Removing nickel plating from copper can seem like a daunting task, especially if you’re concerned about preserving the integrity of the underlying metal. Whether you’re an enthusiast looking to restore vintage items or a professional aiming to refine your technique, understanding the most effective and safe methods is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of nickel plating removal, comparing various techniques and highlighting essential safety precautions. You’ll discover how to protect the copper during the removal process and tackle common challenges that may arise. Ready to dive in and uncover the secrets to achieving a flawless finish? Let’s get started!
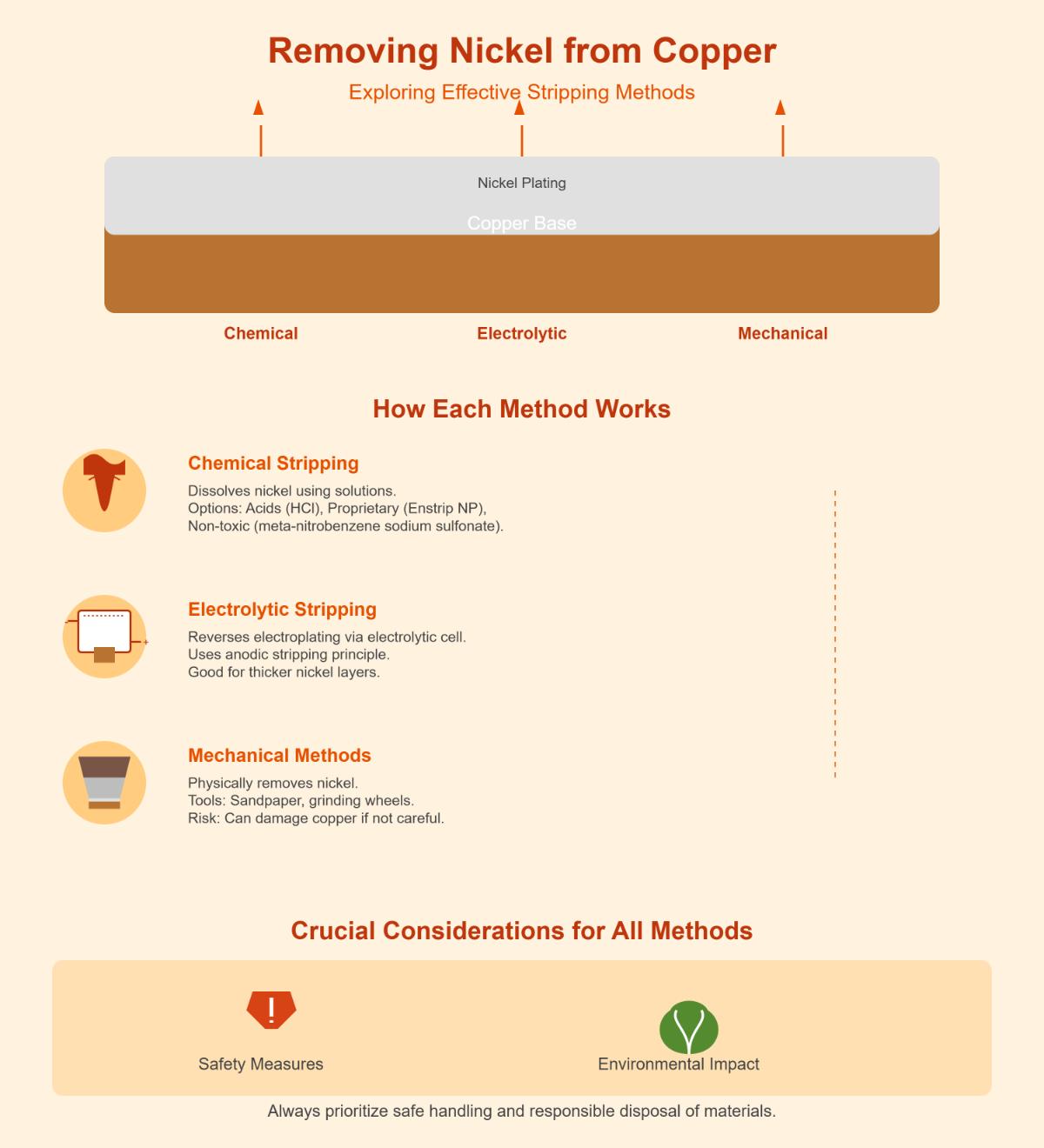
Methods for Removing Nickel Plating
Chemical Stripping
Chemical stripping is a popular method for removing nickel plating from copper due to its efficiency and effectiveness. This process involves using chemical solutions to dissolve the nickel coating without significantly affecting the copper substrate.
Hydrochloric Acid (Muriatic Acid)
Hydrochloric acid, a strong industrial chemical, is frequently used to strip nickel plating. The process involves immersing the nickel-plated copper in a hydrochloric acid solution, which dissolves the nickel. However, care must be taken to avoid prolonged exposure, as it can damage the copper substrate. Always use appropriate safety gear, including gloves and goggles, and work in a well-ventilated area.
Proprietary Solutions
Several proprietary chemical solutions are designed specifically for nickel stripping. Formulated to be safer and more efficient than standard acids, these solutions are commonly used in industrial settings where precision and substrate protection are crucial.
Non-Cyanide Solutions
Non-cyanide solutions are an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional cyanide-based strippers. These solutions often use organic compounds to dissolve the nickel plating. They offer a safer and more sustainable option, reducing the environmental impact of the stripping process. These solutions are becoming increasingly popular due to stringent environmental regulations.
Electrolytic Stripping
Electrolytic stripping, also known as anodic stripping, uses an electrochemical process to remove nickel plating. This method involves placing the nickel-plated copper in an electrolytic bath and applying a reverse current. The nickel dissolves into the solution, effectively stripping the plating.
Anodic Stripping
Anodic stripping is precise and minimizes damage to the copper substrate. The process requires specific equipment, including a power supply and an electrolytic bath. Safety precautions are essential, as the process involves handling electrical currents and potentially hazardous chemicals. Anodic stripping is ideal for applications requiring high precision and substrate protection.
Mechanical Removal
Mechanical removal involves physically abrading the nickel plating from the copper surface. This method is suitable for thicker nickel coatings and robust copper parts.
Sanding and Grinding
Sanding and grinding are common mechanical methods for removing nickel plating. These techniques use abrasive materials to wear down the nickel layer. While effective, they can be labor-intensive and pose a risk of damaging the copper substrate if not done carefully. Sanding and grinding work best for flat or simple-shaped parts.
Blasting Techniques
Blasting techniques, such as sandblasting or bead blasting, use high-pressure streams of abrasive materials to remove the nickel plating. These methods are effective for robust items but may not be suitable for complex shapes or delicate parts. Proper equipment and safety measures, including protective clothing and respiratory protection, are necessary to prevent injury and ensure effective removal.
Vinegar Method
The vinegar method is a safer, DIY-friendly option for removing nickel plating. White vinegar, containing acetic acid, can dissolve nickel plating over time, making it effective for lighter coatings and delicate items.
Acetic Acid (Vinegar)
To use the vinegar method, immerse the nickel-plated copper in white vinegar and allow it to soak. Depending on the thickness of the nickel plating, this process may require repeated soaking and scrubbing. The vinegar method is less aggressive than chemical or electrolytic stripping, making it suitable for delicate items where substrate protection is critical.
Key Considerations
- Safety Precautions: Always use protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, and ensure good ventilation when handling chemicals.
- Substrate Protection: Choose methods that protect the copper substrate from damage, particularly when using chemical or electrolytic processes.
- Environmental Impact: Dispose of chemicals and waste responsibly, and consider using environmentally friendly alternatives.
Post-Removal Steps
After removing the nickel plating, it is essential to thoroughly rinse and clean the copper surface to remove any chemical residues. Buffing or polishing may be necessary to achieve a smooth finish. If the component will be exposed to harsh environments, apply a protective coating to prevent corrosion.
Comparative Analysis of Removal Methods
Chemical Stripping
Chemical stripping is a widely used method for removing nickel plating from copper due to its effectiveness and efficiency. It involves using chemical solutions to dissolve the nickel layer without significantly affecting the copper substrate. There are several types of chemical strippers available, each with its advantages and considerations.
Commercial Strippers
Commercial strippers, such as Enthone Enstrip NP and Metalx B-929, are specifically formulated for nickel removal. These solutions are both efficient and safe for copper, making them ideal for industrial use.
- Advantages: High efficiency, minimal damage to copper, suitable for intricate shapes.
- Considerations: Requires proper handling and disposal, can be costly.
Household Acids
Household acids like acetic acid (vinegar) and hydrochloric acid can also be used for nickel stripping. These acids are readily available and affordable but less efficient and slower.
- Advantages: Easily accessible, cost-effective for small-scale applications.
- Considerations: Slower process, potential hazards if not handled correctly, less control over the stripping process.
Non-Toxic Alternatives
Recent advancements have led to the development of non-toxic, environmentally friendly alternatives for nickel stripping. These solutions often contain organic amines and other non-cyanide compounds that dissolve the nickel plating without posing significant environmental risks.
- Advantages: Safer for users and the environment, compliance with stringent regulations.
- Considerations: May be less effective on thicker coatings, limited availability.
Electrolytic Stripping
Electrolytic stripping, also known as anodic stripping, is an electrochemical process that reverses the electroplating process. This method involves placing the nickel-plated copper in an electrolytic bath and applying a reverse current to dissolve the nickel layer into the solution.
Process
To perform electrolytic stripping, an electrolytic cell is set up with an appropriate electrolyte solution, such as sulfuric acid. The copper part is connected as the anode, and a controlled current is applied to remove the nickel. After understanding the process, let’s look at its advantages:
- Advantages: Controlled and efficient process, minimal damage to the copper, suitable for thicker coatings.
- Considerations: Requires specialized equipment, careful control of current densities, and the use of inhibitors to protect the copper substrate.
Mechanical Removal
Mechanical removal methods involve physically abrading the nickel plating from the copper surface. These methods are suitable for thicker nickel coatings and robust copper parts.
Sanding and Grinding
Sanding and grinding involve using abrasive materials to remove the nickel layer. These techniques are effective but can be labor-intensive and risk damaging the copper substrate if not done carefully.
- Advantages: No chemicals involved, suitable for robust metals.
- Considerations: Time-consuming, risk of scratching the base material, not ideal for delicate or complex shapes.
Blasting Techniques
Blasting techniques, such as sandblasting or bead blasting, use high-pressure streams of abrasive materials to remove the nickel plating. These methods are effective for robust items but may not be suitable for complex shapes or delicate parts.
- Advantages: Effective for thicker coatings, no chemical use.
- Considerations: Requires proper equipment and safety measures, potential risk to intricate designs.
Selection Criteria
Choosing the appropriate method for removing nickel plating from copper depends on several factors, including the thickness of the nickel plating, the type of underlying metal, and the desired outcome. Here is a comparative overview to help with the selection:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Stripping | Efficient for complex shapes | Needs careful chemical handling, potential environmental impact |
| Electrolytic Stripping | Controlled process, efficient for thicker coatings | Requires specialized equipment, careful control to avoid damage |
| Mechanical Methods | No chemicals involved, suitable for robust metals | Time-consuming, risks scratching the base material |
Safety and Environmental Considerations
When removing nickel plating, it is crucial to prioritize safety and environmental considerations:
- Safety Precautions: Always wear protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, and ensure good ventilation when handling chemicals or performing mechanical removal.
- Waste Disposal: Proper disposal of chemical waste is essential to prevent environmental contamination. Always follow local regulations and guidelines.
By carefully selecting the appropriate method based on the specific requirements of the project, one can effectively remove nickel plating from copper while preserving the integrity of the copper substrate.
Safety Precautions and Equipment
Ensuring safety during the removal of nickel plating from copper is essential for protecting both the operator and the environment. Proper safety measures protect against hazards associated with chemical and mechanical methods.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing appropriate PPE is crucial to safeguard against chemical exposure and physical injuries. Essential PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respirators or masks to filter out harmful vapors and particles.
Ventilation
Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated, using exhaust fans or working in open areas to minimize inhalation risks.
Disposal Practices
Chemical waste from nickel removal must be disposed of responsibly to prevent environmental contamination. Follow local regulations for hazardous waste disposal, and never pour chemicals down the drain.
Equipment and Chemicals
Using the right equipment and chemicals is essential for efficient and safe nickel plating removal.
Chemical Strippers
Commercial chemical strippers like Enthone Enstrip NP and Metalx B-929 are specifically formulated for nickel removal. These solutions are effective and minimize damage to the copper substrate. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for safe application.
Household Chemicals
For smaller, less demanding projects, household chemicals such as vinegar (acetic acid) can be used. Soak the item in vinegar for several hours or overnight to dissolve thin layers of nickel plating. This method is less aggressive and suitable for delicate items.
Mechanical Removal Tools
Mechanical tools, including sandpaper, grinding wheels, and abrasive pads, can be employed to physically remove nickel plating. This method requires caution to avoid scratching the copper. Mechanical removal is more time-consuming and may be best suited for thicker coatings.
Environmental Considerations
Removing nickel plating involves environmental responsibilities to prevent harm:
- Chemical Waste Management: Properly dispose of chemical waste to avoid soil and water contamination. Utilize certified disposal services if necessary.
- Eco-Friendly Alternatives: Consider eco-friendly methods like mechanical removal or using household items such as vinegar to reduce chemical usage.
Comprehensive Steps
Begin by thoroughly cleaning the copper component. Apply commercial or household chemicals according to the instructions, ensuring full coverage. Allow adequate time for the chemicals to work. After removing the nickel plating, neutralize any remaining residue with water and mild detergent, then dry the copper surface thoroughly to prevent corrosion.
By following these guidelines, you can safely and effectively remove nickel plating from copper components while maintaining the integrity of the copper substrate.
Advanced Safety Protocols
Preparation and Safety Equipment
To ensure safe and efficient removal of nickel plating from copper components, proper preparation and use of safety equipment are paramount.
Protective Gear
Wearing appropriate protective gear is essential to safeguard against chemical exposure and physical injuries. Essential items include:
- Gloves: Chemical-resistant gloves to protect hands from corrosive substances.
- Goggles: Safety goggles to prevent splashes from entering the eyes.
- Protective Clothing: Full-body coverage, including lab coats or aprons, to shield skin from chemicals.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial to manage fumes and vapors from chemical stripping solutions, so ensure the workspace is equipped with exhaust fans to circulate air and remove hazardous fumes. Additionally, fume hoods can be used to contain and extract fumes directly from the work area.
Chemical Stripping Safety Protocols
Chemical stripping involves using powerful solutions that require careful handling to prevent damage to copper and ensure operator safety.
Chemical Selection
Select stripping solutions that are safe for copper, such as:
- Hydrochloric Acid with Inhibitors: This helps prevent damage to the copper substrate while efficiently removing nickel.
- Non-Cyanide Alternatives: Options like meta-nitrobenzene sodium sulfonate are safer for both the user and the environment.
Handling Chemicals
When handling corrosive acids:
- Dilution: Always dilute acids according to recommended ratios to reduce their strength and minimize risks.
- Safety Measures: Use appropriate containers and tools to avoid spills and splashes.
Monitoring the Process
Regularly monitor the stripping process to prevent prolonged contact with chemicals and protect the copper substrate. Ensure effective removal of the nickel layer without compromising the integrity of the copper.
Electrolytic Stripping Safety Protocols
Electrolytic stripping requires specific precautions to manage electrical and chemical risks.
Electrical Safety
Implement appropriate electrical safety measures:
- Insulation: Ensure all electrical connections are properly insulated to prevent shocks.
- Ventilation: Maintain good airflow to prevent inhalation of fumes from electrolytic solutions.
Current Control
Carefully control current densities to prevent pitting and ensure efficient nickel removal without over-stripping.
Frequent Inspection
Frequently inspect the component during the stripping process to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to current and chemical concentrations based on observations.
Post-Stripping Procedures
After successfully removing the nickel plating, follow these steps to ensure the copper is clean and protected.
Cleaning
Thoroughly clean the copper surface by rinsing with water to remove any residual chemicals or metal residues. Apply mild detergent to neutralize and clean the surface.
Passivation
Apply a protective coating or passivation treatment to prevent immediate corrosion and enhance corrosion resistance.
Waste Disposal
Dispose of all waste materials according to environmental regulations by following guidelines for chemical waste and utilizing certified disposal services for safe and compliant waste management.
Best Practices for Safety and Efficiency
Adhering to best practices ensures a safe and efficient nickel removal process.
Training and Experience
Ensure personnel are trained and experienced in handling chemicals and electrical equipment through regular safety training sessions and hands-on experience under supervision.
Emergency Procedures
Establish clear emergency procedures for spills and other hazards, including protocols for immediate response to chemical spills and equipping the workspace with first aid kits.
Environmental Compliance
Conduct regular environmental impact assessments to evaluate waste disposal and emissions, ensuring all practices adhere to local environmental regulations and implementing eco-friendly methods to minimize environmental footprint.
Protecting Copper During Removal
Copper is a widely used metal known for its excellent conductivity and malleability, making it ideal for industries like electronics, plumbing, and metalwork. Its properties, such as high thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ductility, make it perfect for environments where durability and performance are crucial.
Using Inhibitors and Controlled Environments
Inhibitors are chemical agents added to stripping solutions to protect the copper substrate during the nickel removal process. They work by forming a protective layer on the copper surface, preventing the stripping solution from reacting with the copper. For instance, thiocyanate is commonly used in sulfuric acid solutions to inhibit copper corrosion. Maintaining a controlled environment is essential to minimize the risk of damaging the copper during the nickel removal process. Here are key steps to achieve this:
Ventilation
Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated. Use exhaust fans or work in open areas to disperse harmful fumes and vapors produced by chemical strippers. Proper ventilation helps protect both the operator and the integrity of the copper.
Temperature Control
Keep the temperature of the stripping solution within recommended limits. High temperatures can accelerate the chemical reaction, increasing the risk of copper damage. Monitoring and controlling the solution temperature can help maintain a safe and effective removal process.
Limiting Exposure Time
It’s important to limit how long the copper is in contact with the stripping solution. Prolonged exposure can lead to excessive corrosion or weakening of the copper substrate. Follow these guidelines to limit exposure:
- Monitor Progress: Regularly check the progress of the nickel removal to determine the optimal time for immersion.
- Timed Intervals: Remove the copper from the solution at regular intervals to inspect for any signs of damage.
- Use Mild Solutions: Opt for milder chemical solutions when possible, as they are less aggressive and reduce the risk of copper damage.
Post-Removal Cleaning
Once the nickel plating is removed, it’s essential to thoroughly clean the copper to remove any leftover chemicals and prevent corrosion.
Rinsing
Rinse the copper component with plenty of water to wash away any remaining stripping solution. This step is crucial to prevent the chemicals from continuing to react with the copper.
Neutralization
Neutralize any acidic residues by soaking the copper in a mild alkaline solution, such as a baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) solution. This neutralization step ensures that all acidic compounds are rendered inactive.
Drying
Completely dry the copper component after rinsing and neutralization. Use a clean, lint-free cloth to wipe down the surface, and if possible, use compressed air to remove moisture from hard-to-reach areas.
Preservation Techniques
To maintain the integrity and appearance of the copper, consider applying a protective coating. You can use a clear coat or lacquer to shield the copper from oxidation, or apply metal polishing wax to enhance its appearance and provide extra protection.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Protecting the Copper Substrate
Protecting the copper substrate is one of the main challenges when removing nickel plating, as copper is a soft and reactive metal susceptible to damage.
Use of Gentle Chemical Strippers
To address this issue, it’s essential to use gentle chemical strippers specifically designed for nickel removal from copper. Special solutions like Enthone Enstrip NP protect the copper while removing the nickel layer. These inhibitors form a protective film on the copper surface, preventing it from reacting with the stripping chemicals.
Electrolytic Methods with Controlled Conditions
Carefully controlled electrolytic stripping methods can also be used. Adjusting the current densities and using the right electrolytes allows for precise nickel removal without damaging the copper substrate. Regular monitoring during the process is crucial to prevent over-stripping.
Choosing the Right Stripping Method
Selecting the appropriate method for nickel removal depends on several factors, including the shape and delicacy of the copper component.
Chemical Stripping for Complex Shapes
Chemical stripping is often the most effective method for components with complex geometries. It allows for uniform removal of the nickel layer without the need for mechanical abrasion, which can be challenging on intricate shapes. Non-cyanide solutions are safer alternatives to traditional cyanide-based strippers, offering a balance between effectiveness and environmental safety.
Mechanical Methods for Thick Layers
For thicker nickel coatings, mechanical methods such as sanding and grinding can be more suitable. These techniques involve physically abrading the nickel layer, which can be effective but requires careful handling to avoid damaging the copper. Mechanical methods are generally more labor-intensive and are best suited for robust components with simple geometries.
Electrolytic Methods for Precision
Electrolytic stripping offers precision and control, making it an excellent choice for applications where maintaining the integrity of the copper is critical. This method is particularly effective for components that require high precision and minimal substrate damage. The key is to use moderate current densities and continuously monitor the process to ensure optimal results.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
Managing environmental and safety concerns is another significant challenge when removing nickel plating from copper.
Eco-Friendly Practices
Implementing eco-friendly practices is essential to minimize the environmental impact of the stripping process. This includes using non-toxic chemical solutions, ensuring proper ventilation, and wearing protective gear such as gloves and goggles. Non-cyanide solutions and other environmentally friendly alternatives should be considered to reduce the release of harmful substances.
Proper Waste Management
Proper disposal of chemical waste is crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Always follow local regulations and guidelines for hazardous waste disposal. Using certified disposal services ensures that chemical waste is handled safely and in compliance with environmental standards.
Troubleshooting Steps
When encountering issues during the nickel removal process, follow these troubleshooting steps to address common problems:
Identify the Type of Nickel Plating
Determine if the nickel plating is over a copper layer or directly on the substrate. This distinction affects the choice of removal method. For example, if the nickel is directly on the copper, more gentle methods may be required.
Select Appropriate Chemicals
Choose the right chemicals based on the type and thickness of the nickel plating. Hydrochloric acid is effective but requires careful handling. Non-cyanide solutions are safer and should be preferred when possible.
Monitor and Control the Process
Regularly inspect the stripping process to prevent over-stripping and ensure the integrity of the copper substrate. In electrolytic methods, use moderate current densities to avoid pitting and other forms of damage.
Post-Removal Care
After removing the nickel plating, thoroughly clean the copper surface to remove any residual chemicals. Applying a protective coating can prevent immediate corrosion and extend the lifespan of the copper component.
Solutions for Specific Scenarios
Delicate Components
For delicate components, chemical stripping with gentle solutions is recommended to avoid mechanical damage. Electrolytic methods can also be considered for their precision and control.
Complex Shapes
Electrolytic stripping is particularly effective for maintaining the surface integrity of complex shapes. It allows for uniform removal of the nickel layer without the need for mechanical abrasion.
Environmental Concerns
Opt for non-toxic, eco-friendly chemical solutions or mechanical methods when feasible. These alternatives reduce the environmental impact and ensure safer working conditions.
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study: Chemical Stripping in the Electronics Industry
Context and Challenges
A PCB manufacturing company needed to remove nickel from copper traces without harming the delicate circuits.
Solution
To address this challenge, the company employed a chemical stripping method using a sulfuric acid solution combined with organic oxidants. This ensured selective nickel removal while protecting the copper.
Process
- Preparation: Clean the PCBs to remove contaminants.
- Immersion: Submerge the boards in a sulfuric acid bath with organic oxidants.
- Monitoring: Regularly check progress to prevent over-stripping.
- Post-Process Cleaning: Rinse and neutralize the boards to remove residual acids.
Outcome
The method successfully removed the nickel plating without damaging the copper traces, making the PCBs ready for rework or recycling.
Case Study: Electrolytic Stripping in an Industrial Setting
Context and Challenges
An industrial manufacturer needed to remove thick nickel plating from copper busbars used in electrical applications, ensuring the copper’s structural integrity remained intact.
Solution
To achieve this, electrolytic stripping was chosen for its precision and control. The process involved setting up an electrolytic cell with a sulfuric acid electrolyte and applying a reverse current to dissolve the nickel.
Process
- Setup: Connect the copper busbars as the anode in an electrolytic cell.
- Current Control: Regulate the current density to remove nickel without damaging copper.
- Inhibitors: Add inhibitors to the electrolyte to protect the copper.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor and adjust the process as needed.
Outcome
The method was efficient and safe, making it ideal for large-scale industrial use.
Case Study: Mechanical Stripping in Restoration Projects
Context and Challenges
A restoration company needed to remove nickel plating from antique copper fixtures without damaging their intricate details.
Solution
To address this challenge, mechanical stripping using fine abrasive tools was selected. This allowed careful removal of the nickel while preserving the fixture details.
Process
- Initial Assessment: Determine the thickness of the nickel plating.
- Abrasive Selection: Choose fine-grit sandpaper and micro-abrasive pads.
- Manual Stripping: Perform the stripping manually for precise control.
- Detail Preservation: Use smaller abrasive tools for intricate areas.
Outcome
Mechanical stripping effectively removed the nickel while preserving the antique details.
Case Study: Non-Toxic Alternatives in Small-Scale Applications
Context and Challenges
A small-scale artisan workshop needed an environmentally friendly method to remove nickel plating from copper jewelry pieces.
Solution
To achieve this, the workshop used non-toxic stripping solutions containing meta-nitrobenzene sodium sulfonate and ethylenediamine.
Process
- Solution Preparation: Prepare the non-toxic stripping solution.
- Immersion: Submerge the jewelry pieces in the solution, periodically agitating.
- Safety Measures: Conduct the process in a well-ventilated area with protective gear.
- Post-Process Care: Rinse, neutralize, and dry the jewelry pieces.
Outcome
The non-toxic method effectively removed the nickel plating without posing health risks or harming the environment, integrating seamlessly into the workshop’s sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the most effective methods for removing nickel plating from copper?
The most effective methods for removing nickel plating from copper include chemical stripping, electrolytic stripping, and mechanical methods. Chemical stripping involves using solutions like hydrochloric acid or proprietary solutions such as Enthone Enstrip NP to dissolve the nickel without harming the copper. Non-toxic alternatives using ingredients like meta-nitrobenzene sodium sulfonate also provide an environmentally friendly option. Electrolytic stripping reverses the electroplating process with an electrolytic cell, effectively removing thicker coatings through anodic stripping. Mechanical methods, such as using sandpaper or grinding wheels, physically remove the nickel but require careful handling to avoid damaging the copper. Safety measures and environmental considerations are crucial in all methods to ensure safe and responsible handling of materials.
How can I safely remove nickel plating without damaging the copper?
To safely remove nickel plating from copper without damaging the underlying material, you can utilize chemical stripping or electrolytic stripping methods. Chemical stripping involves using solutions such as hydrochloric acid with inhibitors, proprietary solutions like Enthone Enstrip NP, or non-toxic alternatives containing ethylenediamine and glycine. These solutions effectively dissolve the nickel while protecting the copper. Electrolytic stripping involves setting up an electrolytic cell where the nickel-plated copper acts as the anode. Using a controlled reverse current in an electrolyte solution, typically sulfuric acid, the nickel layer is dissolved. It’s crucial to manage current density and use activators and inhibitors to prevent copper damage. Always wear appropriate PPE, ensure proper ventilation, and dispose of waste according to environmental regulations.
What are the safety precautions needed when removing nickel plating?
When removing nickel plating from copper, it’s crucial to follow strict safety precautions to protect yourself and the environment. First, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety goggles, and a respirator to prevent skin and eye contact with chemicals and to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Ensure that your work area is well-ventilated to disperse any toxic gases produced during the process.
Handle acids like nitric, sulfuric, and hydrochloric with extreme caution, using them only in well-ventilated areas and never mixing them unless you have proper knowledge. Always neutralize acids with baking soda after use and thoroughly clean the area with water. Proper disposal of chemical waste is essential to prevent environmental pollution; use designated facilities for hazardous materials.
If using electrolytic stripping methods, ensure electrical safety to avoid shocks and maintain controlled current levels to prevent damage to the copper. For mechanical removal, use protective gear to avoid inhaling dust and take care not to scratch the copper substrate. Following these guidelines will help ensure a safe and effective nickel plating removal process.
How do environmental regulations impact the removal process?
Environmental regulations significantly impact the removal of nickel plating from copper by mandating safe, efficient, and compliant methods. These regulations often require the use of environmentally friendly stripping solutions and proper wastewater treatment to limit toxic substances, such as nickel, in effluents. Compliance involves adhering to standards that prevent the discharge of pollutants into wastewater systems and the atmosphere, promoting the use of innovative, non-toxic chemical solutions. Additionally, facilities must implement best management practices like chemical precipitation and carbon adsorption to treat wastewater, ensuring minimal environmental pollution.
What should I do if the nickel plating is particularly stubborn?
If the nickel plating is particularly stubborn, you should consider using more aggressive yet controlled methods to ensure the underlying copper is not damaged. One effective approach is to utilize specialized chemical strippers like Enthone Enstrip NP or Metalx B-929, which are formulated to remove nickel plating without harming the copper substrate. For more resilient coatings, a diluted hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution (10-20%) can be employed, though it requires careful handling due to its corrosive nature. Additionally, reverse electroplating can be highly effective for thicker nickel layers by dissolving the nickel through an electrolytic process. If you prefer mechanical methods, sanding or grinding can be used, but these require precision to avoid scratching the copper. Always follow safety precautions, such as wearing protective gear and ensuring proper ventilation, to mitigate risks associated with these methods.
Are there cost-effective methods for small-scale nickel removal?
For small-scale nickel removal from copper, several cost-effective methods can be employed:
- Chemical Stripping: Using household acids like vinegar (acetic acid) offers a gentle and economical option for thin nickel layers. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is stronger but should be used with caution due to its corrosive nature. Protective gear and proper ventilation are essential when handling these chemicals.
- Electrolytic Stripping: This method involves reversing the plating current to strip off the nickel. While it requires specialized equipment, it provides precise and controlled results.
- Mechanical Removal: Techniques such as sanding or grinding can physically remove the nickel plating. However, this method is labor-intensive and poses a risk of scratching the copper surface.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, so the choice depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the project.
