In the world of industrial fluid control, choosing between gate valves and sluice valves can be a pivotal decision. The primary difference lies in their design and application scenarios: gate valves offer tight shut – off for on – off control, while sluice valves are often used for large – scale water flow regulation.
This article is tailored for those with an intermediate understanding of valves. We’ll explore each valve’s overview, applications in industries like manufacturing and water management, technical differences, and cost considerations. So, are you ready to find out which valve will reign supreme for your specific needs?
Gate Valve Overview
Definition and Functionality
A gate valve, also referred to as a sluice valve, is a linear – motion valve. Its main job is to control fluid flow in a pipeline by moving a gate up or down perpendicular to the flow. When fully open, the gate is completely out of the flow path, enabling a straight – through flow with minimal pressure loss. When fully closed, the gate presses against the valve seat, providing a tight seal to halt fluid flow. For instance, in a large – scale water supply pipeline, a gate valve can isolate a section for maintenance, completely stopping the water flow.
Key Features
Operation
Gate valves typically need multiple turns to open or close, which is slower compared to ball valves that only need a quarter – turn. This slow operation reduces the risk of water hammer, a phenomenon that can cause damage to pipelines due to sudden changes in fluid flow velocity.
Flow Path
The flow path in a fully open gate valve is straight and unobstructed, unlike globe valves where the flow path changes direction, leading to a higher pressure drop. The unobstructed flow in gate valves makes them suitable for applications where maintaining a consistent flow with minimal pressure loss is crucial.
Durability
Gate valves have a simple design with fewer parts, making them robust. They are well – suited for larger diameter pipelines, where their durability becomes a significant advantage compared to some other valve types, such as butterfly valves, which may be less durable in large – scale applications.
Common Materials Used
The valve body of a gate valve can be made from various materials. Cast iron is a common choice for its affordability and good corrosion resistance in many water – based applications. Stainless steel is used when dealing with corrosive fluids or in environments where hygiene is a concern, such as in the food and beverage industry. Brass – made valves are often used in smaller – scale plumbing, while stainless – steel gate valves are better for more demanding industrial conditions.
Typical Industrial Applications
Manufacturing and Engineering
In manufacturing plants, gate valves are used in process pipelines to control the flow of various fluids, such as chemicals, oils, and water. For instance, in a chemical manufacturing plant, they can be used to isolate different sections of the production line during cleaning or maintenance. In engineering applications, especially in large – scale infrastructure projects like dams and water treatment plants, gate valves play a vital role. They are used to regulate the flow of water, ensuring proper operation and safety of the entire system.
Construction
In construction projects, gate valves are essential for controlling water flow in plumbing systems. They are used in both residential and commercial buildings to manage the supply of water to different areas, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and fire sprinkler systems.
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, gate valves are used to control the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products in pipelines. Their ability to provide a tight seal and handle high pressures makes them suitable for these critical applications.
Real – world Case Studies
In a large water treatment plant, gate valves were installed in the main intake pipelines. These valves allowed the operators to completely shut off the water flow during routine maintenance of the filtration systems. The slow operation of the gate valves prevented water hammer, protecting the pipelines from damage and saving on repair costs.
In an oil refinery, gate valves were used in the transfer lines between different processing units. Their durability and ability to handle high – pressure and high – temperature conditions ensured reliable operation, reducing the risk of leaks and ensuring the safety of the entire refinery.
Sluice Valve Overview
A sluice valve, sometimes referred to as a gate valve, is a type of linear-motion valve used to control fluid flow by moving a gate perpendicular to the flow direction. When fully open, it offers an unobstructed flow path, minimizing pressure drop. Unlike some other valve types that change the fluid’s flow direction, sluice valves provide a straight-through flow, crucial for systems requiring high flow rates and low resistance.
Key Features
Operation
Sluice valves usually require multiple turns to open or close, which benefits by reducing the risk of water hammer, much like gate valves. Compared to ball valves that only need a quarter-turn, the multi-turn operation of sluice valves provides a more controlled flow adjustment.
Flow Path
When fully open, sluice valves provide a straight-through flow, ensuring minimal flow resistance. This contrasts with valves like butterfly valves, which may cause more turbulence and pressure drop, especially in large-diameter pipelines.
Durability
With a simple design and fewer moving parts, sluice valves are robust and reliable, especially in large-scale applications where they often outperform other valve types in terms of long-term reliability. In large water supply systems, sluice valves can withstand high pressures and continuous use without significant wear.
Common Materials Used
Sluice valves can be made from various materials depending on the application. Cast iron is commonly used for its cost-effectiveness and corrosion resistance in water systems, while stainless steel is chosen for more demanding environments. Brass may be used in smaller plumbing applications, similar to gate valves. However, sluice valves used in large hydraulic structures may require more specialized and robust materials to handle heavy loads and environmental exposure.
Typical Industrial Applications
Water Supply and Distribution
Sluice valves are widely used in water supply networks. They can isolate sections of the pipeline for maintenance or repair, similar to gate valves. However, in large-scale water distribution systems, sluice valves are often preferred due to their ability to handle high-volume water flow with minimal resistance.
Flood Control and Irrigation
In flood control and irrigation systems, sluice valves play a crucial role. They can regulate the flow of water in canals, reservoirs, and dams. Unlike some other valve types, sluice valves can be designed with large, heavy-duty gates to handle the large volumes of water associated with these applications.
Power Generation
In power plants, sluice valves are used to control the flow of cooling water and other fluids. Their ability to provide a tight seal and handle high pressures makes them suitable for these critical applications.
Real-World Case Studies
In a large-scale water treatment plant, sluice valves were installed in the main pipelines. These valves allowed the operators to precisely control the water flow during different treatment processes. The slow operation of the sluice valves prevented water hammer, protecting the pipelines and equipment from damage. In a flood control system, large-scale sluice valves were used to manage the water level in a reservoir. The robust construction of these valves ensured reliable operation even under extreme conditions.
Applications of Each Valve Type
Gate Valve in Industrial Applications
Gate valves are extensively used in many industries because they reliably shut off and control fluid flow while minimizing pressure loss. Their versatility makes them suitable for multiple applications, including:
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, gate valves regulate the flow of liquids and gases in pipelines. They can effectively isolate different sections of a production line for maintenance or cleaning, ensuring operational safety and efficiency. For example, in a chemical plant, gate valves may control the flow of corrosive chemicals and ensure safe isolation during maintenance procedures.
Construction
In construction, gate valves are vital in plumbing systems of residential and commercial buildings, managing water supply to fixtures like bathrooms, kitchens, and fire sprinklers. Their ability to provide a tight seal and control flow precisely makes them ideal for these applications.
Engineering
Gate valves play a critical role in large-scale engineering projects, such as dams and water treatment plants. They regulate water flow, ensuring proper operation and safety of these complex systems. Their robust design and ability to handle high pressures make them suitable for controlling large volumes of water in these applications.
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry relies on gate valves to control the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products in pipelines. Their ability to provide a tight seal and withstand high pressures and temperatures makes them indispensable in this sector. Gate valves ensure safe and efficient operation of pipelines, reducing the risk of leaks and maintaining system integrity.
Sluice Valve in Industrial Applications
Sluice valves, often used in large-scale water management projects, offer effective flow control for high-volume applications. Their design and functionality make them suitable for various industries, including:
Water Supply Systems
Sluice valves are integral to water supply networks, controlling the flow of water and isolating sections of the pipeline for maintenance or repair. Their ability to handle high volumes of water with minimal resistance is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of water distribution systems.
Water Management
In water management projects, such as flood control and irrigation systems, sluice valves regulate the flow of water in canals, reservoirs, and dams. Their strong build manages large water volumes under different conditions, ensuring system stability and safety.
Other Relevant Industries
Sluice valves are also used in power generation plants to control the flow of cooling water and other fluids. Their ability to provide a tight seal and handle high pressures makes them suitable for critical applications in these facilities. Additionally, sluice valves can be found in sewage treatment plants, where they control the flow of wastewater and ensure efficient operation of the treatment processes.
Comparative Analysis of Applications
When comparing the applications of gate valves and sluice valves, each type serves distinct purposes based on their design and operational characteristics. Gate valves are versatile and suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including manufacturing, construction, engineering, and the oil and gas industry. Their ability to provide reliable shut-off and control fluid flow with minimal pressure loss makes them ideal for these sectors.
On the other hand, sluice valves are specifically designed for large-scale water management projects, such as water supply systems, flood control, and irrigation. Their robust construction and ability to handle high-volume water flow with minimal resistance make them essential for these applications. Additionally, sluice valves are used in power generation and sewage treatment plants, where their ability to provide a tight seal and handle high pressures is crucial.
Choosing between gate and sluice valves depends on the fluid type, flow pressure and volume, and system conditions. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the appropriate valve type for any given industrial application.
Technical Differences and Advantages
Flow Control Mechanisms
Gate valves and sluice valves both utilize a gate or disc that moves perpendicular to the flow of the fluid to control its passage. However, the specific mechanisms and designs vary:
Gate Valve Mechanism
Gate valves use a gate or wedge that moves up to allow flow and down to block it. The gate can be solid, flexible, split wedge, or parallel disc, each offering different sealing and operational characteristics. This design ensures minimal pressure drop when fully open due to the straight – through flow path.
Sluice Valve Mechanism
Sluice valves, while similar in basic operation, are typically designed more robustly to handle larger volumes of water and environmental conditions. They typically have two seats that ensure a tight seal when the gate is lowered, optimizing them for water applications where leakage prevention is critical.
Pressure and Temperature Handling
Gate Valve
Gate valves are ideal for high – pressure and high – temperature environments, often used in industrial processes with steam, oil, and gas.
Sluice Valve
Sluice valves, conversely, are primarily designed for water flow control. While they can manage considerable pressure, their focus is on handling large volumes of water rather than extreme temperatures. Their construction supports reliable operation in municipal water distribution and hydraulic engineering projects.
Durability and Maintenance
Gate Valve Durability
Gate valves are known for their robust construction and longevity, especially when dealing with corrosive fluids or high – pressure environments. Materials such as stainless steel and high – grade alloys enhance their durability. Maintenance is relatively straightforward due to the simple design, which minimizes the number of parts that can wear out.
Sluice Valve Durability
Sluice valves are constructed to endure harsh outdoor conditions and continuous exposure to large volumes of water. Materials like cast iron and specialized coatings extend their lifespan. Their design is maintenance – friendly, allowing for easy part replacement without dismantling the entire valve.
Cost Considerations
Gate Valve Costs
Gate valves can be more expensive upfront due to their variety of materials and designs, but their versatility and durability can offer long – term cost savings in maintenance and replacement, especially in high – pressure and high – temperature applications.
Sluice Valve Costs
Sluice valves are generally cost – effective for large – scale water management projects. Their design, optimized for water flow control, ensures reliable performance with lower initial costs compared to other valves designed for similar applications. Additionally, their maintenance costs are typically lower due to the simplicity of their design.
Energy Efficiency and Standards Compliance
Gate Valve Efficiency
Gate valves provide energy efficiency through minimal flow resistance when fully open, reducing the energy required to pump fluids through the system. They often comply with industry standards such as ISO and API, ensuring quality and performance in critical applications.
Sluice Valve Efficiency
Sluice valves also offer low flow resistance, crucial for large – scale water systems where energy efficiency is vital. They adhere to standards specific to water management, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of municipal and agricultural water distribution systems.
Detailed Comparison of Valve Materials
Gate Valve Materials
Gate valves are available in various materials, each suited to specific applications:
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for corrosive environments and high – temperature applications.
- Cast Iron: Commonly used in water – based applications for its corrosion resistance and cost – effectiveness.
- Brass: Suitable for smaller – scale plumbing due to its ease of use and reliability.
Sluice Valve Materials
Sluice valves are designed with materials that ensure durability and performance in water control:
- Cast Iron: Widely used for its robustness and resistance to corrosion in water systems.
- Stainless Steel: Selected for environments where enhanced durability and corrosion resistance are required.
- Specialized Coatings: Applied to extend the life of the valve in harsh environmental conditions.
Each valve type’s material selection aligns with its intended application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in its respective environment.
Comparative Analysis
Performance in Water Control Applications
Both gate valves and sluice valves have distinct performance features in water control applications. Gate valves offer a straight-through flow path with minimal pressure drop when fully open, which is beneficial for maintaining a consistent water flow rate. However, they are not ideal for throttling and are mainly used for on/off control. In cases where precise flow adjustment is required, gate valves may not be the best choice.
On the other hand, sluice valves are specifically designed for large-scale water control. Their robust construction allows them to handle high-volume water flow with ease. They provide a tight seal and are optimized for low-turbulence water flow, making them suitable for applications such as municipal water supply and irrigation systems. However, they are strictly on/off valves and are not designed for flow regulation.
Suitability for Various Industrial Contexts
Manufacturing and Engineering
Gate valves are ideal for manufacturing and engineering due to their versatility in handling various fluids like chemicals, oils, and steam. They withstand high pressure and temperature, ensuring reliable industrial operations, such as isolating sections in a chemical plant.
Sluice valves, while less common in these industries, can be used in areas where large volumes of water are involved, such as cooling systems. However, their limited media compatibility restricts their use compared to gate valves.
Construction
In construction, gate valves are commonly used in plumbing systems of buildings. They can provide a tight seal to control water supply to different fixtures. Their durability and ability to withstand pressure make them a reliable choice for long-term use.
Sluice valves are mainly used in large-scale construction projects related to water management, such as dams and water treatment plants. Their robustness and ability to handle large water volumes are crucial in these applications.
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, gate valves are the preferred choice. They can handle high-pressure and high-temperature fluids like crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. Their tight shut-off capability ensures the safety and integrity of the pipeline systems.
Sluice valves are not typically used in the oil and gas industry due to their design limitations and poor compatibility with non-water media.
Advantages and Disadvantages Summary Table
| Valve Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Gate Valve | Versatile for various fluids; suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments; some throttling possible | More complex maintenance; not ideal for continuous throttling |
| Sluice Valve | Robust for large-volume water control; simple structure for easy maintenance; low-turbulence water flow | Limited to water applications; not suitable for gases or chemicals; no throttling ability |
Comparative Cost Analysis
Gate valves usually have a higher initial cost because of their varied materials and intricate designs. However, their long-term durability and versatility can lead to cost savings in terms of maintenance and replacement, especially in high-demand industrial applications.
Sluice valves are more cost-effective for large-scale water management projects. Their simple design reduces the initial investment, and their maintenance costs are relatively low. However, if used in non-water applications, additional costs may be incurred due to their unsuitability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What is the primary difference between gate valves and sluice valves?
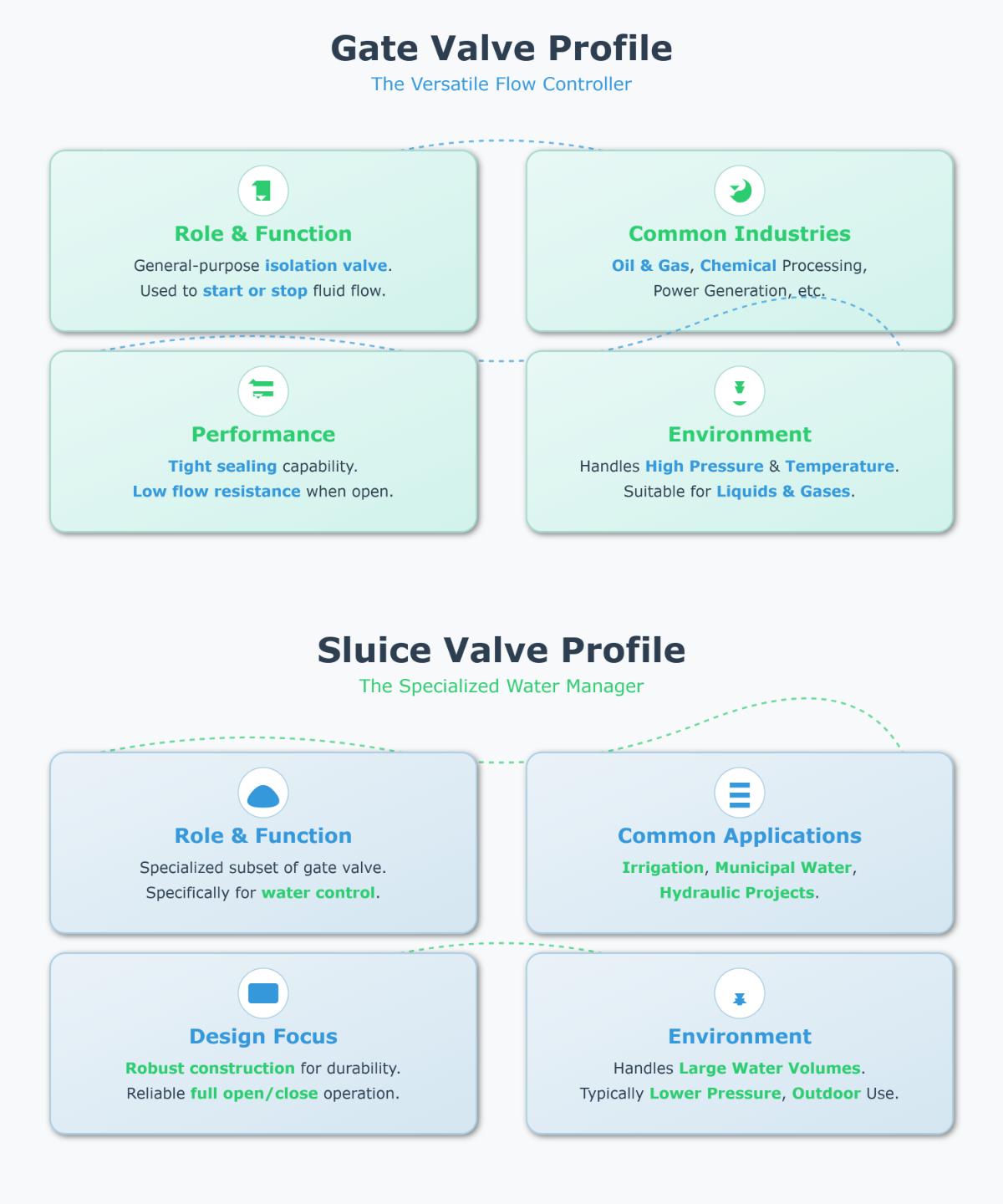
The primary difference between gate valves and sluice valves lies in their design focus, typical applications, and construction robustness. Gate valves are versatile isolation valves used across various industries, including oil, gas, and chemical processes. They are designed to start or stop the flow of liquids or gases by lifting a gate out of the fluid path, offering tight sealing and minimal resistance when fully open. Gate valves are suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature environments and are used for both liquids and gases.
On the other hand, sluice valves are a specialized subset of gate valves designed specifically for water control applications. They are used to manage large volumes of water in systems like irrigation, municipal water distribution, and hydraulic engineering projects. Sluice valves prioritize robust construction to endure outdoor and harsh environmental conditions, ensuring reliable full open/close operation. They typically handle lower pressures compared to gate valves but are optimized for large-scale water flow management.
Which valve is more suitable for water control applications?
For water control applications, sluice valves are generally more suitable due to their robust construction and ability to handle large volumes of water efficiently. Sluice valves are designed to withstand harsh outdoor conditions, making them ideal for municipal water distribution, irrigation systems, and reservoirs. They provide reliable shutoff with minimal pressure drop when fully open, which is crucial for effective water management. Additionally, their simpler structure facilitates easier maintenance, although periodic cleaning may be necessary to remove sediment deposits.
In contrast, gate valves are versatile and suitable for various fluids, including water, oil, and gas, making them more appropriate for industrial applications where tight shutoff and high-pressure tolerance are required. Gate valves are beneficial in confined spaces due to their non-rising stem design and adaptability to different environmental conditions and pressures. However, for general water control, especially involving large volumes, sluice valves are the preferred choice.
How do gate valves and sluice valves compare in terms of maintenance?
Gate valves and sluice valves both require regular maintenance, but there are differences. Gate valves, with their more complex designs involving various gate shapes and packing systems, demand a moderate to high level of maintenance. They are used for on/off and sometimes throttling, which causes variable wear. Regular lubrication, packing adjustment, and internal cleaning are necessary, and major repairs often require valve removal.
Sluice valves, a subtype of gate valves, usually have a simpler flat or wedge – shaped gate. They are mainly used for on/off control, which minimizes wear from throttling. Their maintenance is generally easier, with less frequent major repairs.
Are there specific standards that these valves must comply with?
Yes, both gate valves and sluice valves must comply with specific industry standards to ensure their quality, safety, and performance. Gate valves typically adhere to standards set by organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards ensure that gate valves provide reliable isolation and tight shutoff in various industrial applications, including oil, gas, and water systems.
Sluice valves, often used in large-scale water management systems, follow older waterworks standards. They are designed to handle large water volumes and harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for applications like water distribution networks and irrigation systems. Compliance factors for both valve types include material quality, leak tightness, operational torque, pressure drop, and certifications from regulatory bodies such as the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) or the European Conformity (CE) mark. These standards and certifications ensure the valves meet specific durability and performance requirements.
What are the cost implications of choosing one valve over the other?
When choosing between a gate valve and a sluice valve, cost implications are a key consideration. Sluice valves, typically larger and more robust, are designed for heavy-duty water management systems and are often made from materials like cast iron or ductile iron. This results in a higher initial purchase cost compared to gate valves, which come in a wider range of sizes and materials, making them less expensive for smaller applications.
Installation costs for sluice valves can also be higher due to their size and weight, requiring more substantial support and handling equipment. However, their simpler design for water-only applications can make them more cost-effective in large-scale water projects.
In terms of maintenance, sluice valves generally have lower costs due to their simple structure and fewer parts that need servicing. Gate valves, on the other hand, require more frequent inspections and seal replacements, especially in diverse media applications, leading to higher maintenance expenses.
How do these valves impact energy efficiency in industrial systems?
Gate valves and sluice valves both impact energy efficiency in industrial systems through their design and operational characteristics. When fully open, both valves provide low flow resistance, minimizing energy losses associated with fluid movement. However, gate valves are particularly effective in high-pressure environments due to their robust sealing capabilities, which reduce leakage and maintain system integrity, thereby enhancing energy efficiency.
Sluice valves, on the other hand, are optimized for managing large volumes of water with minimal pressure drop, making them energy-efficient in water supply and hydraulic systems. However, neither valve type is suitable for throttling, as partial openings can lead to wear, vibration, and energy inefficiencies. Proper selection based on fluid characteristics and operational requirements is crucial to maximizing energy efficiency in industrial applications.
