When it comes to copper tubing, not all copper is created equal. In the realms of HVAC systems and plumbing, selecting the right type of copper can make a world of difference in performance and durability. But what sets refrigeration copper apart from plumbing copper? From purity levels to temperature tolerance, each type serves distinct purposes and adheres to specific standards. This article will delve into the nuanced differences between these two types of copper, exploring their material composition, thermal properties, and applications. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or an intermediate learner, understanding these differences will enhance your ability to choose the right copper for your projects. Are you ready to uncover the secrets behind refrigeration and plumbing copper? Let’s dive in.
Overview of Refrigeration Copper and Plumbing Copper
Definition of Refrigeration Copper
Refrigeration copper is copper tubing made specifically for refrigeration systems. It is designed to withstand harsh conditions, including high pressures and a wide range of temperatures. This type of copper tubing is essential in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) applications, where it ensures efficient transfer of refrigerants and maintains the system’s performance.
Definition of Plumbing Copper
Plumbing copper is used primarily in water supply systems. It is made to handle the typical pressures and temperatures found in domestic and commercial plumbing. Known for its durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation, plumbing copper is a preferred choice for water supply lines and other plumbing applications.
Key Applications in HVAC and Plumbing Systems
Refrigeration Copper in HVAC Systems
Refrigeration copper is indispensable in HVAC systems for several reasons:
- Efficient Heat Transfer: Its excellent thermal conductivity ensures that heat is effectively transferred within the system. This capability is crucial for maintaining the system’s efficiency.
- High Pressure and Temperature Resilience: Made to endure high pressures and wide temperature ranges, refrigeration copper can handle the demanding conditions of refrigeration cycles.
- Corrosion Resistance: Its ability to resist corrosion prevents leaks and ensures the system remains efficient over time.
These characteristics make refrigeration copper suitable for use in air conditioners, refrigerators, and other cooling systems.
Plumbing Copper in Water Supply Systems
Plumbing copper is widely used in:
- Water Distribution: Commonly installed in both residential and commercial buildings, it is essential for transporting potable water.
- Hot and Cold Water Lines: Its capability to handle moderate temperature fluctuations makes it ideal for both hot and cold water lines.
- Durability: With its resistance to different water types, plumbing copper ensures long-lasting performance without significant degradation.
Plumbing copper’s reliability and ease of use make it a staple in the construction and plumbing industries.
Comparison of Refrigeration Copper and Plumbing Copper
Material Properties
- Purity: Refrigeration copper often has higher purity levels compared to plumbing copper, enhancing its performance under extreme conditions.
- Thermal Conductivity: Both types offer good thermal conductivity, but refrigeration copper is optimized for maximum heat transfer efficiency.
Suitability for Applications
- Refrigeration Systems: The high purity and corrosion resistance of refrigeration copper make it suitable for the demanding conditions of HVAC systems.
- Plumbing Systems: Plumbing copper’s durability and resistance to different water types make it well-suited for delivering water reliably and safely.
In essence, while both types of copper tubing serve essential roles in their respective applications, their specific properties and manufacturing processes tailor them to the unique demands of refrigeration and plumbing systems.
Material Composition and Purity Differences
Copper Alloy Purity Levels
Refrigeration Copper
Refrigeration copper usually has a purity level of approximately 99.9%. This high purity is crucial for reliable refrigeration system performance. The near-pure copper ensures excellent corrosion resistance, which is vital for preventing leaks and maintaining the efficiency of HVAC systems. Stringent cleanliness standards, like capping tube ends during shipping and installation, prevent contamination and maintain system performance.
Plumbing Copper
Plumbing copper usually has a purity level between 95% and 98%. While this is lower than refrigeration copper, it is adequate for plumbing applications where extreme purity is not as critical. Plumbing copper is designed to handle the typical conditions of water supply systems, focusing more on durability and resistance to various water chemistries rather than the ultra-high purity required for refrigeration systems.
Impact of Purity on Performance
Corrosion Resistance
The higher purity of refrigeration copper leads to a more uniform oxide layer on the surface of the tubing. This layer serves as a protective barrier against corrosion caused by refrigerants and contaminants. This enhanced corrosion resistance is crucial in HVAC applications, where the system is subjected to significant temperature fluctuations and pressure changes.
In contrast, plumbing copper, with its slightly lower purity, still offers good corrosion resistance but may be more susceptible to localized corrosion in certain water chemistries. However, this level of resistance is generally sufficient for plumbing applications, where the water is usually treated, and the operating temperatures are moderate.
Thermal Conductivity
The high purity of refrigeration copper also improves its thermal conductivity. This property is essential for efficient heat transfer in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring effective heat removal from the refrigerant and enhancing overall system efficiency.
Plumbing copper, while still a good conductor of heat, does not require the same level of thermal conductivity since its primary function is water transport rather than heat exchange. Its composition is optimized for mechanical durability and resistance to water-induced corrosion, making it suitable for temperature ranges typically encountered in water supply systems.
Comparative Analysis of Purity in Refrigeration vs. Plumbing Copper
| Aspect | Refrigeration Copper | Plumbing Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Purity Level | ~99.9% copper | 95% – 98% copper |
| Corrosion Resistance | Higher due to uniform oxide layer | Good but more susceptible to localized corrosion |
| Thermal Conductivity | Superior, crucial for heat transfer | Adequate, less critical |
| Cleanliness Standards | Strict, ends capped to avoid contamination | Less strict |
The key difference between refrigeration copper and plumbing copper lies in their purity levels and how this impacts their performance. Refrigeration copper’s high purity ensures better corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for sensitive refrigeration systems. Plumbing copper, while slightly lower in purity, provides sufficient durability and resistance to meet the demands of water distribution systems.
Thermal Conductivity and Temperature Tolerance Comparison
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material can conduct heat and is crucial for applications like refrigeration and HVAC systems.
Refrigeration Copper
Refrigeration copper is engineered to have superior thermal conductivity, which is essential for the efficient operation of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The high purity level of refrigeration copper, typically around 99.9%, significantly enhances its thermal conductivity. This makes it ideal for transferring heat efficiently, ensuring that refrigerants can absorb and dissipate heat quickly.
Plumbing Copper
Plumbing copper also exhibits good thermal conductivity, although it is not as critical for its primary function, which is to transport water. Plumbing systems do not require the same level of heat transfer efficiency as refrigeration systems. Consequently, the purity of plumbing copper is slightly lower, ranging from 95% to 98%, which is sufficient for water supply lines but results in comparatively lower thermal conductivity than refrigeration copper. The focus for plumbing copper is more on durability and resistance to corrosion rather than maximizing thermal conductivity.
Temperature Tolerance
Temperature tolerance refers to the range of temperatures that a material can withstand without degrading. This property is vital for materials used in environments with significant temperature variations.
Refrigeration Copper
Refrigeration copper is designed to tolerate a wide range of temperatures, from -40°F to 400°F (-40°C to 204°C). This broad temperature range is essential for refrigeration and air conditioning systems, which experience extreme temperature fluctuations during operation. The ability of refrigeration copper to maintain its structural integrity under both low and high temperatures ensures its reliability and longevity in demanding thermal environments.
Plumbing Copper
Plumbing copper is suitable for moderate temperature ranges, typically from 32°F to 180°F (0°C to 82°C), common in water supply systems. However, prolonged exposure to temperatures above 180°F can cause plumbing copper to soften, potentially compromising its strength and durability. This temperature limitation makes plumbing copper less suitable for high-temperature applications like those found in refrigeration and HVAC systems.
Comparative Analysis
| Attribute | Refrigeration Copper | Plumbing Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher (due to higher purity and finish) | Good but lower than refrigeration copper |
| Temperature Range | -40°F to 400°F (-40°C to 204°C) | 32°F to 180°F (0°C to 82°C) |
| Material Purity | Approx. 99.9% purity | 95% to 98% purity |
| Application Focus | Efficient heat transfer in HVAC/R systems | Durability and corrosion resistance in water supply |
Additional Considerations
Refrigeration copper often has a polished finish and capped ends to prevent contamination, making it suitable for sensitive HVAC and refrigeration systems. The thicker walls and higher pressure ratings of refrigeration copper contribute to its ability to withstand higher pressures and temperature extremes. On the other hand, plumbing copper is optimized for durability and resistance to varying water chemistries, prioritizing longevity and performance in water supply applications over thermal performance.
Applications and Suitability for HVAC and Plumbing Systems
Specific Uses of Refrigeration Copper in HVAC Systems
Refrigeration copper is crucial in HVAC systems because of its high purity and excellent thermal conductivity. Its high purity and superior thermal conductivity make it ideal for efficiently transferring heat in refrigeration cycles, ensuring the system maintains the desired temperatures and operates efficiently. Refrigeration copper can handle extreme conditions in HVAC systems, withstanding high pressures and temperatures ranging from -40°F to 400°F. Additionally, its excellent corrosion resistance prevents leaks and maintains system integrity over time.
Specific Uses of Plumbing Copper in Water Supply Systems
Plumbing copper is mainly used in water supply systems because it is durable and resists corrosion in different water chemistries. It is suitable for both hot and cold water lines, managing temperatures from 32°F to 180°F. Plumbing copper’s ease of installation and reliability make it a preferred choice for potable water distribution in residential and commercial buildings. Its slightly lower purity compared to refrigeration copper is adequate for these applications, focusing on mechanical strength and longevity rather than extreme thermal performance.
Why Refrigeration Copper is Preferred for HVAC Applications
Refrigeration copper is preferred for HVAC applications due to several key factors:
- High Purity and Thermal Conductivity: Its near 99.9% purity enhances thermal conductivity, crucial for efficient heat exchange in refrigeration cycles.
- Temperature and Pressure Tolerance: Designed to endure extreme temperature fluctuations and high pressures, refrigeration copper maintains its integrity and performance under demanding conditions.
- Corrosion Resistance: Superior corrosion resistance ensures long-term reliability and prevents leaks in HVAC systems exposed to harsh refrigerants and environmental conditions.
Suitability of Plumbing Copper in Various Plumbing Scenarios
Plumbing copper is well-suited for various plumbing scenarios, including:
- Potable Water Distribution: Its corrosion resistance and durability make it ideal for transporting drinking water safely.
- Hot and Cold Water Lines: Capable of handling moderate temperatures, plumbing copper is used extensively in domestic and commercial hot and cold water supply systems.
- Cost-Effective: Plumbing copper, typically Type M, has a thinner wall compared to refrigeration copper, making it more cost-effective for applications where high pressure and extreme temperature tolerance are not required.
Installation Considerations for Refrigeration and Plumbing Copper
Refrigeration Copper
- Bending and Shaping: Soft-annealed refrigeration copper is easy to bend and shape, which is ideal for complex HVAC system layouts.
- Joining Methods: Typically joined by brazing or soldering, ensuring strong, leak-free connections essential for maintaining refrigerant containment.
- Fittings: Long-radius bends in refrigeration fittings minimize pressure drops, enhancing system efficiency.
Plumbing Copper
- Rigid Tubing: Generally uses rigid tubing requiring fittings like elbows and tees for directional changes.
- Joining Methods: Commonly joined via soldering, compression, or crimped connections, optimized for water tightness and durability.
- Fittings: Short-radius bends in plumbing fittings are sufficient for water flow dynamics, differing from the requirements in refrigeration systems.
Understanding the specific applications and suitability of refrigeration copper and plumbing copper ensures the correct selection for HVAC and plumbing systems, optimizing performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance Characteristics
Importance of Corrosion Resistance in Copper Tubing
Corrosion resistance is essential for the durability and efficiency of copper tubing in refrigeration and plumbing systems. The ability of copper to resist corrosion ensures the integrity of the system, prevents leaks, and maintains efficiency over time. Various environmental and chemical factors influence the corrosion resistance of copper, making it crucial to understand how different types of copper tubing respond to these conditions.
Corrosion Resistance in Refrigeration Copper
Material Composition, Manufacturing, and Protective Film Formation
Refrigeration copper, often referred to as ACR (Air Conditioning and Refrigeration) tubing, is typically manufactured with high purity levels and specific compositions to enhance its corrosion resistance. Commonly used alloys include C10200 (oxygen-free high conductivity copper) and C12200 (phosphorus-deoxidized copper). These compositions are designed to minimize the presence of impurities that could contribute to corrosion.
Refrigeration copper develops a protective oxide layer when exposed to air. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, reducing further oxidation and protecting the underlying copper. The effectiveness of this protective layer depends on the operating environment. In low-oxygen, dry environments typical of refrigeration systems, the risk of oxidation is minimal, and the copper remains well-protected. However, residual moisture or acidic refrigerants can cause localized corrosion, known as formicary corrosion, which leads to micro-pitting.
Environmental and Operational Stressors
Refrigeration systems operate under a range of environmental and operational stressors:
- Temperature: Refrigeration copper must withstand temperatures from sub-zero to moderate levels, typically between -40°C to 120°C.
- Fluid Exposure: It is exposed to refrigerants and compressor oils, which are generally non-corrosive. However, hydrolysis of certain refrigerants can produce trace acids.
- Mechanical Stress: Vibrations from compressors and potential fatigue cracking are common mechanical stressors.
Corrosion Resistance in Plumbing Copper
Material Composition, Manufacturing, and Protective Film Formation
Plumbing copper, commonly used in water systems, typically has a lower purity than refrigeration copper. Common types include Type L (C12200) and Type M (C12000), with phosphorus added to improve weldability and corrosion resistance. These types of copper are designed to handle varying water chemistries and mechanical stresses.
Similar to refrigeration copper, plumbing copper relies on the formation of a protective cuprous oxide layer. However, the efficacy of this layer is highly dependent on the water chemistry:
- **Low pH (
Standards Compliance
Industry-Specific Standards for Refrigeration Copper
Refrigeration copper must meet stringent standards due to its critical role in HVAC systems. The primary standard governing refrigeration copper is ASTM B280, which specifies the requirements for seamless copper tubes used in air conditioning and refrigeration field service.
ASTM B280 Requirements
- Purity and Composition: ASTM B280 mandates a high purity level, typically above 99.9%, ensuring optimal thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Wall Thickness: The standard specifies thicker walls, commonly Type L tubing, to handle the high pressures and temperature fluctuations in refrigeration systems.
- Pressure Ratings: The tubes must endure high pressures, often over 800 psi, to ensure system integrity under extreme conditions.
- Finish and Cleanliness: Tubes are required to have a polished finish and capped ends to prevent contamination during installation, maintaining system performance and preventing leaks.
Industry-Specific Standards for Plumbing Copper
Plumbing copper is regulated by ASTM B88, which outlines the specifications for seamless copper water tubes used in potable water distribution systems.
ASTM B88 Requirements
- Purity and Composition: ASTM B88 allows for slightly lower purity levels, typically between 95% and 98%, focusing on durability and resistance to various water chemistries.
- Wall Thickness: The standard includes specifications for Type M tubing, which has thinner walls suitable for the moderate pressures found in residential and commercial water supply systems.
- Pressure Ratings: Plumbing copper is designed to handle pressures up to 200 psi, which is sufficient for water distribution but lower than the requirements for refrigeration copper.
- Finish and Cleanliness: Tubes generally have a standard finish with open ends, sufficient for water supply applications but less stringent than refrigeration copper requirements.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Both refrigeration and plumbing copper should adhere to specific regulatory standards to ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency in their respective applications.
Key Certifications
- ANSI/NSF 61: Certification for plumbing copper, ensuring the material is safe for potable water applications.
- UL Listed: Refrigeration copper often requires UL certification for fire safety and compliance with HVAC system standards.
Importance of Adhering to Standards
Compliance with industry standards is crucial for several reasons:
- System Reliability: This ensures copper tubing performs reliably under specified conditions, preventing failures and maintaining efficiency.
- Safety: Adhering to standards minimizes risks associated with pressure and temperature extremes, protecting both the system and users.
- Longevity: Copper tubing that meets standards is built to endure environmental and operational stressors, thereby extending the lifespan of HVAC and plumbing systems.
- Legal and Regulatory: Meeting standards ensures compliance with local and international regulations, avoiding legal issues and ensuring market acceptance.
Understanding and adhering to these standards is essential for selecting the appropriate copper tubing for refrigeration and plumbing applications, guaranteeing optimal performance and safety.
Cost Considerations
Material Grade and Composition
Refrigeration copper is typically made from higher-grade copper, often referred to as Type L or ACR (Air Conditioning and Refrigeration) tubing. This type of copper has a high purity level, close to 99.9%, which is essential for withstanding extreme pressures and temperature fluctuations ranging from -40°F to 400°F. The high copper content and enhanced quality of refrigeration copper increase its raw material costs compared to plumbing copper.
Plumbing copper generally uses Type M copper tubing, which has a slightly lower purity, typically ranging between 95% and 98%. This copper is designed for moderate temperature ranges (32°F to 180°F) and focuses on durability against variations in water chemistry rather than extreme physical stresses. The lower purity level of plumbing copper results in lower material costs.
Wall Thickness and Pressure Ratings
Refrigeration copper tubing, like Type L, has thicker walls to handle high pressure and prevent leaks in refrigeration and HVAC systems. In contrast, plumbing copper (Type M) has thinner walls suitable for lower pressure water supply systems. The increased wall thickness in refrigeration copper leads to higher material costs per foot of tubing.
Manufacturing and Finishing
Refrigeration copper often features polished finishes with capped ends to prevent contamination during transport and installation. This additional finishing step adds to the cost but is critical for maintaining system integrity in refrigeration applications. On the other hand, plumbing copper generally has a standard finish without contamination prevention measures, contributing to lower manufacturing costs.
Installation Ease and Labor Costs
Refrigeration copper is designed to be flexible (soft annealed) and easy to bend without cracking, which is ideal for complex HVAC system layouts. It can be joined using brazing or soldering, creating strong, leak-free connections crucial for system efficiency. This flexibility can reduce labor time and fitting costs in complex installations, somewhat offsetting the higher material costs.
Plumbing copper is often rigid and requires elbow fittings for bends, potentially increasing the number of fittings and installation time. However, plumbing systems typically have simpler layouts, which can mitigate some labor costs.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Refrigeration copper has superior corrosion resistance due to a uniform oxide layer that protects the tubing from refrigerants and contaminants, reducing maintenance and replacement costs. Plumbing copper also resists corrosion well but may be more susceptible to localized corrosion depending on water chemistry. The longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs of refrigeration copper can justify its higher upfront cost.
Thermal Conductivity and Efficiency
Refrigeration copper’s higher thermal conductivity is essential for efficient heat transfer in refrigeration and HVAC systems, positively impacting energy consumption and operational costs. Plumbing copper’s thermal conductivity is less critical, focusing mainly on water flow rather than heat transfer. Using refrigeration copper in HVAC systems can improve energy efficiency and reduce operating costs, offsetting the higher material costs.
Installation and Handling Differences
Material Properties and Applications
Refrigeration copper is designed for high-pressure applications and can handle significant temperature fluctuations, ranging from -40°F to 400°F. Its superior thermal conductivity and higher corrosion resistance due to its uniform oxide layer make it particularly suited for HVAC systems.
Plumbing copper is primarily used in residential and commercial water supply lines. It is suited for moderate temperatures ranging from 32°F to 180°F. While it has good thermal conductivity, this property is less critical in plumbing applications compared to refrigeration. Plumbing copper is known for its durability and resistance to various water chemistries, making it ideal for potable water distribution.
Installation Techniques
Bending and Shaping
Refrigeration copper, particularly Type L, has thick walls that allow it to be bent and shaped easily without special tools. This flexibility is advantageous in complex HVAC systems where precise routing of tubing is necessary. Soft-annealed refrigeration copper can be bent without cracking, making it easier to install in tight spaces.
In contrast, plumbing copper is usually rigid and cannot be bent without annealing. This rigidity necessitates the use of elbow fittings to navigate corners, which can increase the complexity and cost of installation. Plumbing installations often require more fittings and labor to achieve the desired layout.
Joining Methods
Both refrigeration and plumbing copper can be joined using soldering or brazing. The higher purity and uniformity of refrigeration copper make it ideal for these joining techniques, ensuring strong and leak-free connections that are essential for maintaining refrigerant containment. Brazing, which involves higher temperatures than soldering, is commonly used in refrigeration to create robust joints capable of withstanding high pressures.
Plumbing copper is typically joined by soldering, compression, or crimped connections. These methods are optimized for water tightness and durability. Soldering is the most common method, providing reliable joints for water supply systems. However, the lower purity of plumbing copper may make it more susceptible to localized corrosion at the joints over time.
Corrosion Resistance and Contamination Control
Refrigeration Copper
Refrigeration copper exhibits higher corrosion resistance due to its uniform oxide layer and polished finish. The tubes usually have capped ends to prevent contamination during transport and installation, which is critical for maintaining system efficiency and preventing leaks. This level of contamination control is necessary to ensure the purity of the refrigerant and the overall performance of the HVAC system.
Plumbing Copper
While plumbing copper is also corrosion-resistant, it may be more susceptible to localized corrosion depending on the water chemistry. Plumbing copper does not require the same level of contamination control as refrigeration systems, as the water supply typically undergoes treatment to prevent corrosion. The ends of plumbing copper tubes are generally not capped, which is acceptable for the less stringent requirements of water distribution systems.
Fittings and Configuration
Refrigeration Fittings
Refrigeration systems use long-radius fittings to minimize pressure drop and optimize refrigerant flow. These fittings help maintain system efficiency by minimizing resistance and ensuring smooth refrigerant circulation. The choice of fittings in refrigeration systems is crucial for maintaining high performance and preventing leaks.
Plumbing Fittings
Plumbing systems commonly use short-radius fittings, which are sufficient for the pressure and flow requirements of water supply lines. These fittings are designed to handle moderate pressures and do not need to minimize pressure drop to the same extent as refrigeration fittings. Short-radius fittings are cost-effective and easy to install, making them suitable for the simpler layouts of plumbing systems.
The differences in installation and handling between refrigeration copper and plumbing copper are tailored to their unique applications. Refrigeration copper demands higher durability, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance, whereas plumbing copper focuses on ease of installation and resistance to various water chemistries. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the appropriate copper type for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
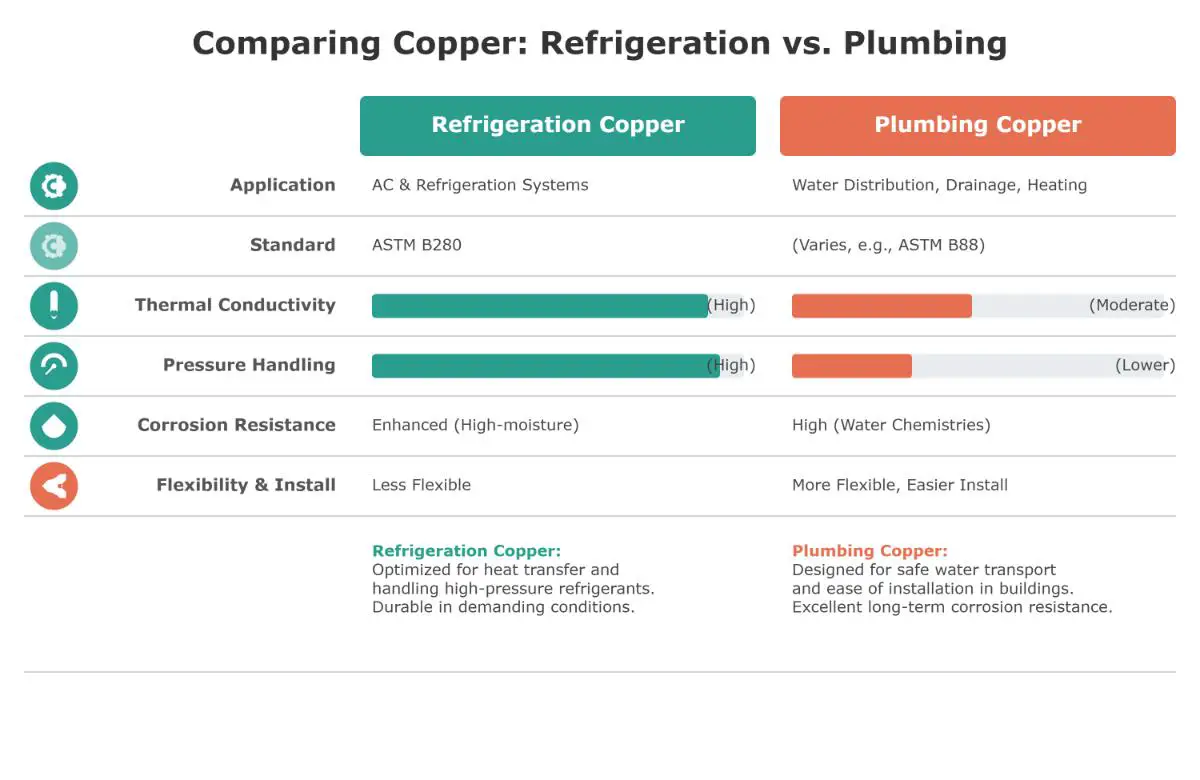
What are the main differences between refrigeration copper and plumbing copper?
Refrigeration copper and plumbing copper have distinct differences primarily based on their applications, material properties, and standards compliance.
Refrigeration copper is designed for use in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, adhering to ASTM B280 standards. It boasts high thermal conductivity, essential for efficient heat transfer, and is capable of handling high pressures typical in refrigerant systems. Its durability and enhanced corrosion resistance make it suitable for high-pressure, high-moisture environments.
Conversely, plumbing copper is used in water distribution, drainage, and heating systems. It is highly resistant to corrosion, ensuring long service life in various water chemistries. Plumbing copper is also more flexible and easier to install, allowing for bending and shaping without cracking, which is advantageous in complex plumbing layouts. Although it offers moderate thermal conductivity, it is not specifically designed for high-pressure applications like refrigeration copper.
How do the purity levels of refrigeration copper and plumbing copper compare?
Refrigeration copper, often referred to as ACR copper, typically has a higher purity level of at least 99.9% copper. This high purity is essential for maintaining system efficiency and enhancing corrosion resistance, which are critical in refrigeration applications where temperature fluctuations and high pressures are common. Refrigeration copper complies with ASTM B 280 standards, which emphasize these high purity levels.
In contrast, plumbing copper generally has a lower purity range, typically between 95% and 98%. While plumbing copper may use similar alloys like C12200, the focus is more on durability and resistance to various water chemistries rather than the high thermal conductivity required in refrigeration systems. This makes plumbing copper well-suited for water supply lines, handling moderate temperatures and different water conditions effectively.
The key differences in purity levels directly impact the performance and suitability of these copper types for their respective applications, with refrigeration copper’s higher purity ensuring better thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
What temperature ranges can refrigeration copper and plumbing copper withstand?
Refrigeration copper and plumbing copper are designed to operate within different temperature ranges due to their specific applications. Refrigeration copper can withstand a wide temperature range from -40°F to 400°F, making it suitable for systems that experience significant temperature fluctuations and high pressures. This range is crucial for maintaining the performance and efficiency of refrigeration systems, where both low temperatures and high thermal conductivity are essential.
On the other hand, plumbing copper is suited for moderate temperature conditions, typically ranging from 32°F to 180°F. Exposing plumbing copper to temperatures above 180°F for prolonged periods can lead to structural compromise due to softening. While plumbing copper also has good thermal conductivity, its primary role is to ensure efficient water flow in plumbing systems rather than maximizing heat transfer.
Why is refrigeration copper more suitable for HVAC systems than plumbing copper?
Refrigeration copper is more suitable for HVAC systems than plumbing copper due to several key factors. Firstly, refrigeration copper is designed to handle the high pressures and temperature fluctuations characteristic of HVAC systems. This type of copper is manufactured according to ASTM B280 standards, ensuring it is seamless and capable of withstanding the rigorous demands of refrigerant lines. Additionally, refrigeration copper has enhanced corrosion resistance, which is crucial for preventing leaks and maintaining system integrity when exposed to refrigerants and moisture.
The thermal conductivity of refrigeration copper is another critical advantage. It allows for efficient heat transfer, improving the overall performance and energy efficiency of HVAC systems. In contrast, plumbing copper, while also thermally conductive, is optimized for transporting potable water and other fluids at lower pressures and temperatures. It meets different standards focused on water safety and corrosion resistance in various water chemistries, making it less suitable for the specific demands of HVAC applications.
Are there cost differences between refrigeration copper and plumbing copper?
Yes, there are cost differences between refrigeration copper and plumbing copper. Refrigeration copper is typically more expensive due to its higher purity levels, stringent manufacturing processes, and compliance with demanding standards such as ASTM B280. These factors ensure that refrigeration copper can withstand high pressures and extreme conditions typical in HVAC and refrigeration systems, contributing to its higher durability and longer service life.
On the other hand, plumbing copper is generally more economical, especially the commonly used Type M tubing in residential water supply systems. It adheres to standards like ASTM B88, which have lower pressure ratings and less stringent purity requirements compared to refrigeration copper. Plumbing copper’s easier installation and compatibility with various fittings further reduce labor costs, making it more cost-effective upfront.
What standards should be considered when choosing refrigeration copper or plumbing copper?
When choosing refrigeration copper or plumbing copper, it is essential to adhere to industry-specific standards to ensure safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance. For refrigeration copper, the primary standard is ASTM B280, which covers seamless copper tube used in air conditioning and refrigeration field service. This standard requires the use of high-purity copper alloy C12200, with strict limits on phosphorus content to ensure optimal performance and corrosion resistance. The tubes must also undergo eddy-current testing and be capped to prevent contamination.
For plumbing copper, the applicable standard is ASTM B88, which specifies requirements for seamless copper water tubes used in plumbing systems. This standard includes different types of copper tubes (Type K, L, and M), each with varying wall thicknesses suitable for different pressure ratings. ASTM B88 ensures that the copper used in plumbing applications has the necessary mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Adhering to these standards ensures that the copper tubing used in refrigeration and plumbing applications meets the necessary performance and safety criteria, providing reliable and long-lasting service.
