When it comes to selecting the right stainless steel pipes for your project, understanding the nuances between different standards is crucial. ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 are two prominent specifications in the industry, each serving distinct purposes and offering unique advantages. But how do you determine which one is best suited for your needs? In this article, we delve into a comprehensive comparison of these two standards, exploring their material compositions, manufacturing processes, mechanical properties, and more. Whether you’re concerned about high-temperature performance or cost-effectiveness, we’ve got you covered. Ready to discover the key differences and decide which standard aligns with your application requirements? Let’s dive in.
Overview of Stainless Steel Pipe Standards
Introduction to ASTM Standards
ASTM standards are essential for ensuring the quality, safety, and performance of materials across various industries. These standards provide clear guidelines for the manufacturing, testing, and application of materials, helping to maintain consistency and reliability across different products and services. In the context of stainless steel pipes, ASTM standards are particularly important for defining the specifications and requirements that these pipes must meet.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 is a widely recognized standard that covers seamless, welded, and heavily cold-worked austenitic stainless steel pipes. These pipes are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Key Features
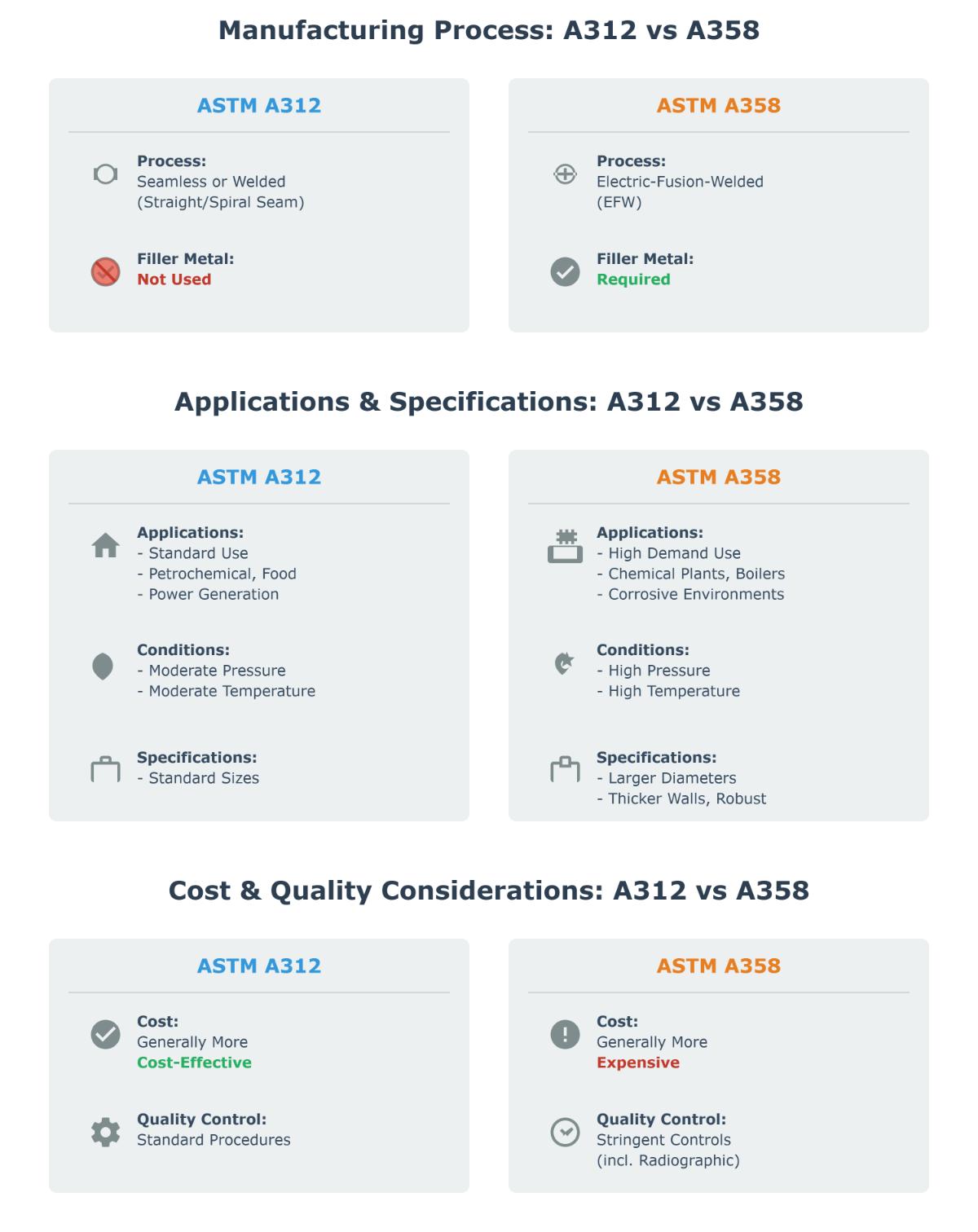
- Manufacturing Processes: The standard includes seamless, welded, and heavily cold-worked manufacturing methods. This flexibility enables manufacturers to choose the most appropriate process based on the specific requirements of the application.
- Grades: Common grades under ASTM A312 include TP304/L, TP316/L, TP321/H, and TP347. Each grade offers unique properties, such as enhanced corrosion resistance or improved performance at high temperatures.
- Applications: ASTM A312 pipes are commonly used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, petrochemical, and oil and gas. Their versatility and reliability make these pipes popular in many different applications.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 is another important standard that covers electric-fusion-welded austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel pipes. These pipes are designed for applications where welding is a critical factor, offering specific advantages in terms of customization and cost-effectiveness.
Key Features
- Manufacturing Processes: ASTM A358 pipes are manufactured using electric-fusion-welding, which includes single- or double-welded butt joints. This process is ideal for large-diameter pipes, providing cost and manufacturing benefits.
- Sub-classes: The standard includes five sub-classes (Class 1 to Class 5), each with different requirements for welding, filler material, and radiographic examination. This allows for customization based on the specific needs of the application.
- Applications: Similar to ASTM A312, ASTM A358 pipes are used in high-temperature and corrosive environments. They are often preferred for large-diameter pipes in industries such as petrochemical, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
Comparative Analysis
When comparing ASTM A312 and ASTM A358, several key differences emerge that can influence the choice of standard for a particular application:
- Manufacturing Flexibility: ASTM A312 offers greater versatility in terms of manufacturing processes, making it suitable for a broader range of applications. In contrast, ASTM A358 is specifically tailored for electric-fusion-welded pipes, which can be advantageous for certain large-diameter applications.
- Cost and Size Considerations: ASTM A358 pipes are usually less expensive and can be made in larger diameters than seamless ASTM A312 pipes. This cost advantage can be significant for projects requiring large-diameter pipes.
- Welding Requirements: ASTM A358 includes specific sub-classes that cater to different welding and inspection requirements, providing greater customization options for applications where welding is a critical factor.
By understanding the distinct features and advantages of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358, engineers and manufacturing professionals can make informed decisions about which standard best meets the needs of their specific projects.
Detailed Comparison of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358
Material Composition
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 covers austenitic stainless steels, mainly composed of chromium and nickel. Common grades include TP304, TP316, and TP321, which are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The standard also allows for the use of low-carbon versions (e.g., TP304L, TP316L) to minimize carbide precipitation during welding.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 covers austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel pipes, including similar grades to ASTM A312, such as 304, 316, and their low-carbon variants. The emphasis on electric-fusion-welding (EFW) and filler metals slightly alters the composition to improve welding and mechanical properties.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes outlined in ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 are distinct, each suited to different applications and performance requirements.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 specifies the following manufacturing methods:
- Seamless pipes: Produced through extrusion or rotary piercing, ensuring a high degree of uniformity and strength.
- Welded pipes: Made using automated welding without filler metal, suitable for moderate conditions.
- Heavily cold-worked pipes: Undergo significant deformation to improve strength and corrosion resistance.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 specifies electric-fusion-welded (EFW) pipes, which involve:
- Single- or double-welded butt joints: Using filler metal to achieve robust joints, suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Radiographic examination: Ensuring the integrity of the welds, particularly important for thick-walled pipes.
- Multiple classes: Classes 1 to 5, each with specific requirements for welding, filler material, and inspection.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of pipes under ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 standards differ due to their manufacturing processes and material compositions.
ASTM A312
- Strength: Generally offers good tensile and yield strength, suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Ductility: High ductility, allowing for easy forming and machining.
- Hardness: Moderate hardness, with options for cold working to increase strength.
ASTM A358
- Strength: Enhanced by the use of filler metals during welding, making it suitable for high-stress environments.
- Ductility: Slightly reduced compared to seamless pipes due to welding processes, but still sufficient for industrial applications.
- Hardness: Comparable to ASTM A312, with potential for higher hardness in thicker walls.
Corrosion Resistance
Both ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance, but their performance can vary based on the specific environment and application.
ASTM A312
- General Corrosion Resistance: High resistance to corrosion in various environments, including chemical processing and food industries.
- Localized Corrosion: Low-carbon variants (e.g., TP316L) are particularly resistant to intergranular corrosion.
ASTM A358
- Enhanced Resistance: The EFW process and filler metals enhance resistance to stress corrosion cracking and pitting.
- Thicker Walls: Provide additional protection in highly corrosive environments, making them suitable for severe conditions.
High-Temperature Applications
The suitability of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes for high-temperature applications depends on their material and manufacturing processes.
ASTM A312
- Temperature Range: Effective for moderate to high temperatures, commonly used in power generation and chemical processing.
- Thermal Stability: Austenitic stainless steels maintain their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures.
ASTM A358
- High-Temperature Performance: Designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as industrial boilers and power plants.
- Thermal Expansion: The presence of welds and filler metals can affect thermal expansion, which should be considered in design.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cost considerations play a crucial role in choosing between ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes.
ASTM A312
- Manufacturing Cost: Generally more cost-effective due to simpler manufacturing processes, especially for standard sizes and applications.
- Operational Cost: Lower maintenance costs in general-purpose applications.
ASTM A358
- Manufacturing Cost: Higher due to the use of filler materials, fusion welding, and stringent quality controls.
- Operational Cost: Higher initial investment but potentially lower long-term costs in high-pressure, high-temperature environments due to enhanced durability.
Technical Specifications for Stainless Steel Pipes
ASTM A312 Technical Specifications
ASTM A312 covers seamless, welded, and heavily cold-worked austenitic stainless steel pipes, known for their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures.
Dimensions and Tolerances
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): Ranges from 1/8 inch to 30 inches.
- Wall Thickness: Varies based on schedule, such as Schedule 5S, 10S, 40S, and 80S.
- Length: Standard lengths are 5.8 meters, 6 meters, or cut to customer requirements.
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength: Minimum of 515 MPa.
- Yield Strength: Minimum of 205 MPa.
- Elongation: At least 35% over 2 inches.
Chemical Composition
- Chromium (Cr): 18-20% for TP304 and 16-18% for TP316.
- Nickel (Ni): 8-10.5% for TP304 and 10-14% for TP316.
- Carbon (C): No more than 0.08% for standard grades and 0.03% for low-carbon variants (L grades).
Manufacturing Processes
- Seamless: Made by extrusion or rotary piercing.
- Welded: Produced by automated welding without filler metal.
- Heavily Cold-Worked: Subjected to significant deformation to enhance strength and corrosion resistance.
ASTM A358 Technical Specifications
ASTM A358 covers electric-fusion-welded austenitic stainless steel pipes, designed for thicker walls and larger diameters.
Dimensions and Tolerances
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): Generally ranges from 8 inches to 48 inches.
- Wall Thickness: Heavier walls, ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Length: Custom lengths available based on project requirements.
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength: Minimum of 515 MPa.
- Yield Strength: Minimum of 205 MPa.
- Elongation: Minimum of 35% in 2 inches.
Chemical Composition
- Chromium (Cr): 18-20% for 304 and 16-18% for 316.
- Nickel (Ni): 8-10.5% for 304 and 10-14% for 316.
- Carbon (C): Maximum of 0.08% for standard grades, 0.03% for low-carbon variants (L grades).
Manufacturing Processes
- Electric-Fusion-Welded (EFW): Utilizes filler metal to enhance joint strength.
- Welding Techniques: Single or double-welded butt joints, subjected to radiographic examination to ensure weld integrity.
- Classes: Five distinct classes (1 to 5), each with specific requirements for welding and inspection.
Comparative Analysis
Size and Thickness
- ASTM A312: Suitable for smaller diameters up to 30 inches with standard wall thickness.
- ASTM A358: Designed for larger diameters up to 48 inches and heavier wall thickness for high-pressure applications.
Joint Efficiency
- ASTM A312: Typically ranges from 60% to 85%.
- ASTM A358: Generally higher, ranging from 85% to 100% due to controlled welding processes.
Application Suitability
- ASTM A312: Versatile for industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and other corrosive environments.
- ASTM A358: Specialized for high-temperature, high-pressure, and highly corrosive environments, particularly where robust welding is crucial.
Applications in Industry
Petrochemical Industry
In the petrochemical industry, the choice between ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 stainless steel pipes is often dictated by the specific requirements of the application.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 pipes are widely used due to their excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. These pipes are suitable for transporting chemicals, oils, and gases, where moderate pressure and temperature conditions are prevalent. The seamless and welded variants without filler metal provide reliability and versatility, making them ideal for various general-purpose applications within the industry.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 pipes are preferred for applications with high pressures and temperatures. The electric-fusion-welded (EFW) process with filler metal enhances the strength and durability of the pipes, making them suitable for critical applications such as high-pressure steam lines, condensate systems, and other high-stress environments. The ability to produce larger diameter pipes also offers an advantage for extensive pipeline systems.
Food Processing Industry
The food processing industry requires materials that ensure hygiene and resist corrosion from various food products and cleaning agents.
ASTM A312
Low-carbon grades like TP304L and TP316L minimize contamination risk and ensure regulatory compliance, making these seamless and welded pipes ideal for transporting food products, water, and other fluids under sanitary conditions.
ASTM A358
Though less common in food processing, ASTM A358 pipes are used when larger diameters and higher pressures are needed. The EFW process and use of filler metals ensure robust joints, which can be beneficial in large-scale processing plants with extensive piping networks. The primary advantage lies in applications that demand greater structural integrity and resistance to high-pressure cleaning systems.
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry demands high standards of cleanliness, corrosion resistance, and reliability for manufacturing and transporting sensitive products.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 pipes are extensively used due to their excellent corrosion resistance, cleanliness, and ability to withstand high temperatures. The seamless and welded pipes without filler metal are ideal for transporting purified water, chemicals, and other pharmaceutical ingredients. The low-carbon variants (e.g., TP316L) are particularly valued for their resistance to intergranular corrosion and compliance with stringent industry standards.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 pipes are used in pharmaceutical settings that require high-pressure steam systems and other high-stress environments. The EFW process ensures strong and reliable joints, suitable for critical applications like autoclaves and high-pressure reactors. The ability to produce thicker walls and larger diameters also provides flexibility in designing robust and efficient pharmaceutical manufacturing systems.
Comparative Analysis
Application Suitability
- General Use: ASTM A312 pipes offer versatility for general-purpose applications across petrochemical, food processing, and pharmaceutical industries. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing make them a preferred choice for moderate conditions.
- High-Pressure and High-Temperature: ASTM A358 pipes are specialized for high-pressure, high-temperature, and highly corrosive environments. The enhanced strength from the EFW process and filler metals makes them suitable for demanding applications where robust performance is critical.
Cost Considerations
- ASTM A312: Generally more cost-effective for standard applications due to simpler manufacturing processes and less stringent testing requirements.
- ASTM A358: Higher initial costs due to complex manufacturing, but potentially lower long-term costs in high-stress environments due to enhanced durability and performance.
ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 standards each offer unique benefits tailored to specific industrial needs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Manufacturing Process and Material Usage
The sustainability and environmental impact of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 stainless steel pipes are largely influenced by their manufacturing processes and material usage.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 covers both seamless and welded austenitic stainless steel pipes. The seamless pipes are produced through extrusion, an energy-efficient process that requires less material. Welded pipes under ASTM A312 are manufactured using automated welding without filler metal, further reducing material usage and energy consumption. This streamlined process results in a lower environmental impact and cost-effectiveness for production.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 specifies electric-fusion-welded (EFW) pipes that require filler metals. The EFW process is more energy-intensive due to the need for additional heating and fusion techniques. However, the use of filler metals can enhance joint strength, potentially reducing material waste and increasing durability. The enhanced durability can offset the higher energy usage by decreasing the frequency of replacements and repairs, contributing to long-term sustainability.
Energy Consumption and Emissions
Energy consumption and emissions during the manufacturing processes of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes are critical factors in their environmental impact.
ASTM A312
The manufacturing process for ASTM A312 pipes is generally simpler and less energy-intensive than that of ASTM A358, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. This makes ASTM A312 pipes a more environmentally friendly option in terms of energy efficiency.
ASTM A358
The EFW process used for ASTM A358 pipes requires more energy due to the heating and melting involved. While this results in higher energy consumption and emissions during production, the stronger welds achieved can extend the lifespan of the pipes. Over time, the reduced need for frequent replacements can lower both maintenance costs and the environmental impact of producing new pipes, potentially offsetting the initial higher energy consumption.
End-of-Life Recyclability
Both ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 stainless steel pipes are highly recyclable, which helps conserve energy and reduce the need for new raw materials. Recycling stainless steel minimizes environmental impact by reducing the demand for new materials and lowering energy consumption associated with raw material extraction and processing. Although specific data on recyclability rates for these pipe types are not widely documented, the inherent recyclability of stainless steel remains a key environmental benefit.
Cost and Resource Efficiency
Cost and resource efficiency are important considerations when evaluating the sustainability of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 pipes are generally more cost-effective due to their simpler manufacturing processes. The reduced complexity translates to lower material and energy usage, enhancing overall production efficiency and reducing costs.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 pipes are more costly due to the complex EFW process and use of filler metals. However, the enhanced durability and performance of these pipes can offset higher upfront costs by reducing maintenance and replacement needs over time. This long-term cost efficiency contributes to resource conservation and sustainability, particularly in high-stress applications.
Applications and Environmental Impact
The applications of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes play a significant role in their environmental impact.
ASTM A312
ASTM A312 pipes are used in a wide range of applications, including petrochemical, food processing, and power generation. Their versatility and cost-effectiveness contribute to widespread use, minimizing waste and optimizing resource usage. This broad application range can reduce environmental impacts by ensuring efficient material utilization and lower overall resource consumption.
ASTM A358
ASTM A358 pipes are primarily used in high-temperature and corrosive environments, such as chemical plants and industrial boilers. Their robust performance in demanding environments helps prevent leaks or failures, avoiding chemical spills and accidents, thus ensuring long-term operational sustainability and enhancing their environmental profile.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the key differences between ASTM A312 and ASTM A358?
ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 are both standards for stainless steel pipes, but they differ significantly in their manufacturing processes, applications, and specifications.
ASTM A312 covers seamless and welded stainless steel pipes without the use of filler metal. These pipes are generally used for standard applications in the petrochemical, food processing, and power generation industries where moderate pressure and temperature conditions are prevalent.
ASTM A358, on the other hand, specifically addresses electric-fusion-welded (EFW) austenitic stainless steel pipes. This process involves the use of filler metal, making the pipes suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments, such as chemical plants and industrial boilers. ASTM A358 pipes are designed for larger diameters and thicker walls, providing robustness in corrosive conditions.
In terms of cost, ASTM A312 pipes are generally more cost-effective due to simpler manufacturing processes, while ASTM A358 pipes are more expensive due to the additional use of filler material and stringent quality controls, including radiographic inspections.
Which standard is better for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, ASTM A358 is generally the better choice. ASTM A358 specifies electric-fusion-welded (EFW) pipes, which are designed for high-temperature and corrosive environments. This standard involves the use of filler metal during the welding process, resulting in stronger welds and higher joint efficiencies (up to 100%). This makes ASTM A358 pipes particularly suitable for demanding conditions found in chemical plants and power plants.
In comparison, ASTM A312 covers both seamless and welded pipes (without filler metal), suitable for general corrosive service and moderate temperatures. While ASTM A312 can be used in high-temperature applications, it is more versatile and typically used in industries where extreme wall thickness is not required, such as petrochemical, food processing, and power generation.
How do ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 standards affect manufacturing processes?
ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 standards affect manufacturing processes primarily through the types of pipes produced and the methods used. ASTM A312 covers both seamless and welded stainless steel pipes, which can be produced via extrusion or automated welding without filler metal. This standard is versatile, suitable for various applications, including those requiring corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance, and generally involves simpler, more cost-effective processes.
In contrast, ASTM A358 focuses specifically on electric-fusion-welded (EFW) austenitic stainless steel pipes, utilizing filler metal during welding. This process enhances the strength and suitability of the pipes for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. ASTM A358 pipes often have larger diameters and thicker walls, necessitating more rigorous quality control measures, such as radiographic inspections, which can increase manufacturing costs.
What are the typical applications of ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 stainless steel pipes?
ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 stainless steel pipes are utilized across various industries due to their distinct properties and manufacturing processes. ASTM A312 pipes are typically used in high-temperature and general corrosive service environments. They are common in the food processing, pharmaceutical, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries. This standard covers seamless, welded, and heavily cold-worked austenitic stainless steel pipes, making them versatile for numerous applications.
On the other hand, ASTM A358 pipes are primarily intended for high-temperature and corrosive service where welding is crucial. These pipes are electric-fusion-welded (EFW), often used in larger diameters, making them suitable for industries such as chemical processing, petrochemical, and power generation. The ASTM A358 standard also includes five subclasses with varying welding and testing requirements, enhancing their suitability for high-pressure applications. Thus, the choice between ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes depends on specific industry requirements, particularly concerning temperature, corrosion resistance, and welding needs.
Are there any cost differences between ASTM A312 and ASTM A358?
Yes, there are cost differences between ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 stainless steel pipes. ASTM A312 pipes, which include both seamless and welded types, generally have a lower cost due to their simpler and more straightforward manufacturing process. This standard is suitable for general-purpose applications, making it cost-effective for moderate pressure and temperature conditions.
On the other hand, ASTM A358 pipes are produced using the electric-fusion-welding (EFW) process, which involves the use of filler material. This method, while providing high joint efficiency and suitability for thicker walls and larger diameters, tends to increase the cost due to additional material and more complex quality control measures. ASTM A358 pipes are designed for high-temperature and corrosive environments, reflecting the higher manufacturing costs required for these demanding applications.
What is the environmental impact of using ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes?
The environmental impact of using ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes is generally positive due to the recyclable and durable nature of stainless steel. Both standards involve the use of stainless steel, which is 100% recyclable, reducing the need for raw materials and minimizing environmental impact. This recyclability allows stainless steel pipes to be reused multiple times without losing quality, contributing to sustainability efforts.
ASTM A312 covers both seamless and welded austenitic stainless steel pipes, which are versatile and widely used. The manufacturing processes for these pipes may vary, but the
ASTM A358 specifically addresses electric-fusion-welded pipes, often used in large-diameter applications. Although the electric-fusion welding process may require more energy compared to other methods, the durability and recyclability of the final product still contribute positively to environmental sustainability.
In summary, both ASTM A312 and ASTM A358 pipes offer excellent environmental benefits due to the inherent properties of stainless steel, such as long lifespan and recyclability. While the specific manufacturing processes may differ slightly in energy requirements, both standards ultimately support sustainable practices across various industries.
