Choosing the right flange for your piping system can be a critical decision, impacting both performance and maintenance. Whether you’re dealing with high-pressure environments or managing the effects of thermal expansion, understanding the differences between floating and fixed flanges is essential. Floating flanges offer unique advantages in certain applications, but fixed flanges might be the better choice for others. How do you decide which is right for your project?
In this article, we’ll delve into the key distinctions between floating and fixed flanges, examining their construction, functionality, and ideal use cases. We’ll explore how each type handles thermal expansion, the specific maintenance challenges they present, and which industries favor one over the other. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of when to use a floating flange versus a fixed flange and the factors that should influence your decision. Ready to navigate the complexities of flange selection? Let’s dive in.
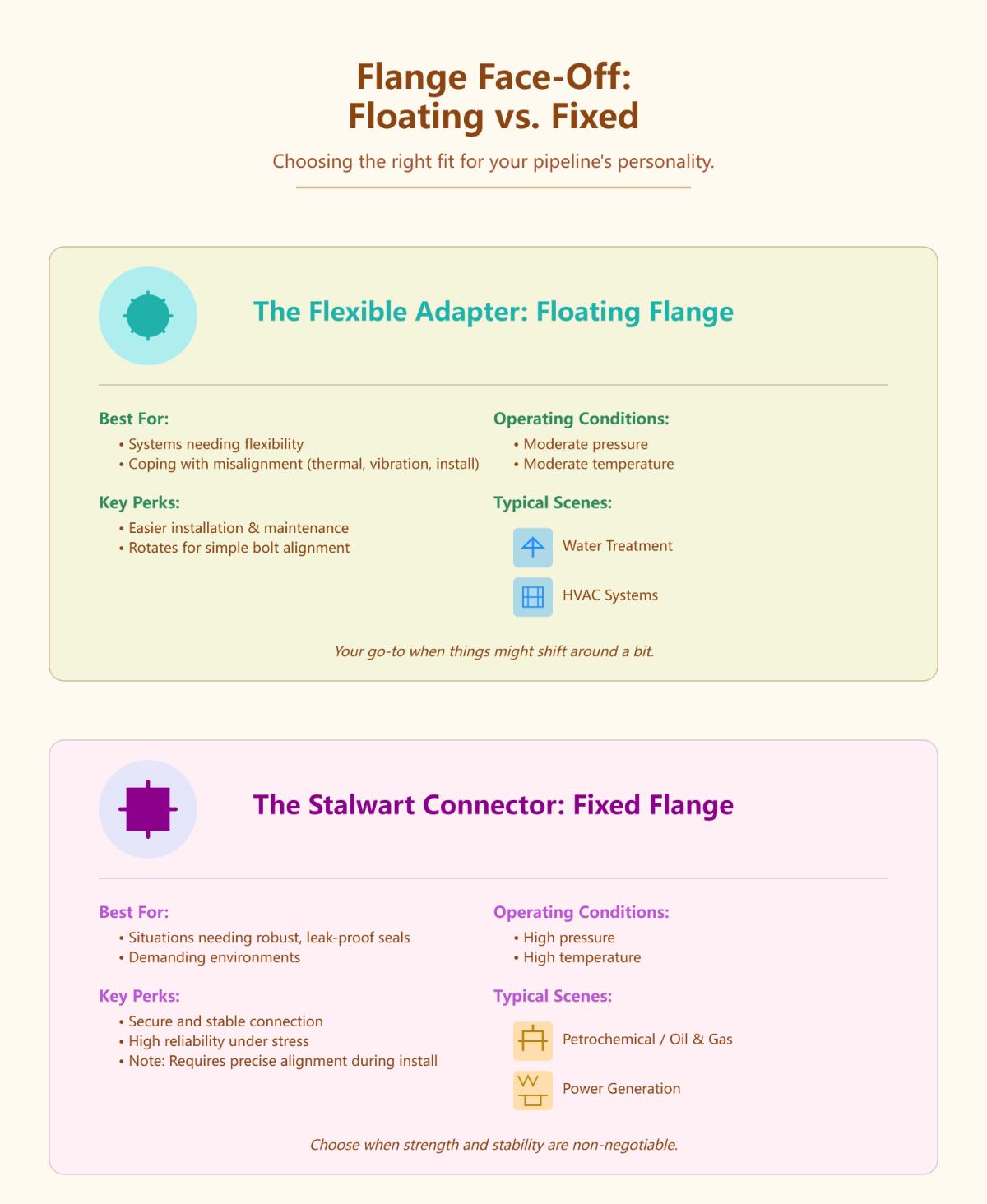
Comparing Flange Types: Floating vs Fixed
Overview of Floating Flange
Floating flanges enhance flexibility in piping systems. They are not permanently attached to the pipe, allowing for axial movement and slight misalignments. This type of flange is typically used with a gasket to ensure a flexible seal, which is beneficial in systems subject to thermal expansion or vibration. Floating flanges are often preferred in scenarios where ease of alignment and installation is critical, such as in systems with frequent maintenance or adjustments.
Structural Characteristics
- Connection Type: The floating flange is not welded or permanently fixed to the pipe, enabling movement.
- Design Flexibility: Ideal for compensating minor misalignments, which can occur due to thermal expansion or vibrations.
Applications
Floating flanges are commonly used in industries such as HVAC and water treatment, where pipelines often shift due to temperature changes or need frequent disassembly for maintenance.
Overview of Fixed Flange
Fixed flanges, welded or bolted to the pipe, create a rigid connection suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. This rigidity makes them essential where stability is crucial. Fixed flanges require precise alignment during installation, which is a key consideration in their application.
Structural Characteristics
- Connection Type: Permanently attached through welding or bolting, creating a stable and immovable joint.
- Installation Requirements: Demands precise alignment and often more complex installation processes.
Applications
Fixed flanges are extensively used in the petrochemical and oil and gas industries, where the ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures is essential. Their robust nature makes them ideal for permanent setups where stability is paramount.
Key Differences and Similarities
Flexibility and Movement
- Floating Flange: Allows for movement and misalignment, making it adaptable to changing conditions.
- Fixed Flange: Lacks flexibility after installation, requiring precise initial alignment.
Pressure and Temperature Handling
- Floating Flange: Suitable for low-to-medium pressure applications and less stable under high temperatures.
- Fixed Flange: Capable of handling high-pressure and high-temperature environments with greater integrity.
Installation and Maintenance
- Floating Flange: Easier to install due to its alignment flexibility, but requires regular maintenance of gaskets due to potential wear.
- Fixed Flange: Demands precise installation but offers reduced maintenance needs post-installation, focusing mainly on weld integrity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
Floating Flange
- Advantages:
- Easier alignment during installation.
- Adaptable to thermal expansion and vibration.
- Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
- Requires regular gasket maintenance.
Fixed Flange
- Advantages:
- Suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature environments.
- Provides a stable and durable connection.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex and precise installation process.
- Lack of flexibility for pipe movement or misalignment adjustments.
Understanding Flange Applications
In high-pressure environments, choosing between floating and fixed flanges is crucial because they handle stress and maintain integrity differently. Fixed flanges, with their rigid attachment to the pipe, are ideal for high-pressure applications, ensuring a secure, leak-proof connection essential in settings like petrochemical plants and offshore oil rigs. These flanges reliably maintain their seal under extreme conditions, reducing leak risks and enhancing system safety and efficiency.
On the other hand, floating flanges offer flexibility, making them suitable for systems where pressure variations are moderate. Their ability to accommodate movement and misalignment can be beneficial in applications where thermal expansion or contraction occurs, allowing the system to adjust without compromising the connection’s integrity. However, they may not provide the necessary stability in environments with constant high pressure.
The applicability of floating and fixed flanges varies significantly across industries. In manufacturing and engineering, floating flanges are often used in systems requiring frequent maintenance or adjustments. Their ease of alignment and flexibility simplifies installation and enables rapid disassembly and reassembly, which is essential in dynamic environments where pipeline configurations might change regularly.
In the oil and gas industry, fixed flanges are predominantly used due to their robust design, which is critical for maintaining system integrity under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. The permanent nature of fixed flanges makes them ideal for pipelines transporting volatile substances, where safety and reliability are paramount.
Floating flanges find their niche in sectors such as HVAC and water treatment. These flanges adapt well to temperature fluctuations, allowing the system to adjust without stressing the pipeline. Additionally, they accommodate vibration, making them a practical choice for applications requiring a flexible yet secure connection.
Lap Joint Flange
Lap Joint Flanges are a unique type of flange used in piping systems, known for their versatility and ease of installation. They consist of two main components: the stub end, which is welded to the pipe, and the lap joint flange, which slides over the stub end. This design offers the advantage of rotational flexibility, allowing the flange to rotate and align easily without being welded directly to the pipe, facilitating easier maintenance and installation.
Key Features and Benefits
Design and Flexibility
Lap Joint Flanges are distinguished by their ability to accommodate misalignments and provide rotational flexibility. Their design allows the flange to rotate and align easily without being welded directly to the pipe, facilitating easier maintenance and installation. This feature is particularly advantageous in situations where precise alignment is challenging or frequent adjustments are required.
Cost-Effectiveness
The flange can be reused, reducing material costs in systems needing frequent disassembly. Additionally, the simple installation process lowers labor costs, making them an economical choice for large projects. This makes Lap Joint Flanges a practical option for applications where cost efficiency is a priority.
Leakage Prevention
Lap Joint Flanges prevent leaks effectively through the stub end’s solid connection, allowing adjustments without compromising the seal, making them ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance. This reliable design ensures that the integrity of the system is maintained even when adjustments are necessary.
Comparison with Floating and Fixed Flanges
Flexibility and Movement
Lap Joint Flanges provide similar flexibility to floating flanges, accommodating movement and thermal expansion, unlike fixed flanges which offer a rigid connection. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications where shifts in the piping system need to be accommodated.
Installation and Maintenance
Compared to fixed flanges, Lap Joint Flanges facilitate easier installation and maintenance. They do not require precise alignment during installation, reducing complexity and time. Maintenance is simplified as the flange can be removed without cutting or welding, similar to the advantages provided by floating flanges.
Cost Considerations
Lap Joint Flanges are generally more economical than floating flanges, particularly in scenarios involving large pipes or systems requiring regular disassembly. While fixed flanges may offer lower initial costs due to their simpler design, the long-term benefits of reusability and reduced maintenance often make Lap Joint Flanges a more cost-effective solution.
Leakage Prevention
Both Lap Joint and fixed flanges offer robust leakage prevention. However, Lap Joint Flanges rely on the quality of the stub end connection rather than weld integrity, as seen with fixed flanges. This design difference enhances their reliability in systems where frequent adjustments or maintenance are necessary.
Material Standards and Compliance
Material Composition and Standards
Material standards are vital for ensuring the durability and reliability of floating and fixed flanges in various applications. These standards dictate the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances, ensuring that flanges can withstand specific operational conditions.
Fixed Flanges
Fixed flanges are typically made from durable materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, or cast iron, chosen for their ability to withstand high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Standards such as ASTM and ASME outline the necessary mechanical properties and chemical composition to ensure these flanges maintain structural integrity under stress. The stringent standards ensure that fixed flanges do not deform or fail, even under extreme operational stresses.
Floating Flanges
Floating flanges, a type of flange that allows for pipe movement, generally consist of a backing flange and a stub end welded to the pipe. The flange material is often carbon steel or stainless steel, following standards like ASTM A182 or A105, which ensure they are resistant to corrosion and strong enough for moderate conditions. This flexibility makes floating flanges suitable for applications with moderate pressure and temperature but less so for extreme conditions.
Compliance in Application Context
Compliance with industry standards is essential for the safe and efficient use of both floating and fixed flanges. These standards govern the pressure-temperature ratings, material traceability, and installation procedures necessary for each flange type.
Fixed Flanges
Fixed flanges are critical in industries where safety and reliability are paramount, such as oil and gas, chemical plants, and geothermal energy. The compliance requirements for fixed flanges are more demanding, especially in sectors where safety and reliability are critical. Standards like ASME B16.5 ensure that these flanges can handle extreme pressure and temperature without compromising safety. Non-destructive testing (NDT) and quality assurance protocols are typically employed to verify the integrity of fixed flanges before installation.
Floating Flanges
Floating flanges are used in applications where pipe misalignment or movement due to thermal cycling is expected, such as HVAC and water treatment systems. Although they must comply with standards like ASME B16.5, the focus is on flexibility and corrosion resistance rather than extreme strength. This makes floating flanges suitable for systems where precise alignment is challenging but where high-pressure conditions are not prevalent.
Installation and Maintenance Implications Affecting Compliance
The installation and maintenance of flanges significantly affect their compliance with operational safety codes, influencing the overall performance and reliability of piping systems.
Fixed Flanges
Fixed flanges require precise alignment and skilled installation to prevent stress and gasket failure, with regular inspections mandated by compliance standards. Since fixed flanges do not allow for movement, any pipe stress is directly transferred to the flange, necessitating high material quality and installation accuracy.
Floating Flanges
Floating flanges offer easier installation due to their ability to adjust for misalignment, requiring regular checks to ensure ongoing performance, especially in environments prone to vibration or temperature changes. While compliance protocols might be less stringent regarding installation precision, they still require proper material selection and gasket types suitable for the operating environment.
Flange Selection Criteria
When choosing between floating and fixed flanges, it is crucial to consider the system’s pressure and temperature requirements.
Pressure and Temperature Requirements
Fixed Flanges
Fixed flanges are ideal for applications demanding high pressure and temperature resistance. Their robust construction and rigid attachment make them suitable for environments requiring secure, leak-proof connections, such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation industries.
Floating Flanges
Floating flanges are better suited for systems with lower to medium pressure and temperature requirements. They offer flexibility to accommodate minor misalignments and thermal expansion without compromising system integrity, commonly used in HVAC systems and water treatment facilities.
System Alignment and Expansion
Managing system alignment and thermal expansion is also crucial.
Floating Flanges
Floating flanges can move along the pipe to compensate for minor misalignments and thermal expansion, helping to prevent stress and reduce damage risk. This makes them advantageous in systems where thermal expansion is a concern.
Fixed Flanges
Fixed flanges provide a rigid connection, requiring precise alignment during installation. This rigidity ensures stability but does not accommodate thermal expansion or misalignment, suitable for static systems with minimal temperature fluctuations.
Maintenance and Inspection
Floating Flanges
Due to their detachable nature, floating flanges are easier to inspect and maintain. They can be easily disassembled for routine checks, making them ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance.
Fixed Flanges
Despite being harder to maintain, fixed flanges provide long-term stability and lower leak risk, which can outweigh the initial installation complexity. Accessing them for inspection often requires more effort, potentially leading to more downtime.
Environmental Conditions
The operating environment significantly impacts flange selection, especially concerning corrosion resistance.
Material Selection
Choosing the appropriate material is crucial for durability and resistance to environmental factors. Stainless steel flanges may be preferred in corrosive environments, while carbon steel flanges suit less aggressive conditions.
Cost Considerations
Cost, though not always the primary factor, can influence the choice between floating and fixed flanges.
Floating Flanges
Floating flanges may have higher initial costs due to their design and material requirements. However, their ease of maintenance and reusability can result in lower long-term operational costs.
Fixed Flanges
Fixed flanges might be less expensive initially, but precise installation and potential maintenance difficulties can lead to higher long-term costs. They are economical for stable systems with minimal maintenance needs.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Installation Considerations
Floating Flange Installation
Floating flanges are known for their flexibility, which makes installation easier. These flanges can adjust to minor misalignments because they are not permanently affixed to the pipe, which is particularly helpful in systems where precise alignment is difficult. This adaptability allows for slight movement, accommodating thermal expansion and vibration, thus reducing installation complexity.
Moreover, the ease of correcting alignment during assembly is a notable benefit. Installers can adjust the flange position to align bolt holes and position gaskets correctly without needing perfect initial pipe placement. This flexibility lowers the risk of installation errors and reduces the time and effort required for setup. Floating flanges are typically made from materials like carbon steel or stainless steel, suitable for environments with fluctuating temperature and pressure conditions.
Fixed Flange Installation
Fixed flanges are welded or bolted directly to the pipe, requiring precise alignment to prevent stress and potential leaks. This rigid attachment demands careful planning and execution, as any misalignment can lead to gasket failure or leaks, especially in high-pressure or high-temperature conditions. Despite the increased complexity and time required for installation, the stability and strength of fixed flanges make them ideal for demanding environments such as chemical processing or power generation industries.
Maintenance Considerations
Floating Flange Maintenance
Floating flanges offer maintenance advantages primarily due to their flexible design, which reduces stress from pipe movement or thermal expansion and may reduce how often maintenance is needed in systems prone to vibration or misalignment. However, in environments with very high pressure or temperature, the risk of leakage is greater, potentially requiring more frequent gasket inspections and replacements.
The ease of disassembly is another significant advantage. The non-fixed nature of floating flanges allows for straightforward removal and replacement during maintenance operations, which is beneficial in systems requiring realignment post-servicing, such as HVAC or water treatment facilities.
Fixed Flange Maintenance
Fixed flanges are robust and provide a stable connection that can withstand high pressures and temperatures, often requiring minimal maintenance. However, when maintenance is needed, it tends to be more labor-intensive. Repairs often involve welding or unbolting, which can be costly and time-consuming. Any misalignment during reinstallation can lead to seal failures or mechanical stress.
Despite these challenges, the reliability of fixed flanges in harsh environments makes them a preferred choice in critical industrial applications where downtime is costly, and secure connections are essential. Their ability to maintain integrity under stress is a significant factor in their selection for such roles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
When should I use a floating flange vs fixed flange?
When deciding between a floating flange and a fixed flange, consider the specific requirements of your piping system. Floating flanges are ideal when flexibility is necessary, such as in systems that may experience misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or installation tolerances. They allow for easier installation and maintenance because they can rotate and adjust, making them suitable for applications like water treatment and HVAC systems where moderate pressure and temperature are involved.
Conversely, fixed flanges are best used in situations demanding robust, leak-proof connections under high pressure and high temperature. They provide a secure and stable connection, crucial for industries such as petrochemical, oil & gas, and power generation. Fixed flanges require precise alignment during installation, as they are permanently attached to the pipe, ensuring reliability and stability in demanding environments.
How does thermal expansion affect flange choice?
Thermal expansion significantly influences flange choice due to the differential expansion rates between materials when subjected to temperature variations. Floating flanges accommodate axial pipe expansion, reducing stress on bolts and minimizing the risk of leaks. They are ideal for systems experiencing frequent or rapid temperature changes, as they allow for movement and compensate for misalignment. Fixed flanges, however, restrict movement, inducing higher stress and requiring precise bolt preload calculations. They are better suited for stable thermal environments where temperature fluctuations are minimal. Proper material pairing and insulation strategies are crucial for managing thermal effects and ensuring reliable flange performance.
What maintenance challenges exist for fixed flanges?
Fixed flanges present several maintenance challenges due to their rigid attachment to pipelines or equipment surfaces. One primary issue is their inability to accommodate thermal expansion or contraction, which can lead to stress concentration on the flange, bolts, and gasket during temperature fluctuations. This immobility can cause bolt loosening, gasket failure, and even flange warping. Regular monitoring and maintenance, such as frequent bolt torque checks and the use of specialized gaskets, are necessary to address these challenges.
Additionally, fixed flanges are prone to corrosion, particularly around the flange face and bolt holes. Regular cleaning, protective coatings, and thorough inspections are crucial to prevent corrosion-related failures. Mechanical vibrations transmitted through fixed flanges can also lead to bolt fatigue and surface wear, necessitating vibration monitoring and proper bolt maintenance.
