and cost-effectiveness, is widely used for body panels, fuel tanks, and other exterior parts. Its good formability enables it to be shaped into various designs, while its corrosion resistance ensures the longevity of the automotive parts.
Pressure Vessels
For pressure vessel construction, both alloys have their advantages. Aluminium 5083’s high strength and corrosion resistance make it a reliable choice for vessels that need to withstand high internal pressures and harsh chemical environments. It can be used in industrial pressure vessels for storing and transporting corrosive fluids.
Aluminium 5754 is also used in pressure vessels, especially when a balance between strength and cost is required. Its excellent weldability and good fatigue strength make it ideal for pressure vessel fabrication, ensuring reliable joints and long-term performance under repeated use.
How Chemical Compositions Affect Properties
Impact of Chemical Composition on Strength and Durability
The chemical makeup of Aluminium 5083 and 5754 significantly influences their strength and durability. Aluminium 5083 contains a higher percentage of magnesium (4 – 4.9%) compared to Aluminium 5754 (2.6 – 3.6%). This higher magnesium content in 5083 contributes to its high tensile strength, making it suitable for applications where robust structural integrity is required, such as construction equipment and marine vessels.
On the other hand, Aluminium 5754, with its relatively lower magnesium content, has slightly lower tensile strength. However, its chemical composition gives it superior fatigue strength. The presence of elements like copper (max 0.5%) in Aluminium 5754 may also play a role in enhancing its fatigue resistance, making it ideal for applications like sheet metal fabrication, tank bodies, and heat exchangers that are subject to cyclic loading.
Influence on Corrosion Resistance
Both alloys owe their excellent corrosion resistance, especially in seawater, to their magnesium content. Magnesium helps form a protective oxide layer on the alloy’s surface, preventing further oxidation and damage.
Aluminium 5083, with its higher magnesium percentage and the presence of other alloying elements such as chromium (max 0.1%), is noted for its superior chemical and atmospheric resistance. The chromium in 5083 can enhance the stability of the protective oxide layer, providing better protection against a wider range of corrosive environments.
Aluminium 5754 also performs well in seawater due to its balanced composition but has slightly lower corrosion resistance compared to 5083. While it still offers good protection, the slightly less robust protective oxide layer makes it more vulnerable in highly corrosive settings.
Effect on Weldability
The chemical compositions of these two alloys also affect their weldability. Aluminium 5083 has excellent weldability and retains most of its strength after welding. The specific combination of elements in 5083, such as manganese (0.4 – 1%), helps maintain the alloy’s integrity during the welding process. Manganese can improve the fluidity of the molten metal and reduce the formation of defects, ensuring a strong weld joint.
Aluminium 5754 also has good weldability but may not retain as much strength post – welding as 5083. The lower manganese content (max 0.5%) and different chemical balance in 5754 might lead to a slightly less stable weld structure, resulting in a greater loss of strength after welding.
Role in Formability
Formability is another property influenced by the chemical composition. Aluminium 5754 is highly formable and resistant to hot and cold deformation. Its lower magnesium content and the presence of elements like iron (max 0.7%) contribute to its ability to be easily shaped. Iron can act as a grain refiner, improving the alloy’s ductility and making it more malleable.
Aluminium 5083 is suitable for bending and cold working but is less formable than 5754 under high stress. The higher magnesium content and different alloying element ratios in 5083 make the alloy more rigid, reducing its formability in high – stress forming operations.
In – depth Comparison for Project Selection
Key Considerations for Selecting Aluminium 5083 or 5754
When choosing between Aluminium 5083 and 5754 for a project, it’s essential to consider several critical factors to ensure the material’s performance and cost-effectiveness.
Strength and Structural Integrity
Aluminium 5083 is renowned for its high tensile strength, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring robust structural integrity, such as marine constructions and pressure vessels. Its ability to maintain strength under severe conditions is a decisive factor for projects involving heavy loads or extreme environmental stress.
In contrast, Aluminium 5754 offers medium strength but excels in fatigue resistance. This makes it particularly suitable for components subjected to cyclic stresses, like automotive parts, where durability over repeated use is essential.
Corrosion Resistance
Both alloys provide good corrosion resistance, but Aluminium 5083 is superior, especially in marine environments. This makes it ideal for shipbuilding projects and applications where exposure to seawater or industrial chemicals is prevalent. Aluminium 5754, while slightly less resistant than 5083, still offers substantial protection against corrosion. It is often preferred in environments where formability is more crucial than maximum corrosion resistance.
Weldability and Formability
Aluminium 5754 is highly valued for its excellent formability and weldability, making manufacturing and processing easier. It is particularly advantageous for projects requiring complex shapes and extensive fabrication processes, such as automotive manufacturing and sheet metal applications.
Aluminium 5083 also offers good weldability, maintaining its structural integrity post-welding. However, its formability is not as high as 5754, which might limit its application in intricate designs.
Cost-Effectiveness
Budget considerations often play a significant role in material selection. Aluminium 5754 is generally more cost-effective than 5083 due to its lower magnesium content and balanced properties, making it suitable for projects where cost is a primary concern without compromising too much on performance.
Aluminium 5083, though more expensive, provides superior strength and corrosion resistance, justifying its higher cost in applications where these properties are critical.
Long-Term Performance Considerations
Environmental and Operational Conditions
The operational environment significantly impacts the long-term performance of these alloys. For projects in harsh marine or industrial settings, Aluminium 5083’s superior corrosion resistance offers prolonged durability and reliability.
Aluminium 5754’s high fatigue resistance ensures longevity in applications involving frequent load cycles, such as automotive components and storage tanks.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
The choice between these alloys can influence maintenance requirements and lifecycle costs. Aluminium 5083 may require less frequent maintenance due to its higher durability and resistance to environmental degradation.
Aluminium 5754, while requiring potentially more frequent checks in highly corrosive environments, benefits from lower initial costs and ease of processing, which can offset lifecycle expenses in less demanding conditions.
Examples of Projects and Alloy Choices
Marine Applications
In marine construction projects, Aluminium 5083 is often chosen for its unrivaled strength and corrosion resistance, essential for hulls and structural components exposed to seawater.
Automotive Manufacturing
For automotive body panels and structural elements, Aluminium 5754 is preferred due to its cost-effectiveness, good formability, and adequate strength, providing a balanced solution for performance and budget constraints.
Pressure Vessels
Pressure vessels benefit from the high strength and corrosion resistance of Aluminium 5083, ensuring safety and reliability in storing or transporting pressurized substances.
Aluminium 5754 is also used in pressure vessels where ease of fabrication and fatigue resistance are prioritized, offering a practical alternative for less critical applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the key differences in strength and durability between Aluminium 5083 and 5754?
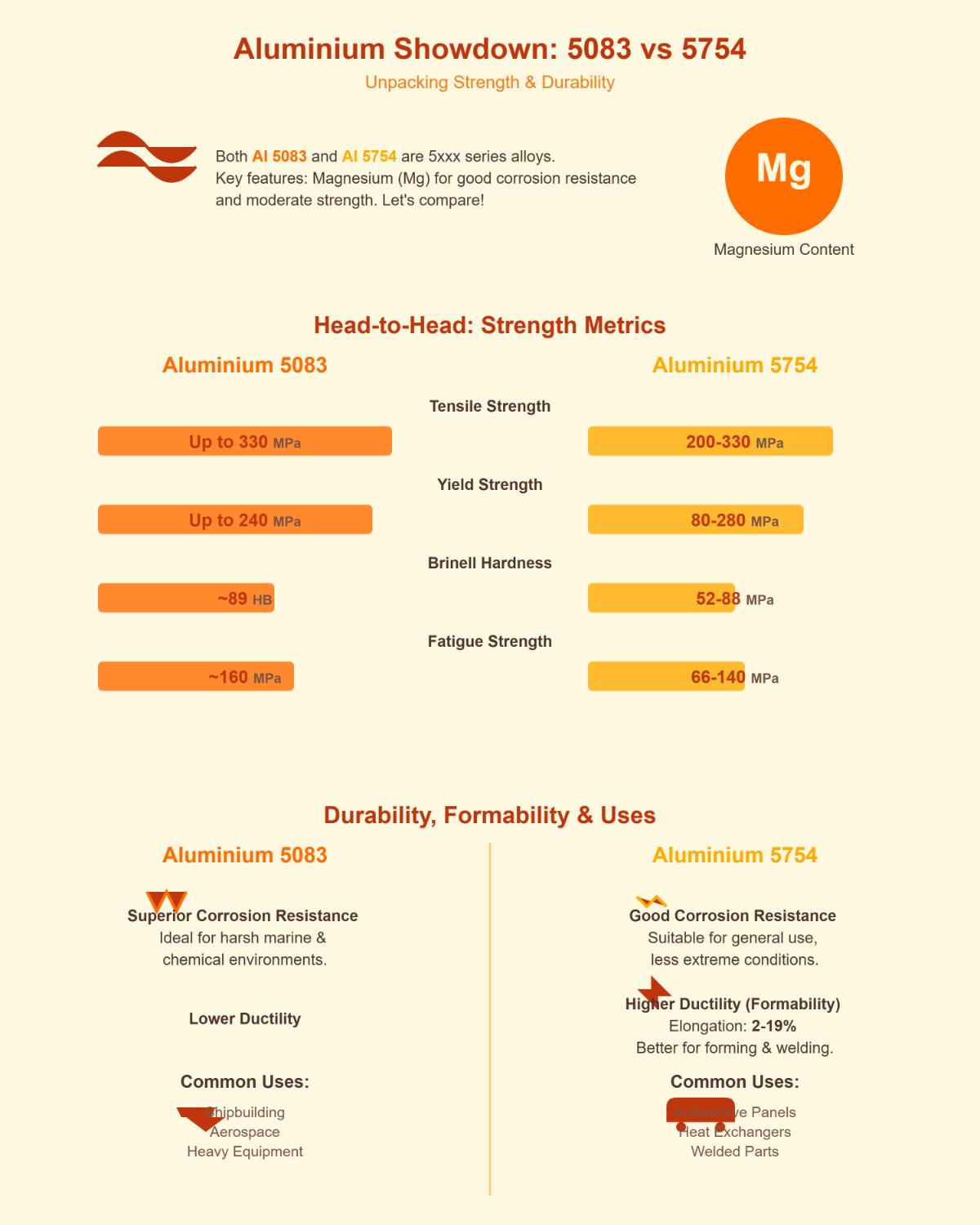
Aluminium 5083 and 5754 are both part of the 5xxx series, known for their magnesium content, which enhances corrosion resistance and provides moderate strength. However, they differ significantly in terms of strength and durability.
Aluminium 5083 is recognized for its high tensile strength, reaching up to 330 MPa, and superior yield strength of up to 240 MPa. It also has a higher Brinell hardness (around 89) and excellent fatigue strength (approximately 160 MPa). These properties make it highly durable and suitable for demanding applications like shipbuilding, aerospace, and construction equipment, where high strength and resistance to harsh environments are essential.
In contrast, Aluminium 5754 offers a lower tensile strength range of 200 to 330 MPa and yield strength between 80 to 280 MPa. It has a slightly lower Brinell hardness (52 to 88) and fatigue strength (66 to 140 MPa) compared to 5083. However, 5754 exhibits better elongation at break (2 to 19%), indicating higher ductility, which is advantageous in applications requiring formability and welding, such as automotive body panels and heat exchanger shells.
Both alloys have excellent corrosion resistance, but Aluminium 5083 is more suited for extreme marine environments due to its superior resistance to seawater and industrial chemicals. Aluminium 5754 also offers good corrosion resistance but is slightly less effective in harsh conditions.
Which applications are most suited for Aluminium 5083 and 5754?
Aluminium 5083 is best suited for applications that require high strength and exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and shipbuilding industries. It is commonly used for ship hulls, offshore platforms, and other marine structures due to its ability to withstand seawater corrosion. Additionally, Aluminium 5083 is ideal for automotive and railcar parts, as well as pressure vessels and storage tanks where high strength and durability are crucial.
On the other hand, Aluminium 5754 is more versatile for automotive and industrial applications. It is frequently used in car doors and molds, as well as in welding structures and storage tanks. Its good corrosion resistance and weldability make it suitable for marine components and transportation tanks, including nuclear applications. While Aluminium 5754 offers moderate strength compared to 5083, its cost-effectiveness and broad application range make it a preferred choice for less demanding structural applications.
How do the chemical compositions of Aluminium 5083 and 5754 affect their properties?
The chemical compositions of Aluminium 5083 and 5754 significantly influence their respective properties. Aluminium 5083 contains higher magnesium content (4.0-4.9%) compared to Aluminium 5754 (2.6-3.6%), contributing to its superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as construction equipment and ship structures. The higher manganese content in 5083 (0.4-1.0%) also enhances its strength and corrosion resistance. Additionally, 5083 has excellent weldability, retaining much of its strength post-welding, which is beneficial for transportation vehicles and pressure vessels.
In contrast, Aluminium 5754, with its lower magnesium content, offers slightly less tensile strength but higher fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. This makes it suitable for applications requiring good formability and ductility, such as sheet metal fabrication for tank bodies and heat exchangers. Although its weldability is good, it is not as high as 5083. Both alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments, but 5083 generally performs better in this regard.
What factors should be considered when choosing between Aluminium 5083 and 5754 for a project?
When choosing between Aluminium 5083 and 5754 for a project, consider several factors. Aluminium 5083 has higher magnesium content, leading to greater strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high – strength applications like shipbuilding. It offers high tensile strength and superior durability. However, it is more expensive. Aluminium 5754, with lower magnesium, has medium strength, excellent formability, and good fatigue strength. It’s ideal for applications where formability is key, such as automotive parts. Also, consider corrosion resistance (5083 is better in harsh environments), and budget (5754 is more economical).
Are there any cost differences between Aluminium 5083 and 5754?
Yes, there are cost differences between Aluminium 5083 and 5754. Aluminium 5083 generally costs more due to its higher magnesium content and superior mechanical properties. This increased cost reflects its enhanced strength and corrosion resistance, important in demanding environments like marine applications. However, prices for both alloys can fluctuate based on market demand, thickness, size, and manufacturing processes. For less demanding applications where medium strength suffices, Aluminium 5754 can be a more cost – effective option.
What are the long – term performance differences of Aluminium 5083 and 5754 in industrial applications?
The long-term performance differences between Aluminium 5083 and 5754 in industrial applications primarily hinge on their distinct properties and suitable use cases. Aluminium 5083, known for its high tensile strength and superior durability, excels in environments requiring high structural integrity, such as shipbuilding and pressure vessels. Its excellent resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures, combined with superior corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments, makes it ideal for long-term applications exposed to harsh conditions.
Conversely, Aluminium 5754, while offering slightly lower tensile strength, provides exceptional fatigue strength and stress corrosion cracking resistance. This makes it particularly advantageous for components subject to cyclic loads, such as those in automotive manufacturing and storage tanks. Its good corrosion resistance and formability also contribute to its effectiveness in varied industrial conditions.
In summary, Aluminium 5083 is favored for its durability and extreme condition resistance, while Aluminium 5754 is preferred for applications requiring high fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. The choice between the two depends on the specific demands of the project, including strength, corrosion resistance, and environmental exposure.
