Imagine a material that not only withstands immense pressure but also reduces friction and wear in the most demanding mechanical systems. This is the world of SAE 841 Bronze, a remarkable alloy celebrated for its unique composition and exceptional properties. Whether you’re an engineer, a manufacturer, or simply someone with a keen interest in metals, this comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate details of SAE 841 Bronze, from its precise chemical makeup to its versatile applications.
Throughout this article, we will explore the key elements that give SAE 841 its distinctive characteristics, such as its self-lubricating properties and impressive durability. We’ll compare it with other bronze alloys, highlighting its advantages and specific uses in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
Ready to uncover the secrets behind one of the most robust and reliable bronze alloys in the market? Let’s dive deep into the world of SAE 841 Bronze and see what makes it an indispensable material in modern engineering.
Overview of SAE 841 Bronze
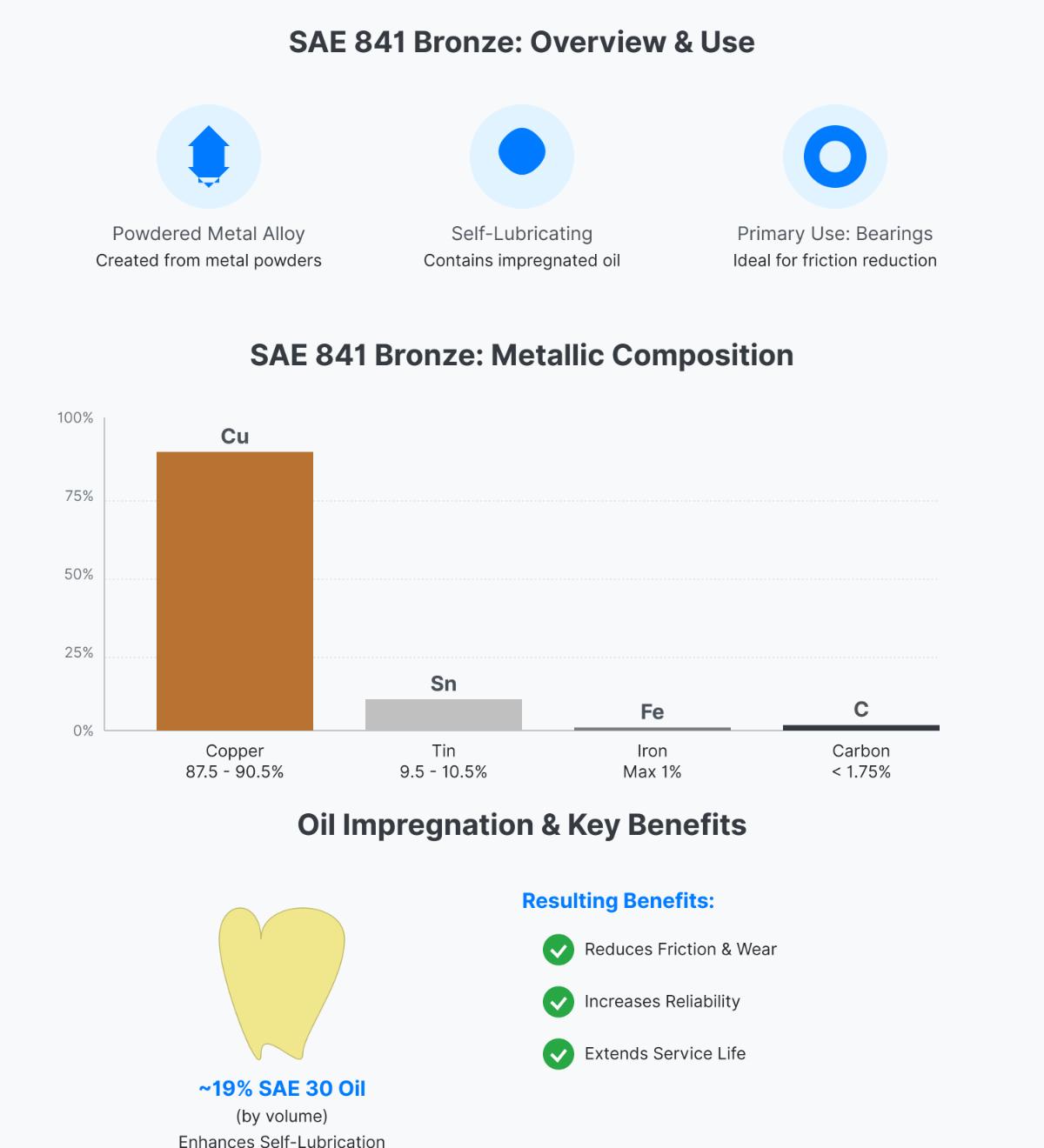
SAE 841 Bronze, also known as oil-impregnated bronze, is a specialized powdered metal alloy celebrated for its self-lubricating properties and robust mechanical qualities. This material is particularly valuable in applications where maintenance is challenging and lubrication is critical, as it releases lubricating oil during operation to significantly reduce friction and wear.
SAE 841 Bronze is made according to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standards, ensuring consistent quality and performance. The development of oil-impregnated bronze can be traced back to advancements in powder metallurgy techniques, which allowed for the creation of porous materials capable of holding and releasing lubricants. This innovation has made SAE 841 Bronze a preferred choice in various industries, particularly for applications involving bearings and bushings.
Self-Lubrication
SAE 841 Bronze’s standout feature is its self-lubricating ability. The material is impregnated with oil, which is stored in its porous structure. As the bearing or bushing heats up during operation, the oil is released, providing continuous lubrication. This not only reduces the need for regular maintenance but also enhances the reliability and efficiency of the machinery.
Mechanical Strength
SAE 841 Bronze exhibits impressive mechanical properties, including high tensile and yield strength. This makes it suitable for applications that require durability and the ability to withstand heavy loads. The material’s inherent strength ensures that it can perform effectively under various operational conditions without deforming or failing.
Wear Resistance
The sintered structure of SAE 841 Bronze provides excellent wear resistance. This characteristic is crucial for applications involving high friction and contact stress. The material’s ability to resist wear and tear extends the service life of components, making it a cost-effective solution for long-term use.
Thermal Stability
SAE 841 Bronze is capable of withstanding high temperatures, which is essential for applications that operate under extreme thermal conditions. The material maintains its mechanical integrity and continues to provide effective lubrication even at elevated temperatures, ensuring consistent performance.
Applications
Due to its self-lubricating properties, SAE 841 Bronze is ideal for bearings and bushings, reducing friction and wear in moving parts. The material’s durability and wear resistance make it suitable for components in pumps and motors, where reliable operation is essential. In the automotive industry, SAE 841 Bronze is used in engine components and suspension systems, where high strength and resistance to wear are required. The self-lubricating properties of SAE 841 Bronze make it a reliable choice for household appliances that require maintenance-free operation, such as washing machines and dryers. In medical devices, where hygiene and low maintenance are critical, SAE 841 Bronze provides a dependable solution due to its self-lubricating nature.
By leveraging its unique characteristics, SAE 841 Bronze enhances the performance and longevity of components in various demanding applications.
Chemical Composition of SAE 841 Bronze
Detailed Breakdown of Elements
SAE 841 Bronze is a sintered, oil-impregnated alloy known for its self-lubricating properties and mechanical strength. The chemical composition of SAE 841 Bronze is crucial to its performance characteristics. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the elemental composition and the significance of each component.
Copper (Cu) and Tin (Sn)
Copper constitutes the majority of SAE 841 Bronze, typically ranging from 87.5% to 90.5%. It is essential for the alloy’s strength, thermal and electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Tin, present in the range of 9.5% to 10.5%, enhances the alloy’s hardness and wear resistance, crucial for applications involving high friction and load. Tin also improves corrosion resistance, making the alloy suitable for harsh environments.
Iron (Fe)
Iron content is kept to a maximum of 1.0%, adding strength and hardness without making the alloy brittle. While not a primary component, iron can improve the alloy’s strength and hardness. However, excessive iron can lead to brittleness, so its content is carefully controlled.
Carbon (C)
Carbon, up to a maximum of 1.75%, contributes to the porous structure necessary for oil impregnation, enabling self-lubrication. It also influences the alloy’s microstructure to achieve the required mechanical properties.
Significance of Each Component
Each element in SAE 841 Bronze contributes uniquely to its performance. Copper provides the base matrix, ensuring good conductivity and corrosion resistance. Tin enhances hardness and wear resistance, crucial for friction-intensive components. Iron adds strength without compromising ductility, and carbon supports the porous structure essential for self-lubrication and influences the microstructure for desired mechanical properties.
Comparison with Other Bronze Alloys
Compared to other bronze alloys, SAE 841 stands out due to its specific composition tailored for self-lubrication and wear resistance. For instance, traditional bronze alloys like SAE 660 (bearing bronze) contain higher levels of lead and zinc, which offer different properties such as better machinability but lack the self-lubricating feature of SAE 841.
SAE 841’s unique composition makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring minimal maintenance and continuous lubrication, such as in bushings and bearings. Its ability to release oil during operation reduces the need for external lubrication, enhancing the longevity and reliability of mechanical components.
Mechanical and Physical Properties of SAE 841 Bronze
SAE 841 Bronze has a density of 6.4 to 6.8 g/cm³, a result of its composition and the powder metallurgy process used in its production. Porosity is a significant feature of SAE 841 Bronze, with a porosity level of approximately 20-25% by volume. This high porosity is crucial for the alloy’s self-lubricating properties, as it allows the material to be impregnated with oil, which is then gradually released during operation.
The hardness of SAE 841 Bronze typically falls within the Rockwell B scale, ranging from 30 to 40. This level of hardness ensures that the material is resistant to wear and deformation, making it suitable for high-friction applications.
The ultimate tensile strength of SAE 841 Bronze ranges from 14,000 to 18,000 psi (approximately 97 to 124 MPa), while the yield tensile strength is around 11,000 psi (about 76 MPa). These strength characteristics are crucial for components that need to endure significant mechanical loads.
SAE 841 Bronze also demonstrates impressive compressive strength, with values reaching up to 35,000 psi. Compressive strength is essential for materials used in applications where they are subjected to compressive forces, ensuring that the material can withstand substantial pressure without experiencing failure.
With an elongation at break of about 1%, SAE 841 Bronze is strong but has limited flexibility. This relatively low elongation indicates that while the material is strong, it has limited ductility, which is important for applications requiring some degree of flexibility.
Thanks to its copper and tin content, SAE 841 Bronze is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments, including marine settings.
SAE 841 Bronze has good thermal conductivity, which allows it to efficiently dissipate heat generated during operation. This property is particularly beneficial in applications involving high-speed or high-load conditions, where heat buildup can be a concern.
While not as critical as its thermal properties, the electrical conductivity of SAE 841 Bronze is also noteworthy. The copper content ensures that the alloy can conduct electricity to a certain extent, which can be advantageous in specific applications where both mechanical strength and electrical conductivity are required.
SAE 841 Bronze’s self-lubricating property is a standout feature. The material’s porous structure is impregnated with oil, which is released during operation to reduce friction and wear, extending the lifespan of components and minimizing maintenance needs.
SAE 841 Bronze performs well across a wide range of temperatures, maintaining its mechanical integrity and self-lubricating properties even at elevated temperatures. This temperature stability makes it suitable for applications in environments where temperature fluctuations are common.
Comparison with Other Bronze Materials
Strengths and Weaknesses Relative to Other Alloys
Bronze alloys are known for their diverse properties and applications, each offering unique benefits and limitations. Comparing SAE 841 bronze to other common bronze alloys highlights its unique benefits and potential limitations.
Phosphor Bronze
Phosphor bronze, composed of copper, tin, and a small amount of phosphorus, is known for its high strength, low friction, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical connectors, springs, and bushings.
- Strengths: Phosphor bronze has superior tensile strength and excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for high-stress applications. It also offers good corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
- Weaknesses: Phosphor bronze requires additional maintenance and lubrication in high-friction applications because it is not self-lubricating like SAE 841 bronze.
Aluminum Bronze
Aluminum bronze, made of copper, aluminum, iron, and nickel, offers exceptional strength and excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation. This alloy is commonly used in marine hardware, valve components, and pump parts due to its durability and non-sparking properties.
- Strengths: Aluminum bronze’s high strength and corrosion resistance make it ideal for harsh environments and heavy-duty applications. Its non-sparking characteristic is crucial for applications in explosive environments.
- Weaknesses: The lack of self-lubrication in aluminum bronze means it requires regular maintenance and lubrication, unlike SAE 841 bronze, which is oil-impregnated for continuous lubrication.
Silicon Bronze
Silicon bronze, primarily composed of copper and silicon, is known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and good weldability. It is often used in architectural features, hardware, and electrical components.
- Strengths: Silicon bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance and is easy to weld, making it suitable for structural applications and components exposed to the elements.
- Weaknesses: Similar to other traditional bronze alloys, silicon bronze does not possess self-lubricating properties, which can limit its effectiveness in applications where continuous lubrication is essential.
Application-Specific Comparisons
Different bronze alloys are tailored for specific applications, and understanding their strengths and weaknesses helps in selecting the most appropriate material.
Bearings and Bushings
SAE 841 bronze’s self-lubricating property makes it highly suitable for bearings and bushings, reducing maintenance needs and extending the lifespan of moving components. In contrast, phosphor bronze and aluminum bronze require additional lubrication, which can increase maintenance costs and downtime.
Marine and Harsh Environments
Aluminum bronze and silicon bronze are preferred for marine and harsh environments due to their superior corrosion resistance. While SAE 841 bronze also offers good corrosion resistance, its primary advantage lies in its self-lubrication, which may not be as critical in static marine applications.
Electrical and Structural Components
Phosphor bronze and silicon bronze are often chosen for electrical and structural components due to their excellent strength and conductivity. SAE 841 bronze, with its focus on self-lubrication, is less commonly used in these applications but can be beneficial where reduced friction and maintenance are needed.
Market Availability and Cost Considerations
The cost and availability of bronze alloys vary significantly depending on their composition and intended use.
- SAE 841 Bronze: Generally available in various forms such as rods and bushings, SAE 841 bronze is moderately priced due to its specialized manufacturing process involving powder metallurgy and oil impregnation.
- Phosphor Bronze: Widely available and commonly used, phosphor bronze is typically cost-effective for applications requiring high strength and low friction.
- Aluminum Bronze: Often more expensive due to its complex alloying elements and high-performance characteristics, aluminum bronze is available in a range of forms for industrial applications.
- Silicon Bronze: With its good weldability and corrosion resistance, silicon bronze is moderately priced and readily available for architectural and electrical uses.
Choosing the right bronze alloy depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing factors such as self-lubrication, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Applications and Uses of SAE 841 Bronze
Automotive Industry
SAE 841 bronze is widely used in the automotive industry, especially in parts that need continuous lubrication and high durability. The self-lubricating properties of SAE 841 bronze ensure reduced friction and wear, which is crucial for reliable operation in high-load automotive systems, including clutch parts and transmission components. Additionally, its ability to withstand significant mechanical stress makes it ideal for high-load areas within engines and suspension systems.
Aerospace Applications
SAE 841 bronze is used in crucial aerospace components like control systems and landing gear, where its strength and self-lubricating qualities are essential. The material’s ability to perform consistently in high-stress environments ensures the safe and efficient operation of critical aerospace systems.
Industrial Machinery
SAE 841 bronze is preferred in industrial machinery for its wear resistance and self-lubricating capabilities, commonly used in wear plates and bushings. The continuous lubrication provided by the oil-impregnated structure of SAE 841 bronze minimizes maintenance requirements and extends the lifespan of machinery parts, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. This makes SAE 841 bronze an ideal choice for applications where consistent performance and reliability are critical.
Agricultural Equipment
Agricultural equipment requires materials that can endure tough outdoor conditions while performing reliably; SAE 841 bronze is ideal for components like guide plates and bearing surfaces due to its self-lubricating properties and durability. Its resistance to wear makes it a cost-effective solution for long-term use in agriculture.
Marine Applications
Marine environments demand materials with excellent corrosion resistance and durability. SAE 841 bronze is well-suited for marine applications, providing long-lasting performance in saltwater conditions. Its self-lubricating nature ensures that components such as bearings and bushings continue to operate smoothly, reducing the need for external lubrication and maintenance.
Household Appliances and Office Machinery
In household appliances and office machinery, reliability and low maintenance are crucial. SAE 841 bronze is used in bearings and bushings for applications like washing machines and printers, where its self-lubricating properties ensure smooth operation and extend component lifespan. This reduces maintenance frequency and enhances the overall efficiency of the equipment. By minimizing friction and wear, SAE 841 bronze helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs, contributing to more reliable performance and lower operational costs over time.
Heavy Industrial Equipment
SAE 841 bronze is also employed in heavy industrial equipment such as conveyors, cranes, and hydraulic systems. The material’s ability to handle heavy loads and provide continuous lubrication makes it a dependable choice for these demanding applications. Its wear resistance and mechanical strength ensure that components remain functional and efficient over extended periods of use.
Benefits of Using SAE 841 Bronze
- Reduced Maintenance: The self-lubricating properties of SAE 841 bronze minimize the need for regular lubrication, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The material offers a cost-effective solution due to its long lifespan and lower maintenance requirements.
- Environmental Sustainability: By eliminating the need for external lubrication in certain environments, SAE 841 bronze reduces the risk of contamination and supports environmental sustainability.
SAE 841 bronze’s unique properties make it an invaluable material across various industries, providing reliable performance, reduced maintenance, and cost-effective solutions for demanding applications.
Manufacturing Process of SAE 841 Bronze
Overview of Production Techniques
The manufacturing process of SAE 841 bronze involves several critical steps to ensure the material’s unique properties, such as self-lubrication and mechanical strength. The process is largely based on powder metallurgy, which allows for the creation of a porous structure capable of holding lubricating oil.
Powder Production
The initial step in producing SAE 841 bronze involves converting the alloy into a fine powder. This can be achieved through various methods:
- Atomization: This process involves melting the bronze alloy and then dispersing it into fine droplets using a high-velocity stream of gas or liquid. The droplets solidify into fine powder particles.
- Grinding: Mechanical grinding of the bronze alloy to produce fine powder particles is another common method, though it is less precise compared to atomization.
Compaction
The bronze powder is then poured into a die or mold and compressed under high pressure. This process serves to:
- Adhere Particles: The high pressure causes the individual powder particles to adhere to one another, forming a “green” compact with sufficient strength for handling.
- Shape Formation: The die or mold shapes the compact into the desired form, which can be bushings, bearings, or other components.
Sintering
Next, the compacted bronze powder undergoes sintering:
- Heating: The green compact is placed in a furnace and heated to a temperature below the melting point of bronze. This causes the particles to bond together metallurgically.
- Porous Structure: Sintering results in a solid piece with a controlled level of porosity, essential for the self-lubricating properties of SAE 841 bronze.
Oil Impregnation
The final step is to impregnate the sintered bronze with lubricating oil:
- Vacuum Impregnation: The sintered bronze components are placed in a vacuum chamber filled with oil, typically SAE 30. The vacuum helps to draw the oil into the pores of the material.
- Self-Lubrication: This process enables the bronze to release lubrication during use, which significantly reduces friction and wear.
Quality Control Measures
To ensure the consistent quality and performance of SAE 841 bronze, several quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process:
- Powder Consistency: The particle size and distribution of the bronze powder are closely monitored to ensure uniformity.
- Compaction Pressure: Compaction pressure is regulated to achieve the desired density and strength.
- Sintering Parameters: The temperature and duration of the sintering process are carefully regulated to ensure proper bonding and porosity.
- Oil Impregnation: The amount of oil impregnated into the bronze is measured to ensure optimal self-lubricating properties.
Environmental Considerations
The manufacturing process of SAE 841 bronze also takes into account environmental considerations:
- Recycling: Bronze powder and scrap materials can be recycled, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Energy Efficiency: Advances in sintering technology aim to reduce energy consumption, making the process more sustainable.
- Emissions Control: Measures are implemented to minimize emissions during the powder production and sintering processes.
By following these detailed steps and maintaining strict quality control, manufacturers can produce SAE 841 bronze components that meet the high standards required for their diverse applications.
Trending Factors in SAE 841 Bronze
Advancements in Self-Lubrication Technology
Recent improvements in the oil impregnation process and vacuum techniques have significantly enhanced the self-lubrication performance of SAE 841 bronze. Enhanced vacuum techniques ensure even oil distribution throughout the material’s porous structure, while new high-performance lubricants further increase the effectiveness and lifespan of SAE 841 bronze components.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance has always been a key feature of SAE 841 bronze, but recent innovations have made it even more robust. Advances in alloying techniques and the incorporation of trace elements have improved the material’s resistance to various forms of corrosion, including pitting and crevice corrosion. These improvements make SAE 841 bronze even more suitable for use in harsh environments, such as marine and industrial applications where exposure to corrosive elements is a concern.
Increased Wear Resistance
Advances in manufacturing techniques have made SAE 841 bronze more wear-resistant. By optimizing the sintering process and controlling the particle size distribution, manufacturers can produce components with a more uniform and fine-grained microstructure. This refinement leads to better wear characteristics, reducing the rate of material loss in high-friction applications and extending the service life of components.
Customization for Specific Applications
There is a growing trend towards customizing SAE 841 bronze for specific applications by adjusting its composition and manufacturing parameters. For instance, changing the tin content or adding other elements can improve properties like hardness or thermal stability, making the material more versatile and adaptable.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
More recycled materials are now used in producing SAE 841 bronze, which helps reduce its environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in energy-efficient sintering processes help lower the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing. These improvements not only contribute to a more sustainable production cycle but also align with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote environmental stewardship.
Integration with Modern Manufacturing Techniques
The integration of SAE 841 bronze with modern manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized components that were previously difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods. The ability to 3D print SAE 841 bronze parts opens up new possibilities for innovative designs and applications, further expanding the material’s utility across various industries.
Improved Quality Control Measures
Enhanced quality control measures have been implemented to ensure the consistent performance of SAE 841 bronze. Advanced testing techniques, including non-destructive testing and real-time monitoring during the manufacturing process, help identify and rectify potential issues before they affect the final product. These measures ensure that each batch of SAE 841 bronze meets the stringent standards required for high-performance applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What is the composition of SAE 841 Bronze?
SAE 841 Bronze is a powdered metal alloy notable for its self-lubricating properties, primarily used in bearing applications. The chemical composition of SAE 841 Bronze is primarily copper (Cu), ranging from 87.5% to 90.5%. It also contains 9.5% to 10.5% tin (Sn), with a maximum of 1% iron (Fe). Trace amounts of carbon (C), typically less than 1.75%, are present. Additionally, SAE 841 Bronze is impregnated with approximately 19% SAE 30 weight oil by volume, enhancing its self-lubricating characteristics. This specific composition makes SAE 841 Bronze highly effective in reducing friction and wear in various mechanical applications, providing reliability and extended service life.
What are the properties of SAE 841 Bronze?
SAE 841 bronze is a powdered metal alloy known for its self-lubricating properties, making it ideal for applications requiring low maintenance and high reliability. The mechanical properties include an ultimate tensile strength of approximately 14,000 PSI (97 MPa), a yield tensile strength of around 11,000 PSI (76 MPa), and a compressive strength up to 35,000 PSI. The material has a density of 6.4 – 7.0 g/cm³ and a Rockwell B hardness of 30 – 40.
One of its defining features is its self-lubricating nature, achieved by infusing the alloy with about 18-20% SAE 30 oil by volume. This results in a porosity of 20-25%, allowing the material to release and reabsorb oil, providing continuous lubrication. Additionally, SAE 841 bronze exhibits good thermal stability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of temperatures and environments, including marine applications. These properties make SAE 841 bronze a versatile and durable choice for bearings, bushings, and other high-load, low-maintenance components.
What are the typical uses of SAE 841 Bronze?
SAE 841 bronze, also known as Oilite bronze or sintered bronze, is widely used in various industrial applications due to its self-lubricating properties and high wear resistance. Typical uses include:
- Bearings and Bushings: Its self-lubricating nature makes it ideal for bearings, bushings, and wear plates in machinery, reducing friction and wear.
- Industrial Machinery: Employed in components where friction reduction is essential, enhancing the smooth operation and longevity of machinery parts.
- Automotive and Agricultural Equipment: Used in high-load applications such as clutch components, transmission parts, guide plates, and bearing surfaces due to its durability and self-lubrication.
- Aerospace: Suitable for precision components like control systems and landing gear, where reliable lubrication is crucial.
- Home Appliances and Office Machinery: Provides quieter operation and reduced maintenance in components requiring self-lubrication.
- Marine Applications: Its corrosion resistance and self-lubricating properties make it beneficial for marine environments.
These applications leverage the unique properties of SAE 841 bronze, ensuring efficient, reliable, and long-lasting performance.
How does SAE 841 Bronze compare to other bronze alloys?
SAE 841 Bronze distinguishes itself from other bronze alloys through its self-lubricating properties, achieved via the impregnation of SAE 30 oil within its structure. This unique feature, combined with its powdered metal and sintered manufacturing process, ensures consistent lubrication and enhanced wear resistance, making it ideal for applications where regular maintenance is challenging. While other bronze alloys might offer superior mechanical strength or corrosion resistance depending on their specific compositions, SAE 841 Bronze excels in applications requiring minimal maintenance and reliable performance under varying conditions due to its integrated lubrication system. This makes it particularly suitable for use in bearings, bushings, and other components subjected to constant motion.
What are the key benefits of using SAE 841 Bronze in manufacturing?
SAE 841 Bronze offers several key benefits in manufacturing, primarily due to its unique properties and composition. One of the most significant advantages is its self-lubricating feature, which stems from the oil impregnation process. This reduces the need for external lubricants, thereby minimizing maintenance costs and efforts. Additionally, SAE 841 Bronze exhibits excellent wear resistance and durability, which extends the lifespan of components made from this material, such as bushings and bearings. Its good corrosion resistance makes it suitable for use in harsh environmental conditions, further enhancing its versatility across various industries. Moreover, the material’s stability over a wide temperature range ensures reliable performance in diverse applications. These benefits collectively contribute to cost-effectiveness, as the reduced need for maintenance and replacements leads to long-term savings.
How is SAE 841 Bronze manufactured?
SAE 841 Bronze is primarily manufactured through the powdered metallurgy (P/M) process. This method begins with the production of metallic powders, including copper and tin, through grinding or atomization. These powders are then compacted in a die under high pressure to form a “green” compact. The compact is subsequently sintered in a furnace at temperatures below the melting point of the alloy, causing the particles to bond and create a porous structure. After sintering, the parts are vacuum-impregnated with oil, typically SAE 30, which fills about 19% of the material’s volume. This process results in a material with uniform grain structure, spheroidized porosity, and excellent self-lubricating properties, making SAE 841 Bronze ideal for applications requiring low friction and high wear resistance.
