Ever wondered why some pipelines have smooth transitions while others have a slight shift in alignment? The answer lies in the often-overlooked heroes of the piping world: reducers. Specifically, concentric and eccentric reducers play a crucial role in managing fluid flow and pressure within piping systems. But what sets these two apart, and how do you determine which one to use? In this article, we’ll delve into the intricate differences between concentric and eccentric reducers, examining their designs, applications, and impacts on fluid dynamics. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of when to opt for each type and why these choices matter. Ready to dive into the world of reducers? Let’s get started.
Understanding Pipe Fittings and Piping Systems
Overview of Piping Systems
Piping systems are essential in both industrial and residential settings, serving as channels for transporting fluids such as water, gases, and chemicals. These systems are meticulously designed networks that include pipes, fittings, valves, and other components to ensure efficient and safe fluid conveyance. Piping systems can be found in various applications, including water supply networks, HVAC systems, chemical processing plants, and oil refineries.
Pipe Fittings in Piping Systems
Pipe fittings are crucial elements within piping systems, responsible for connecting pipe segments, changing directions, and controlling fluid flow. They are essential for maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of the system. Common types of pipe fittings include:
- Adapters and Bushings: Adapters extend the length of pipe runs and can change the type or size of the connections, while bushings reduce the size of pipes and occupy less space compared to other fittings.
- Couplings: Used to join two pipes together, couplings can also change pipe sizes.
- Elbows: Elbows alter the direction of flow, typically available in 45° and 90° angles.
- Flanges: Flanges provide strong connections and are used in both high and low-pressure systems.
- Tees: Tees connect three pipe sections at a 90° angle, facilitating fluid distribution.
- Wyes: Wyes connect pipes at a 45° angle, commonly used in drainage applications to prevent clogging.
Importance of Pipe Fittings in Piping Systems
Pipe fittings are indispensable in ensuring the functionality and reliability of piping systems. They enable the customization and adaptation of piping layouts to fit specific spatial and operational requirements. Proper selection and installation of fittings can greatly influence the efficiency and safety of the entire system. For instance, the use of appropriate reducers can minimize turbulence and pressure losses, which are critical for maintaining fluid flow and system performance.
Concentric vs Eccentric Reducers
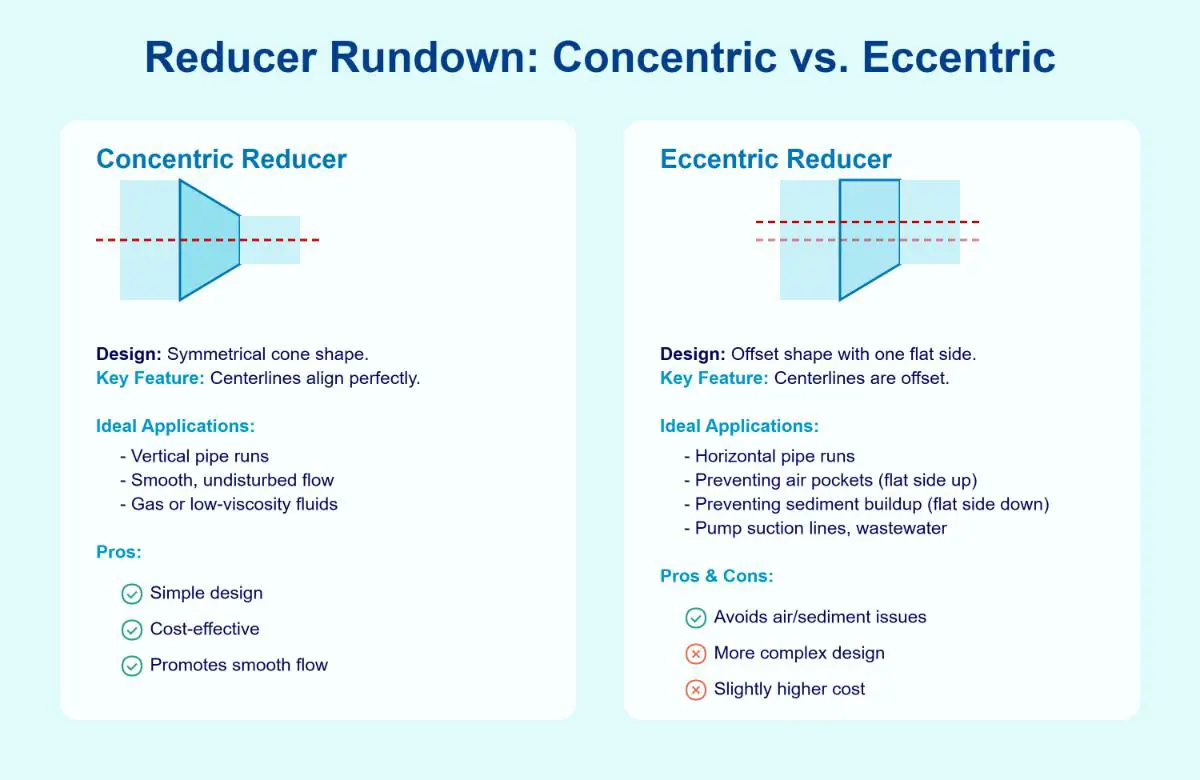
Reducers connect pipes of different diameters and come in two types: concentric and eccentric.
Concentric Reducers
- Design: Concentric reducers have both ends aligned along the same central axis.
- Application: Ideal for vertical piping systems, such as those found in HVAC and water distribution systems, where maintaining a continuous centerline is essential.
- Advantages: Facilitate smooth transitions in fluid flow, minimizing turbulence and flow disruptions. Their symmetrical design also makes them easier to install.
Eccentric Reducers
- Design: Eccentric reducers feature an offset centerline, with the smaller pipe positioned off-center from the larger one.
- Application: Suitable for horizontal piping systems, such as those in oil refineries, where preventing air or liquid trapping is important.
- Advantages: Prevent the accumulation of air or gas pockets, ensuring efficient drainage and system operation. However, they require precise orientation during installation to function correctly.
Material Selection in Piping Systems
Common materials used in piping systems include:
- Mild Steel: Strong and durable, used in high-pressure applications.
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, suitable for harsh chemical environments.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for low-pressure applications.
- Brass and Copper: Resistant to corrosion and easy to install, commonly used in plumbing.
- Plastic: Includes PVC and HDPE, known for chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness in low-pressure systems.
Ensuring the compatibility and durability of these materials is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of the piping system.
Detailed Comparison of Concentric and Eccentric Reducers
Concentric reducers are pipe fittings that connect pipes of different diameters while keeping the centerline consistent. Their design features a symmetrical, cone-like shape, ensuring that the smaller end is centered within the larger end. This design is particularly suited for applications requiring a smooth transition, minimizing turbulence and pressure loss.
Eccentric reducers, on the other hand, have an offset centerline. This design creates one side that is straight and one side that is cone-shaped, making it crucial for applications where preventing air pockets or ensuring a constant fluid level is necessary. Eccentric reducers are commonly used in horizontal piping systems.
Key Differences Between Concentric and Eccentric Reducers
Design and Structure
Concentric reducers have a symmetrical shape with both ends aligned along the same axis, while eccentric reducers feature an offset centerline, creating one straight side and one cone-shaped side.
Applications
Concentric reducers are ideal for vertical piping systems, such as HVAC systems, water supply lines, and vents. Their symmetry ensures a smooth transition for fluid flow, minimizing turbulence.
Eccentric reducers are best suited for horizontal piping systems, such as wastewater management and gas pipelines. The design prevents air pockets and maintains a constant fluid level, essential in systems where gas and liquid flows coexist.
Fluid Flow Characteristics
Concentric reducers ensure a smooth flow with minimal turbulence, which is crucial for maintaining uniform flow.
Eccentric reducers effectively prevent air or gas entrapment, which can disrupt flow. Their design is particularly beneficial in reducing noise and vibration in the system.
Installation Considerations
Their symmetrical design makes concentric reducers easier to install, requiring less precise alignment.
Eccentric reducers require more precise alignment during installation to ensure that the flat side is oriented correctly—upward for liquid lines and downward for vapor lines—to prevent fluid or gas accumulation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Concentric Reducers
Advantages:
- Simplified installation due to symmetrical design.
- Ideal for vertical systems where maintaining a continuous centerline is essential.
- High stability and resistance to wear and tear from chemicals.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for horizontal applications where air pockets could form.
- Less effective in noise and vibration reduction compared to eccentric reducers.
Eccentric Reducers
Advantages:
- Prevents air or gas entrapment, ensuring efficient drainage and system operation.
- Effective in reducing noise and vibration, making them suitable for quiet operation systems.
- Ideal for horizontal piping applications.
Disadvantages:
- More complex and precise alignment required during installation.
- Generally more expensive due to their complex design and installation requirements.
Industry-Specific Applications
In chemical processing, both types of reducers are used depending on the specific fluid dynamics and pressure requirements. In the oil and gas industry, eccentric reducers are commonly used to prevent air pockets in horizontal pipelines, whereas concentric reducers are used in vertical sections. In water treatment, concentric reducers are often used in vertical water supply lines, while eccentric reducers are employed in horizontal drainage systems to prevent air entrapment.

Applications and Use Cases
When to Use Concentric Reducers
Concentric reducers are primarily used in vertical piping systems where maintaining a smooth and centered flow is crucial. This design is particularly beneficial in applications involving low-viscosity fluids and gases, as it helps to minimize turbulence and pressure loss.
Vertical Pipelines
In vertical pipelines like water supply systems, concentric reducers ensure a smooth, centered flow. This uniform transition maintains fluid flow efficiency and stability, preventing disruptions and operational inefficiencies.
HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, concentric reducers connect different pipe sizes while maintaining a centered flow path. This is important for ensuring the consistent distribution of air or fluids throughout the system, which is critical for maintaining desired environmental conditions.
Petrochemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
In industries like petrochemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing, concentric reducers handle various fluids and gases. Their symmetrical design prevents interruptions in chemical processes caused by sudden pipe diameter changes, ensuring that the processes run smoothly and efficiently.
When to Use Eccentric Reducers
Eccentric reducers are best suited for horizontal piping systems where preventing air or gas pockets is essential. Their design, with the offset centerline, ensures that the fluid flow remains consistent and prevents the accumulation of gases or vapors that could disrupt the system.
Horizontal Pipelines
Eccentric reducers are essential in horizontal pipelines like those in wastewater management or gas pipelines, as they maintain a consistent bottom elevation. This design prevents the formation of air pockets, which can lead to blockages or reduced flow efficiency.
Pump Suction Lines
Eccentric reducers are often used on the suction side of pumps to prevent cavitation, which occurs when air bubbles form and collapse in the pump, potentially causing damage. The offset design ensures that any air present in the system is not trapped at the pump inlet, thus preventing cavitation and ensuring smooth operation.
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, eccentric reducers are commonly used in horizontal pipelines to prevent the accumulation of gases. This is particularly important in ensuring the safe and efficient transport of oil and gas, as trapped gases can lead to pressure build-up and potential safety hazards.
Industry-Specific Applications
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing plants, both concentric and eccentric reducers are used based on specific requirements. Concentric reducers are typically used in vertical applications where maintaining a smooth flow is critical, while eccentric reducers are used in horizontal pipelines to prevent gas entrapment and ensure consistent fluid levels.
Water Treatment
Water treatment facilities use concentric reducers in vertical water supply lines to ensure a steady and uniform flow. Eccentric reducers are employed in horizontal drainage systems to prevent air pockets that could disrupt the flow and reduce the efficiency of the treatment process.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, concentric reducers in vertical piping systems ensure consistent liquid flow and product quality, while eccentric reducers in horizontal systems prevent air or gas accumulation, maintaining hygiene and efficiency.
Impact on Fluid Flow and Pressure
How Concentric Reducers Affect Fluid Flow and Pressure
Concentric reducers feature a symmetrical, cone-shaped design that aligns the centerlines of both the larger and smaller pipes.
Fluid Dynamics
The symmetrical shape of concentric reducers allows for a smooth transition between different pipe sizes, reducing turbulence and pressure loss. This is particularly beneficial when transporting gases and low-viscosity liquids. By maintaining a smooth flow, these reducers help reduce the chances of flow disruptions and pressure drops, making them ideal for systems where stable and consistent flow is critical.
Pressure Characteristics
Concentric reducers maintain uniform pressure across the piping system by ensuring the pressure is evenly distributed, preventing localized spikes that can cause damage or inefficiencies. This characteristic is especially important in applications such as HVAC systems and water distribution lines, where consistent pressure is necessary for optimal performance.
How Eccentric Reducers Affect Fluid Flow and Pressure
Eccentric reducers, featuring an offset centerline, are designed to handle specific challenges in horizontal piping systems. Their unique design impacts fluid dynamics and pressure in ways that cater to horizontal flow requirements.
Fluid Dynamics
The offset design of eccentric reducers prevents air or gas pockets from accumulating, which can disrupt fluid flow. By ensuring that the smaller end is aligned to one side, eccentric reducers facilitate the smooth transition of fluids, preventing pooling and ensuring a consistent flow. This is particularly advantageous in systems where maintaining fluid levels and preventing gas entrapment are essential, such as in pump suction lines and pipe racks.
Pressure Characteristics
Eccentric reducers can create asymmetrical flow conditions, which can lead to a differential pressure along the angled side. This characteristic is useful in systems that require controlled flow rates. The design ensures that any gas or air present in the system is not trapped but is instead moved along with the fluid, preventing the formation of air pockets that can lead to pressure drops and flow inefficiencies.
Technical Considerations for Fluid Dynamics and Pressure Control
When selecting between concentric and eccentric reducers, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the piping system. Each type of reducer affects fluid flow and pressure differently, and understanding these impacts can help optimize system performance.
Installation Orientation
Installing concentric reducers is straightforward because of their symmetrical design. However, eccentric reducers need precise alignment. In liquid lines, the flat side should face up to prevent air pockets, and in vapor lines, it should face down to avoid liquid buildup.
System Application
Concentric reducers are ideal for vertical systems where maintaining a smooth and steady flow is critical. Their design minimizes turbulence and pressure losses, making them suitable for applications requiring minimal pressure drop. Eccentric reducers are better suited for horizontal systems where preventing air or gas buildup is crucial. Their offset design helps maintain a consistent flow and prevents fluid pooling, which is essential for efficient system operation.
Understanding the distinct fluid dynamics and pressure characteristics of concentric and eccentric reducers is crucial for optimizing the performance and reliability of piping systems. The choice between these reducers should be based on the specific needs of the application, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Design Differences
Concentric Reducers
Concentric reducers have a symmetrical design where both ends align along the same central axis, facilitating a smooth transition of fluid flow and minimizing turbulence and cavitation. This design makes them particularly suitable for vertical piping systems, such as those used in HVAC, water lines, and vents.
Eccentric Reducers
Eccentric reducers have an offset centerline, with one side straight and the other cone-shaped. This design helps prevent air pockets and sediment buildup, making them ideal for horizontal piping applications like wastewater management or gas pipelines.
Installation Considerations
Alignment
Concentric reducers are generally easier to install due to their symmetrical design, which does not require precise alignment adjustments. This ease of installation can save time and reduce labor costs. In contrast, eccentric reducers require careful orientation to ensure that the flat side is correctly positioned. This precise alignment is crucial for achieving the desired flow dynamics and preventing issues such as air entrapment.
Material Compatibility
Metal reducers are typically installed using butt-welding techniques, providing strong and durable connections, while PVC and other plastic reducers are usually fitted and glued. Some materials may also involve push-to-fit or crimp installation methods. The choice of installation method impacts both the ease of installation and the long-term maintenance requirements.
Maintenance Considerations
Flow Dynamics
Concentric reducers maintain a smooth, steady flow, which is beneficial in systems where minimizing turbulence is essential. This characteristic makes them ideal for vertical systems where the consistent flow of fluids or gases is necessary to maintain system efficiency and performance.
Eccentric reducers excel in preventing air entrapment and sediment accumulation, making them suitable for systems prone to these issues. Their design ensures that any air or gas present is not trapped, which is particularly important in horizontal systems where maintaining a consistent fluid level is critical.
Cost and Durability
Concentric reducers often have lower manufacturing costs compared to eccentric reducers due to their simpler design. This cost-effectiveness can be a significant factor in large-scale installations where budget constraints are a concern. However, the installation of eccentric reducers can be more labor-intensive due to the need for precise alignment. Despite the higher initial installation cost, eccentric reducers may offer long-term maintenance benefits in applications where air or sediment management is critical.
Application Scenarios
Vertical Systems
Concentric reducers are preferred in vertical piping systems due to their ability to maintain centered flow and minimize turbulence. This makes them suitable for applications like HVAC and water distribution systems where maintaining a smooth and continuous flow is essential.
Horizontal Systems
Eccentric reducers are used in horizontal applications to prevent air pockets and manage sediment buildup. This design ensures efficient drainage and proper system operation, making them ideal for wastewater management and gas pipelines. The ability to prevent air entrapment and maintain consistent fluid levels is crucial in these applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Processes
When assessing the cost-effectiveness of concentric and eccentric reducers, it’s important to consider factors like manufacturing complexity, material costs, and installation requirements.
Concentric reducers have a simpler, symmetrical design, generally making them easier and less expensive to manufacture. This straightforward geometry allows for more efficient production processes, resulting in lower costs for both the manufacturer and the end user. Eccentric reducers, on the other hand, have an asymmetrical design that requires more precise fabrication techniques. The offset centerline necessitates additional alignment and quality control measures during production, potentially increasing the manufacturing costs. However, advancements in manufacturing technology, such as CNC machining and 3D printing, have helped mitigate some of these cost differences by improving precision and efficiency. Both types of reducers can be made from various materials, including different types of metal and plastics such as PVC and HDPE. The choice of material can significantly impact the
The cost-effectiveness of reducers is also influenced by the ease and speed of installation. The symmetrical design of concentric reducers simplifies installation, requiring fewer alignment adjustments. This ease of installation can lead to reduced labor costs and shorter installation times, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications. Eccentric reducers require more precise alignment during installation to ensure the flat side is correctly positioned. This necessity for careful orientation can increase labor costs and extend installation times. Although installation may cost more, the benefits of preventing air pockets and sediment buildup can make eccentric reducers worthwhile, particularly in systems prone to these issues.
The manufacturing processes for concentric and eccentric reducers involve several common steps, but the complexity and precision required can differ significantly. The manufacturing process for concentric reducers typically involves cutting and shaping raw materials into the desired symmetrical form, welding sections together if necessary, and finishing the reducer to meet specific tolerances and surface quality requirements. This relatively straightforward process benefits from automated machinery and can be completed quickly and efficiently. Manufacturing eccentric reducers involves precision cutting to achieve the offset centerline, precise alignment during welding to ensure the correct orientation of the offset, and additional quality control measures to verify that the offset design functions correctly. These additional steps make the manufacturing process for eccentric reducers more complex and time-consuming, potentially leading to higher production costs.
Advancements like CNC machining and 3D printing have improved the precision and efficiency of producing both types of reducers, reducing costs and making complex designs more accessible. These technological advancements have helped bridge the cost gap between concentric and eccentric reducers, making both options more accessible and cost-effective for various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the main differences between concentric and eccentric reducers?
The main differences between concentric and eccentric reducers lie in their design, applications, and impact on fluid flow. Concentric reducers have a cone-shaped design where the centerlines of the larger and smaller pipes match, making them ideal for vertical piping systems and applications requiring smooth, symmetrical flow, such as gas and low-viscosity fluid transport. They are also simpler and more cost-effective to manufacture.
In contrast, eccentric reducers have an offset design with one side flat, resulting in mismatched centerlines. This design is beneficial for horizontal pipelines to prevent air pockets and sediment buildup, making them suitable for systems with mixed fluids or where maintaining a constant fluid level is crucial, such as pump suction lines or wastewater management. Eccentric reducers are more complex and slightly more expensive due to their design requirements.
When should I use a concentric reducer versus an eccentric reducer?
The choice between a concentric reducer and an eccentric reducer largely depends on the orientation of your piping system and the specific requirements of your application.
Concentric reducers are typically used in vertical piping systems where maintaining a consistent centerline is crucial. Their symmetrical, cone-like design ensures smooth fluid flow with minimal turbulence, making them ideal for applications requiring uniform flow, such as HVAC systems and chemical plants.
On the other hand, eccentric reducers are better suited for horizontal piping systems. Their offset design helps prevent air pockets in liquid lines and avoids liquid entrapment in vapor lines, which is essential for maintaining consistent fluid levels and efficient drainage. They are particularly effective in systems transporting viscous fluids, oils, or sludges, where preventing sediment buildup and managing flow without pressure drops are critical.
How do the designs of concentric and eccentric reducers affect fluid flow?
The designs of concentric and eccentric reducers significantly influence fluid flow within piping systems. Concentric reducers feature a symmetrical, conical shape that aligns the centerlines of the inlet and outlet pipes, promoting smooth and uniform fluid flow with minimal turbulence and pressure loss. This design is particularly advantageous for handling gases and low-viscosity liquids, making it ideal for vertical pipelines and applications where maintaining a centered flow is essential.
In contrast, eccentric reducers have an asymmetrical design with the smaller pipe offset from the centerline of the larger pipe, which includes a flat side. This design helps prevent the formation of air pockets and sediment buildup, making them suitable for horizontal pipelines. Eccentric reducers are crucial in systems prone to air or gas accumulation, such as oil refineries and chemical plants, and are effective in maintaining a uniform velocity profile necessary for efficient pump operation. They are particularly beneficial for systems handling viscous fluids or slurries.
What are the cost implications of choosing between concentric and eccentric reducers?
The cost implications of choosing between concentric and eccentric reducers are influenced by several factors, including manufacturing, installation, material, and application-specific costs.
Concentric reducers tend to be more cost-effective to manufacture due to their symmetrical design, which simplifies production processes. This simplicity also translates to easier installation, as their alignment with pipe centerlines reduces labor costs. In applications where smooth fluid flow and minimal turbulence are required, such as vertical piping systems, concentric reducers can help minimize energy losses and operational costs.
Eccentric reducers, on the other hand, have an offset design that makes them more complex and expensive to manufacture. Their installation demands greater precision to ensure proper alignment, particularly in horizontal piping systems, which can increase labor costs. However, they offer unique benefits in preventing air pockets and maintaining fluid levels, reducing long-term operational costs in specific applications like preventing pump cavitation.
What industries typically use concentric and eccentric reducers?
Concentric reducers are primarily used in industries where vertical piping systems are common, such as chemical processing, oil and gas, water treatment, and HVAC systems. These reducers ensure a smooth and uniform fluid flow, minimizing turbulence and pressure losses. Eccentric reducers, on the other hand, are essential in horizontal piping systems found in industries like sewage and wastewater management, gas pipelines, oil refineries, and chemical plants. Their offset design helps prevent air pockets and maintain consistent fluid levels, which is crucial for efficient operation in these sectors.
How does the installation process differ between concentric and eccentric reducers?
The installation process of concentric and eccentric reducers differs primarily due to their design characteristics. Concentric reducers, which have a symmetrical design with both inlet and outlet aligned along the same centerline, are generally easier to install. This ease is particularly notable in vertical piping systems where precise alignment is less critical. Concentric reducers can be connected through welding or threading, offering flexibility and straightforward installation.
In contrast, eccentric reducers feature an offset design where the inlet and outlet ends are not aligned along the same centerline. This design necessitates more precision during installation, especially in horizontal systems. The flat side of an eccentric reducer must be correctly positioned—upwards for liquid lines to prevent air pockets and downwards for vapor lines to avoid liquid accumulation. Although they can be welded or flanged like concentric reducers, the need for accurate alignment increases the complexity and potential labor costs of installation. Eccentric reducers are thus more challenging to install but essential for applications requiring specific fluid dynamics, such as wastewater management and gas pipelines.
