Have you ever wondered why bolts come in so many different shapes and sizes? Understanding the various types of bolt heads and their specific uses is crucial for anyone involved in construction, machinery, furniture assembly, or electronics. From the ubiquitous hex head to the less common truss head, each type of bolt head is designed with a particular application in mind, balancing factors like torque, load distribution, and even aesthetics.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of bolt heads, exploring the unique characteristics of each type and their ideal applications. Whether you’re selecting the right bolt for a high-stress construction project or a delicate piece of furniture, you’ll learn how to make informed decisions to ensure safety, efficiency, and durability. We’ll also cover the essential tools required for different bolt heads and delve into industry standards to ensure compliance.
Ready to become a bolt head expert? Let’s start by unraveling the complexities of the most common types of bolt heads and discover how to choose the perfect one for your next project.
Introduction to Bolt Heads
Bolt heads are essential parts of fastening systems, serving as the point where the bolt and the driving tool connect. The design of a bolt head can significantly influence the fastening process’s efficiency, stress distribution, and the assembly’s final appearance.
Key Characteristics
Drive Type: Drive type refers to the shape of the recess or protrusion that allows a tool to apply torque to the bolt, such as hex, Phillips, Torx, and slotted drives.
Head Style: Head styles affect installation ease and stress distribution, with common styles including hex, flat (countersunk), round, and square.
Common Bolt Head Types
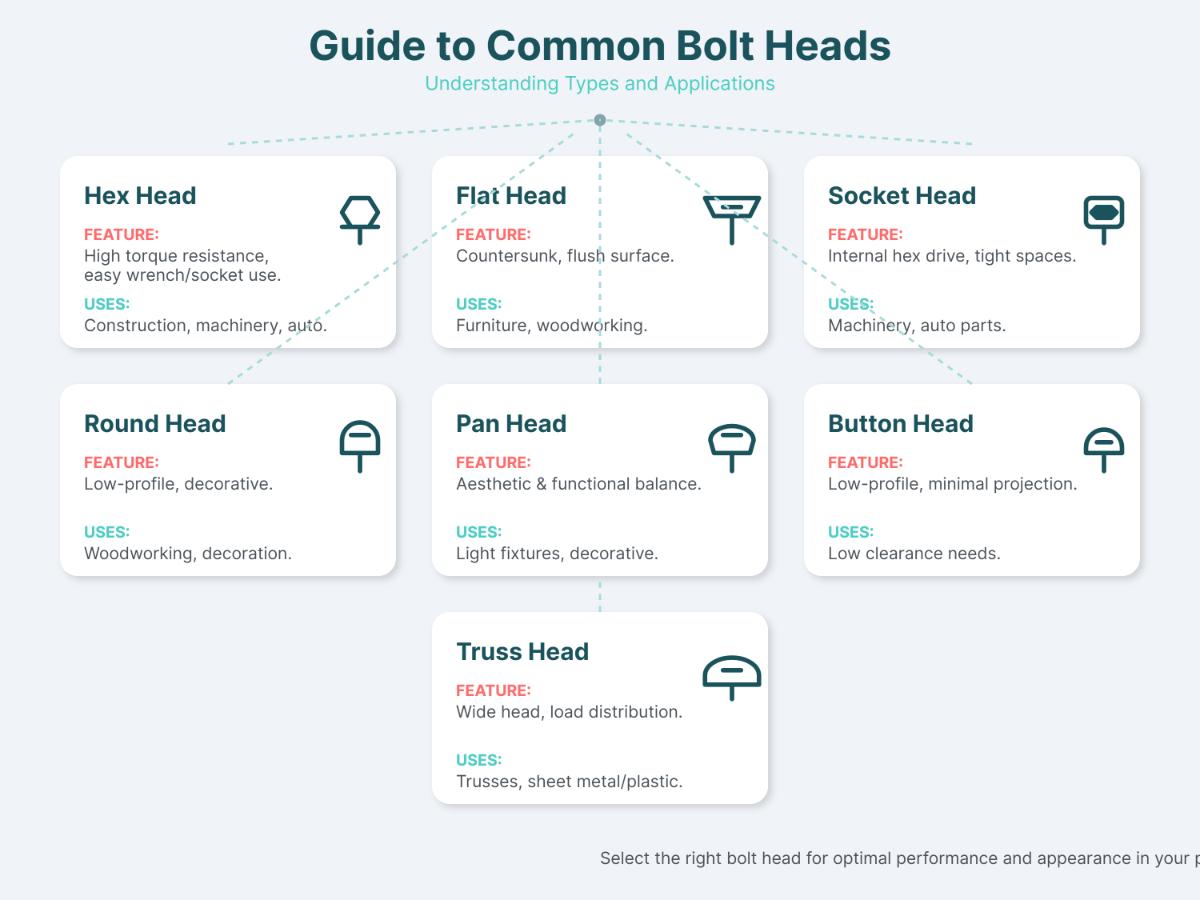
- Hex Head: Recognizable by its six-sided shape, the hex head is designed for use with wrenches and sockets. It provides excellent torque application, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications in construction and machinery.
- Flat Head (Countersunk): Designed to sit flush with the surface, the flat head creates a smooth finish. It is commonly used in woodworking and applications where a sleek appearance is desired.
- Round Head: Featuring a rounded top and flat bearing surface, round heads are often used in electrical fittings and decorative applications, offering a neat appearance while ensuring functionality.
- Pan Head: With a slightly rounded top and flat bearing surface, pan heads are used in sheet metal work and electronics, providing a secure fastening and increased holding power.
- Button Head: Similar to pan heads but with a lower profile, button heads are used in applications where a lower head height is required without sacrificing strength.
- Truss Head: Featuring a wide, flat head, truss heads are used in applications requiring high clamping force, such as in truss assemblies in construction.
Importance of Bolt Head Selection
Choosing the right bolt head ensures easy installation, even force distribution, and meets aesthetic needs, making it crucial for both function and appearance in any project. Hex heads are preferred in heavy-duty applications for their ability to handle high torque, while flat heads are chosen for their flush fit in furniture assembly. Understanding the different types of bolt heads and their specific uses allows engineers and DIY enthusiasts to make informed decisions, ensuring both functionality and durability in their projects.
Types of Bolt Heads
Hex Head Bolts
Hex head bolts have a six-sided head, making them compatible with wrenches and sockets. They are known for their strong grip and efficient torque application. Hex head bolts are commonly used in construction, machinery, and automotive industries due to their robustness and ease of use in high-torque applications.
Flat Head Bolts
Flat head bolts, also known as countersunk bolts, are designed to sit flush with the surface they are installed into. Their tapered heads enable countersinking, which is ideal for applications needing a smooth surface, such as furniture assembly, woodworking, and machinery. Flat head bolts provide a neat appearance and reduce snagging.
Socket Head Bolts
Socket head bolts, or socket cap bolts, have a cylindrical head with a hexagonal recess. They are tightened using a socket driver, offering high torque capacity and a streamlined appearance. These bolts are suitable for applications where a low-profile fastener is needed, such as in machinery and high-torque scenarios.
Round Head Bolts
Round head bolts have a dome-shaped head, offering a low-profile finish. They are commonly used in electrical fittings, appliances, and decorative work due to their neat appearance. Round head bolts provide both functionality and a decorative look.
Pan Head Bolts
Pan head bolts feature a slightly rounded head with a flat top, providing a balance between aesthetics and functionality. They are commonly used in sheet metal work, electronics, and appliance assembly. Pan head bolts offer increased holding power due to their larger contact area.
Button Head Bolts
Button head bolts feature a small, rounded head with a low profile, akin to smaller flat heads. They are often used in applications where a low-profile fastener is desired, such as furniture and appliances. Button head bolts provide a smooth finish while offering necessary strength.
Truss Head Bolts
Truss head bolts have wide, flat heads designed for even load distribution. They are essential in construction for joining trusses and securing thin materials like sheet metal. Truss head bolts prevent material deformation by distributing loads evenly, making them ideal for applications requiring high clamping force.
Oval Head Bolts
Oval head bolts feature an oval-shaped head, slightly domed for a polished look. They are suitable for decorative fixtures and furniture where aesthetics are important. Oval head bolts provide a countersunk finish with a decorative appearance.
Slotted Hex Washer Bolts
Slotted hex washer bolts combine a hexagonal head with a built-in washer and a slot, allowing use with both a wrench and a screwdriver. They are perfect for light-duty tasks that benefit from versatile tool usage and even load distribution.
Square Head Bolts
Square head bolts feature a square head for a strong grip, often used in vintage or heavy-duty projects. They provide high torque resistance and are suitable for applications where visibility is restricted. Square head bolts are easy to grip with wrenches or pliers in tight spaces.
Slotted Head Bolts
Slotted head bolts have a single slot across the head, designed for use with a flathead screwdriver. They are common in light-duty applications, household projects, and older constructions. Slotted head bolts are simple in design, making them easy to install and remove.
Applications of Bolt Heads
Construction
Bolt heads are vital in the construction industry, providing strength and stability for structures. Hex head bolts are commonly used due to their ability to withstand high torque, making them ideal for securing structural components such as beams and columns. Truss head bolts are also widely utilized for their broad head, which distributes loads evenly and prevents material deformation, essential in truss assemblies and sheet metal work. Square head bolts, with their excellent grip, are favored in historical restorations and applications where a vintage aesthetic is desired.
Machinery
In machinery applications, bolt heads must endure significant stress and provide reliable fastening. Socket head bolts are preferred for their high torque capacity and streamlined appearance, making them suitable for high-precision machinery assemblies, while hex head bolts are popular for their robustness and ease of use. Button head bolts, with their low profile, are often used in machinery where space constraints are a concern, ensuring a secure fit without protruding parts that could interfere with moving components.
Furniture
The furniture industry benefits from a variety of bolt head types to achieve both functionality and aesthetics. Flat head bolts are used in furniture assembly because they sit flush with the surface, creating a smooth finish that enhances the overall appearance and prevents snagging on clothing or other materials. Round head bolts, on the other hand, are often chosen for their decorative appeal and ease of installation. Hex bolts provide a strong and secure fastening option, ideal for heavy-duty furniture pieces that require additional support. Each type of bolt head serves a specific purpose, contributing to the durability, safety, and visual appeal of the final product.
Electronics
In the electronics industry, bolt heads must be carefully selected to ensure both functionality and a sleek appearance. Pan head bolts, with their rounded head and flat bearing surface, provide a secure fit and are commonly used in electronics. Truss head bolts are popular in electronics, particularly for securing plastic components and sheet metal parts, as their wide head prevents material damage and distributes loads evenly. Oval head bolts are often chosen for their decorative appearance and countersunk finish, making them suitable for applications where a polished look is required.
Automotive
The automotive industry relies on various bolt head types to ensure the safety and reliability of vehicles. Hex head bolts are crucial in automotive applications, offering strong grip and high torque capacity needed for assembling engines and transmissions. Socket head bolts are also favored in this industry, especially in areas with limited space where a low-profile fastener is necessary. Button head bolts, with their smooth and rounded head, are used in applications where a low-profile, snag-free finish is essential, such as interior fittings and trim.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing processes often require bolt heads that can provide high precision and strength. Socket head bolts are preferred for their ability to endure high torque and provide a streamlined appearance, making them suitable for precision machinery and equipment assemblies. Hex head bolts are also widely used in manufacturing due to their robustness and compatibility with standard tools. Truss head bolts, with their wide and flat head, are essential for securing thin materials and preventing deformation during the manufacturing process.
Choosing the Right Bolt Head
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Bolt Head
Selecting the appropriate bolt head for your project is critical to ensure both functionality and aesthetics. Various factors must be considered to make an informed choice.
Application Requirements
First, consider the specific needs of your project when selecting a bolt head. Different bolt heads serve distinct purposes:
- Countersinking: If your project requires a smooth, flush surface, flat head bolts are ideal. They are commonly used in furniture assembly and woodworking where a sleek appearance is crucial.
- High-Torque Applications: For applications demanding high torque, such as construction and machinery, hex head bolts are preferred due to their strong grip and compatibility with standard tools like wrenches and sockets.
- Compact Spaces: In confined spaces, socket head bolts are advantageous due to their cylindrical head with a recessed hexagonal drive, allowing for high torque application without protruding parts.
Material Compatibility
It’s important to choose a bolt head that works well with your materials to avoid damage:
- Thin Materials: For securing thin materials like sheet metal, truss head bolts are ideal as their wide, flat head distributes force evenly, minimizing deformation.
- Soft Materials: When working with softer materials, selecting bolt heads that do not exert excessive localized pressure is crucial. Button head bolts, with their wide bearing surface, are suitable for such applications.
Aesthetics
The visual aspect of bolt heads can be significant, especially in projects where bolts are visible:
- If appearance matters, round head and oval head bolts offer a neat, decorative finish.
- Flat head bolts are designed to sit flush with the surface, offering a clean and smooth look suitable for furniture and cabinetry.
Torque and Space Constraints
Consider the torque requirements and the available space for installation:
- High Torque Needs: Hex head bolts and socket head bolts are excellent choices for applications requiring high torque. They provide robust fastening and can be easily tightened with common tools.
- Limited Space: In areas with space constraints, button head bolts and socket head bolts are preferred. Their low profile and compact design ensure secure fastening without protruding parts.
Tools Required
Using the right tools for your bolt head makes installation and removal easier:
- Wrenches and Sockets: Hex head bolts are compatible with wrenches and sockets, making them easy to install in various applications.
- Screwdrivers: Slotted head bolts can be installed using a standard flathead screwdriver, suitable for light-duty tasks and household projects.
- Allen Keys: Socket head bolts require an Allen key for installation, providing precise torque application in confined spaces.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right bolt head to meet the specific needs of your project, ensuring both functionality and visual appeal.
Tools Needed for Different Bolt Heads
Tools Needed for Different Bolt Heads
Selecting the appropriate tool for each type of bolt head is crucial for ensuring proper installation and removal. Different bolt head designs require specific tools to apply the correct amount of torque and achieve a secure fit. Here, we will explore the common tools needed for various bolt heads.
Wrench or Socket
Hex Head Bolts:
Hex head bolts are characterized by their six-sided heads. These tools grip the head securely, enabling the application of high torque. Wrenches, including open-end and box wrenches, provide excellent grip and torque transfer. Sockets, used with ratchets, offer efficiency and speed, especially in repetitive tasks.
Square Head Bolts:
Square head bolts, with their four-sided heads, are compatible with wrenches and sockets, providing a strong grip ideal for high-torque applications. Wrenches and sockets ensure a firm hold and precise torque application.
Truss Head Bolts:
Truss head bolts, with their wide and flat heads, typically require a socket or wrench for installation. These tools help distribute the load evenly, preventing material deformation. Sockets are preferred for their efficiency in driving these bolts in high-torque scenarios.
Screwdrivers
Flat Head Bolts:
Flat head bolts, or countersunk bolts, have a tapered head that sits flush with the surface. These bolts require a flathead or Phillips screwdriver for installation. The choice between a flathead or Phillips driver depends on the specific recess design of the bolt.
Round Head Bolts:
Round head bolts feature a smooth, rounded top and a flat bearing surface. They are installed using either a Phillips or slotted screwdriver. These screwdrivers fit into the bolt head recess, providing the torque needed for secure fastening.
Pan Head Bolts:
Pan head bolts, with their slightly rounded top and flat bearing surface, also require a Phillips or slotted screwdriver. These screwdrivers ensure a secure fit and proper torque application, making pan head bolts suitable for electronics and light-duty mechanical assemblies.
Oval Head Bolts:
Oval head bolts, which offer a decorative finish, are driven using flathead or Phillips screwdrivers. The choice of screwdriver depends on the specific drive type of the bolt.
Allen Key or Hex Wrench
Socket Head Bolts:
Socket head bolts, or socket cap bolts, have a cylindrical head with a recessed hexagonal drive. These bolts are tightened using an Allen key or hex wrench. This tool fits into the recessed drive, allowing for high torque application in confined spaces. Allen keys are particularly useful in precision machinery and automotive assemblies.
Torx Driver
Torx Head Bolts:
Torx head bolts feature a star-shaped drive that provides excellent torque transfer and resistance to stripping. These bolts require a Torx driver, which matches the star-shaped recess. Torx drivers are available in various sizes to fit different Torx bolts, ensuring precise and secure fastening.
Key Considerations
When choosing tools for bolt heads, consider the following:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the tool fits the bolt head properly to prevent slippage and damage.
- Torque Requirements: Use the appropriate tool to achieve the desired torque without over-tightening, which can damage both the bolt and the material.
- Accessibility: Choose tools that can easily reach the bolt head, especially in confined or awkward spaces.
Standards Compliance
Bolts must adhere to various standards to ensure they meet specific mechanical properties, dimensions, and performance criteria. Compliance with these standards guarantees reliability, safety, and interchangeability in different applications.
ISO Standards
ISO 898 and ISO 3506: ISO 898 defines the mechanical properties of fasteners made from carbon and alloy steel, specifying requirements for tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. Fasteners under ISO 898 are categorized by property classes (e.g., 8.8, 10.9) that denote their mechanical characteristics. ISO 3506, on the other hand, covers the mechanical properties of corrosion-resistant stainless steel bolts, including austenitic, martensitic, and ferritic grades, ensuring these bolts can withstand various environmental conditions without compromising strength.
ASTM Standards
ASTM A307: This standard specifies the chemical and mechanical properties of carbon steel bolts and studs with tensile strength up to 60,000 PSI. It is commonly used for general-purpose applications in construction and machinery.
ASTM A325 and A490: ASTM A325 specifies high-strength carbon steel bolts for structural steel connections, while ASTM A490 covers alloy steel bolts that need higher tensile strength. Both standards ensure bolts can withstand significant loads in construction applications.
ASTM A354: This standard specifies the properties of quenched and tempered alloy steel bolts, including grades BD and BC, suitable for applications requiring high tensile strength and durability.
SAE Standards
SAE J429: This standard defines the mechanical and material requirements for automotive bolts. It includes grades such as Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8, indicating different levels of tensile strength and hardness. SAE J429 ensures bolts used in automotive applications can endure the stresses and strains encountered in vehicle assemblies.
ANSI/ASME Standards
ASME B18.2.1: This standard specifies the dimensions and tolerances for hex bolts and other types. It provides guidelines for bolt head size, thread length, and other critical dimensions, ensuring compatibility with various tools and applications.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with these standards is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Ensuring bolts meet specific mechanical properties reduces the risk of failure under load, enhancing the safety of structures and machinery.
- Interchangeability: Standardized dimensions and properties allow bolts to be easily replaced and used interchangeably across different projects and regions.
- Performance: Standards ensure bolts perform reliably under specified conditions, whether in high-stress environments, corrosive settings, or general-purpose applications.
Testing and Verification
Bolts undergo rigorous testing to ensure they comply with these standards. Common tests include:
- Proof Load Testing: Ensures bolts can withstand a specified load without permanent deformation.
- Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the maximum load a bolt can endure before breaking.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s resistance to deformation and wear.
- Fatigue Testing: Evaluates the bolt’s ability to withstand cyclic loading over time, ensuring long-term durability.
By adhering to these standards and conducting thorough testing, manufacturers can guarantee that their bolts meet the necessary requirements for diverse applications, providing confidence in their use across various industries.
Comparison of Bolt Heads
Hex Head Bolts
Hex head bolts have a six-sided head that ensures a strong grip and can handle high torque. They are commonly used in construction, machinery, and automotive industries due to their robustness and ease of use with wrenches and sockets. These bolts offer a strong grip and high torque capability, making them ideal for demanding applications. However, their bulkier head may not be suitable for situations requiring a low-profile finish.
Flat Head Bolts
Next, we have flat head bolts, which are designed to sit flush with the material surface. These are perfect for applications needing a smooth finish, like furniture assembly and woodworking. Flat head bolts provide a neat and clean look, minimizing the risk of material deformation. However, they may not be suitable for high-torque applications due to their limited torque capacity.
Round Head Bolts
Round head bolts, featuring a dome-shaped head, are often used in electrical fittings, appliances, and decorative applications. They offer a neat appearance and are easy to install with Phillips or slotted screwdrivers. While they are functional and attractive, their torque capability is limited, making them less suitable for high-torque applications.
Pan Head Bolts
Pan head bolts have a slightly rounded head with a flat top, offering a balance between aesthetics and functionality. Commonly used in sheet metal work and electronics, they provide increased holding power and a clean appearance. However, their torque capability is moderate, which may not suffice for very high-torque applications.
Socket Head Bolts
Socket head bolts, or socket cap bolts, feature a cylindrical head with a recessed hexagonal socket. They are tightened using an Allen key or hex wrench, making them suitable for high-strength applications in confined spaces. These bolts allow for significant torque application and a streamlined appearance. However, they require specialized tools for installation.
Square Head Bolts
Square head bolts have a four-sided head, providing a strong grip and high torque resistance. They are often used in vintage or heavy-duty projects where a secure grip is needed. While they offer excellent grip and are suitable for heavy-duty applications, their bulky head may not be ideal for low-profile needs.
Truss Head Bolts
Truss head bolts have wide, flat heads designed to distribute force over a larger area. They are essential in applications like sheet metal work and HVAC systems. These bolts minimize material deformation and offer significant clamping force. However, their limited torque capability may not be suitable for very high-torque needs.
Oval Head Bolts
Oval head bolts feature an oval-shaped head that is partially countersunk with a rounded top. Suitable for decorative fixtures and marine hardware, they offer an aesthetic and polished appearance while sitting flush with the surface. However, they are not ideal for high-torque applications.
Button Head Bolts
Button head bolts have a low-profile, rounded top with a wide bearing surface, making them ideal for applications requiring a smooth finish, such as bicycle components and electronics enclosures. They provide a sleek appearance and increased holding power. Their moderate torque capability may not suffice for very high-torque applications.
Hex Flange Head Bolts
Hex flange head bolts feature a hexagonal head with a built-in washer to distribute load and prevent loosening. Commonly used in automotive assemblies and construction equipment, they offer added stability and high torque capability. However, their bulkier head may not be suitable for low-profile applications.
Hex Washer Head Bolts
Hex washer head bolts are similar to hex flange bolts but with a separate washer. They are used in roofing and outdoor applications. These bolts provide additional stability and high torque capability, making them ideal for demanding environments. However, their bulky head may not be suitable for low-profile needs.
When selecting a bolt head, consider application requirements, material compatibility, and aesthetics. Each bolt head type serves a distinct purpose, from providing a strong grip for high-torque applications to offering a decorative finish. Understanding the specific uses and benefits of each head type is crucial for ensuring project durability and meeting both functional and aesthetic needs.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on various bolt head types to ensure the safety and durability of vehicle components. Hex head bolts are frequently used in assembling chassis and engine components because they can handle high torque and are easy to use with standard tools like wrenches and sockets. For instance, in the assembly of a vehicle’s chassis, hex head bolts provide the necessary strength to secure heavy and critical parts, ensuring structural integrity and safety.
Socket head bolts are essential in automotive applications, particularly in tight spaces, as they offer a streamlined appearance and can be precisely tightened with an Allen key. This is particularly important in the assembly of engines and transmissions, where space constraints are significant, and reliable fastening is essential for performance and safety.
Construction Sector
In construction, selecting the right bolt head is crucial for ensuring the stability and safety of structures. Truss head bolts are widely used in this industry due to their broad, flat heads, which distribute loads evenly and prevent material deformation. These bolts are essential in applications like securing trusses and attaching sheet metal components. For example, during the installation of HVAC systems, truss head bolts ensure that sheet metal parts are securely fastened without causing deformation, which is critical for maintaining efficient airflow and structural integrity.
Hex head bolts are also prevalent in construction, particularly for structural framing and securing heavy loads. Their ability to handle high torque makes them ideal for connecting beams and columns, ensuring that the structure remains stable and secure under various loads. In decking and fencing applications, lag bolts, a type of hex head bolt, provide the necessary strength to hold heavy wooden components together, enhancing the durability and longevity of the structures. The hexagonal head design allows for easy gripping by wrenches and other tools, facilitating efficient installation and removal.
Furniture Manufacturing
In the furniture industry, aesthetics and functionality are equally important when selecting bolt heads. Flat head bolts are commonly used in furniture assembly because they can be countersunk, sitting flush with the surface and providing a smooth, finished look. This is particularly important in high-end furniture pieces where visible hardware can detract from the
Button head bolts are also favored in furniture manufacturing, particularly for applications requiring a low-profile fastener. These bolts provide a sleek finish and are often used in assembling furniture pieces that require a smooth surface to prevent snagging or injury. For instance, in the construction of office chairs and desks, button head bolts offer a clean appearance while providing the necessary strength to hold the components together securely.
Electronics Manufacturing
In the electronics industry, bolt heads must meet specific requirements for functionality and aesthetics. Pan head bolts are frequently used in this sector due to their slightly rounded top and flat bearing surface, which provide a secure fit and a neat appearance. These bolts are ideal for securing components in electronic devices, where space is often limited, and a streamlined finish is necessary to maintain the compact design of the product.
Truss head bolts also play a significant role in electronics manufacturing, particularly for attaching plastic components and sheet metal parts. The wide head of these bolts distributes the load evenly, preventing damage to delicate materials and ensuring a secure fit. This is crucial in applications like assembling computer cases and other electronic enclosures, where maintaining the integrity of the materials is essential for the device’s performance and longevity.
Case Study: Robotics
In the field of robotics, precision and reliability are paramount. Socket head bolts are extensively used in robotic assemblies due to their high torque capacity and compact design. These bolts provide precise torque control, essential for the reliable operation of robotic joints and mechanisms. In a specific case study, a robotics company used socket head bolts to assemble critical joints in their robotic arms. The result was enhanced performance and reduced maintenance requirements, as the bolts provided a secure and durable fastening solution in the confined spaces of the robotic assembly.
Case Study: Historical Restoration
Square head bolts are often used in historical restoration projects to maintain the original look and feel of old machinery and structures. In a notable restoration project of a 19th-century mill, square head bolts were chosen to replace the original fasteners. These bolts provided the necessary strength to secure the heavy wooden beams while preserving the historical authenticity of the structure. The use of square head bolts ensured that the restored mill retained its vintage appearance while benefiting from modern fastening technology.
By understanding the specific applications and benefits of different bolt head types, engineers and manufacturers can make informed decisions that enhance the functionality, durability, and aesthetics of their projects. Whether in automotive manufacturing, construction, furniture assembly, electronics, robotics, or historical restoration, selecting the right bolt head is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Custom Bolt Head Selection Guide
Types of Bolt Heads and Their Uses
Hex Head Bolts
Hex head bolts are characterized by their six-sided heads, allowing for easy application of high torque using a wrench or socket. These bolts are commonly employed in construction, automotive, and machinery industries due to their robustness and ability to handle high-stress applications.
Square Head Bolts
Square head bolts feature a four-sided head, offering a secure grip with a wrench. Though less common, they are still utilized in industrial settings, particularly in older machinery and construction projects where a strong grip is necessary.
Flat Head Bolts
Flat head bolts, also known as countersunk bolts, are designed to sit flush with the surface they are installed into. This makes them ideal for applications requiring a smooth finish, such as furniture assembly, woodworking, and machinery.
Oval Head Bolts
Oval head bolts have a slightly domed top, providing a low-profile fastening solution with an aesthetic appeal. They are often used in decorative fixtures and furniture, where appearance is important.
Round Head Bolts
Round head bolts have a rounded top and are commonly used in general assembly where a low-profile finish is not critical. They are suitable for decorative purposes or applications with low to moderate stress.
Pan Head Bolts
Pan head bolts feature a flat top and rounded body, balancing aesthetics and functionality. They are typically used in decorative applications and scenarios where a smooth finish is desirable.
Truss Head Bolts
Truss head bolts have wide, rounded heads that distribute loads evenly, making them perfect for securing thin materials such as sheet metal. These bolts are used in applications requiring load distribution without material deformation.
Socket Head Bolts
Socket head bolts, also known as cylindrical head bolts, have an internal hex drive that provides a flush fit and secure grip. They are suitable for precision applications where space is limited, such as machinery and automotive assemblies.
Torx Head Bolts
Torx head bolts feature a star-shaped drive, offering better torque transfer and reducing the risk of stripping. These bolts are used in precision applications requiring high reliability.
Pentagon Head Bolts
Pentagon head bolts are specialized bolts used in high-security applications. Their unique design makes them difficult to tamper with, ensuring secure fastening in specialized settings.
Bolt Head Selection Criteria
Application Requirements
Consider the specific requirements of the application, such as strength, load-bearing capacity, and environmental conditions (e.g., corrosion resistance, temperature resistance). These factors play crucial roles in determining the most suitable bolt head type.
Aesthetic Considerations
The visual appeal and design harmony of the bolt head can be important, especially in applications where the bolts are visible. Choosing colored or coated bolts can help match specific color schemes and enhance the overall aesthetic of the project.
Tools Compatibility
Make sure the selected bolt head matches the tools you have, like wrenches, sockets, or Torx drivers. This compatibility ensures efficient installation and removal.
Material Compatibility
Matching the bolt material to the application environment is essential to avoid corrosion or material incompatibility. Consider the material properties and ensure that the bolt head type is suitable for the intended environment.
Standard Compliance
Adhering to industry standards such as ASTM or ISO guarantees quality assurance and reliability. Ensure that the selected bolt heads comply with relevant standards to meet performance and safety requirements.
Manufacturing Processes
Cold Forging
Cold forging involves molding steel at room temperature, making it suitable for most bolt types. This process enhances the strength and precision of the bolts.
Hot Forging
Hot forging heats the material before shaping, ideal for larger bolts or complex geometries. This process allows for greater malleability and the creation of intricate designs.
CNC Machining
CNC machining provides high precision and can achieve complex geometries. This manufacturing process is essential for producing bolts with tight tolerances and detailed features.
Thread Rolling
Thread rolling creates stronger threads and a better surface finish compared to cutting threads. This process is crucial for ensuring the durability and reliability of bolt threads.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment improves hardness and tensile strength, making bolts more robust for high-stress uses.
Recent Trends and Innovations
3D Printing
3D printing enables rapid prototyping and production of complex bolt designs. This technology allows for customization and quick iteration of bolt head types.
Smart Bolts
Smart bolts feature embedded sensors for real-time monitoring and condition assessment. These bolts are valuable in applications requiring precise control and maintenance.
Sustainable Materials
The use of recycled metals is increasing to promote environmental sustainability. Bolts made from sustainable materials help reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing processes.
Automation
Advanced CNC machines enhance production speed and precision, allowing for efficient and accurate manufacturing of bolt heads. Automation in bolt production ensures consistency and reduces human error.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the common types of bolt heads and their uses?
Common types of bolt heads include hex head, flat head, socket head, round head, pan head, button head, and truss head, each serving distinct purposes.
Hex head bolts are widely used in construction, machinery, and automotive applications due to their high torque resistance and ease of use with wrenches or sockets. Flat head bolts, featuring a countersunk design, are ideal for furniture assembly and woodworking where a smooth surface is required. Socket head bolts, with a cylindrical head and hexagonal recess, are suitable for industrial machinery and auto parts, especially in tight spaces. Round head bolts provide a low-profile finish and are often used in woodworking and decorative applications. Pan head bolts balance aesthetics and functionality, making them suitable for lightweight fixtures and decorative purposes. Button head bolts offer a low-profile finish and are used in applications requiring minimal surface projection. Truss head bolts, with their wide, rounded heads, ensure even load distribution, making them perfect for joining trusses in construction and attaching sheet metal or plastic without causing damage.
How do I choose the right bolt head for a specific application?
To choose the right bolt head for a specific application, consider the following factors:
- Functional Requirements: Assess the torque and load distribution needs. Hex heads are ideal for high-torque applications, while truss heads distribute loads evenly to prevent material deformation.
- Aesthetic Considerations: If appearance matters, such as in furniture or decorative projects, opt for round, oval, or pan heads that provide a sleek look.
- Space Constraints: For confined spaces, socket head bolts with recessed drives are more suitable.
- Material and Environmental Conditions: Select bolt materials that match the environmental conditions, like stainless steel for corrosion resistance in marine applications.
- Tool Compatibility: Ensure the bolt head type is compatible with the tools available, such as wrenches for hex heads or screwdrivers for flat and pan heads.
By evaluating these factors, you can select a bolt head that meets both functional and aesthetic requirements for your specific application.
What tools are needed for different types of bolt heads?
Different bolt heads require specific tools for proper installation and removal. Hex head bolts are commonly used in construction and machinery, requiring wrenches or sockets for high-torque applications. Flat head bolts, often used in furniture assembly and woodworking, need flathead or Phillips screwdrivers to create a smooth, flush surface. Socket head bolts, also known as Allen bolts, are ideal for confined spaces in machinery, utilizing an Allen wrench (hex key). Round, pan, and truss head bolts, used in various applications such as electronics and appliance assembly, typically require Phillips or slotted screwdrivers. Ensuring the correct tool is used for each bolt head type is crucial to avoid damage and ensure secure fastening.
What standards should bolt heads comply with?
Bolt heads should comply with several key standards to ensure their quality, performance, and suitability for specific applications. In North America, the ANSI/ASME standards are prevalent, with ASME B18.2.1 specifying dimensions for hex bolts and ASME B1.1 defining threading systems such as UNC and UNF. The ASTM standards focus on material properties and performance, including ASTM A325 (now ASTM F3125) for high-strength structural bolts and ASTM A490 for heavy-duty structural applications. In the automotive and aerospace industries, SAE standards specify mechanical properties for hex bolts. Additionally, BS standards are widely used in the UK for general-purpose and high-strength structural bolting assemblies. Compliance with these standards ensures bolt heads meet the necessary requirements for safety, reliability, and performance in their intended applications.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of different bolt heads?
Different bolt heads offer various advantages and disadvantages depending on the application. Hex head bolts are highly versatile, providing strong torque resistance and ease of installation, making them ideal for construction and machinery. However, they may not be suitable where a flush finish is needed. Flat head bolts, on the other hand, create a smooth, flush surface, perfect for furniture and woodworking, but require precise countersinking and may lack the holding power of other types.
Round head bolts are aesthetically pleasing and suitable for decorative work, but they are not suitable for high-torque applications. Pan head bolts offer a larger contact area and are commonly used in electronics and sheet metal work, although they can protrude above the surface. Allen (socket) head bolts are excellent for high-stress environments and tight spaces, but they can be prone to stripping.
Phillips head bolts are easy to align and install, making them suitable for general use, but they are not ideal for high-torque applications. Square head bolts, although less common, provide a secure grip and are used in vintage or heavy-duty projects, but can be harder to install and remove. Oval head bolts offer a polished look with a countersunk finish, but they are not as widely available. Lastly, truss head bolts provide high clamping force and are critical in structural applications, though they may require specialized tools.
Can you provide real-world examples of bolt head applications?
Real-world examples of bolt head applications vary across industries, highlighting the importance of selecting the right type for specific tasks. In construction, hex head bolts are widely used to assemble steel frameworks of buildings and bridges due to their strong grip and high torque capabilities. In the automotive industry, flat head bolts are essential for securing components in engines, chassis, and suspension systems, providing a flush surface and ensuring tight connections. In electronics manufacturing, pan head bolts are commonly utilized to fasten components in devices and appliances, offering a larger contact area for secure fastening. Furniture assembly often employs flat head bolts to achieve a smooth, flush finish that enhances the aesthetic appeal. Each application underscores the need to choose bolt heads that meet the demands of strength, load distribution, and appearance.
