When it comes to constructing or maintaining a robust piping system, the choice of flanges plays a critical role in ensuring reliability and efficiency. Two popular types of flanges, slip-on and weld neck, often become the focal point of this decision-making process. But how do you determine which one is right for your application? Each has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and their suitability can vary depending on specific use cases.
Slip-on flanges are known for their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness, making them a go-to option for many industries. However, when it comes to handling high pressure and extreme conditions, weld neck flanges often take the lead due to their superior strength and durability. So, in which scenarios should you opt for slip-on flanges, and when are weld neck flanges the better choice?
This article dives deep into the differences between slip-on and weld neck flanges, providing a comparative analysis to help you make an informed decision. From understanding the structural nuances to evaluating performance in various applications, we will explore everything you need to know. Ready to find out which flange fits your needs best? Let’s get started.
Understanding Pipe Flanges
What are Pipe Flanges?
Pipe flanges are crucial components that connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment, forming a unified piping system. They provide a mechanical connection that can be easily assembled and disassembled, facilitating maintenance, inspection, and modification of the piping system. Flanges are typically used in industrial applications where secure, leak-proof connections are required.
Definition and Types
Pipe flanges are defined as protruding rims or collars used to join sections of pipe or other equipment. The most common types of pipe flanges include slip-on, weld neck, blind, socket weld, threaded, and lap joint flanges, each designed for specific pressure and temperature needs.
Importance in Piping Systems
Pipe flanges play a crucial role in piping systems by ensuring secure connections and providing flexibility for maintenance and inspection. They help in:
- Sealing: Flanges, combined with gaskets and bolts, create a tight seal that prevents leaks.
- Alignment: Flanges allow for precise alignment of pipes and components, ensuring proper flow and system integrity.
- Flexibility: The ability to easily assemble and disassemble flanged connections makes it convenient for maintenance and system modifications.
- Strength: Flanged connections can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Slip-On and Weld Neck Flanges in Pipe Systems
Slip-on and weld neck flanges are among the most commonly used types of flanges in industrial piping systems. Each type has unique features and benefits that make them suitable for specific applications.
Role and Function
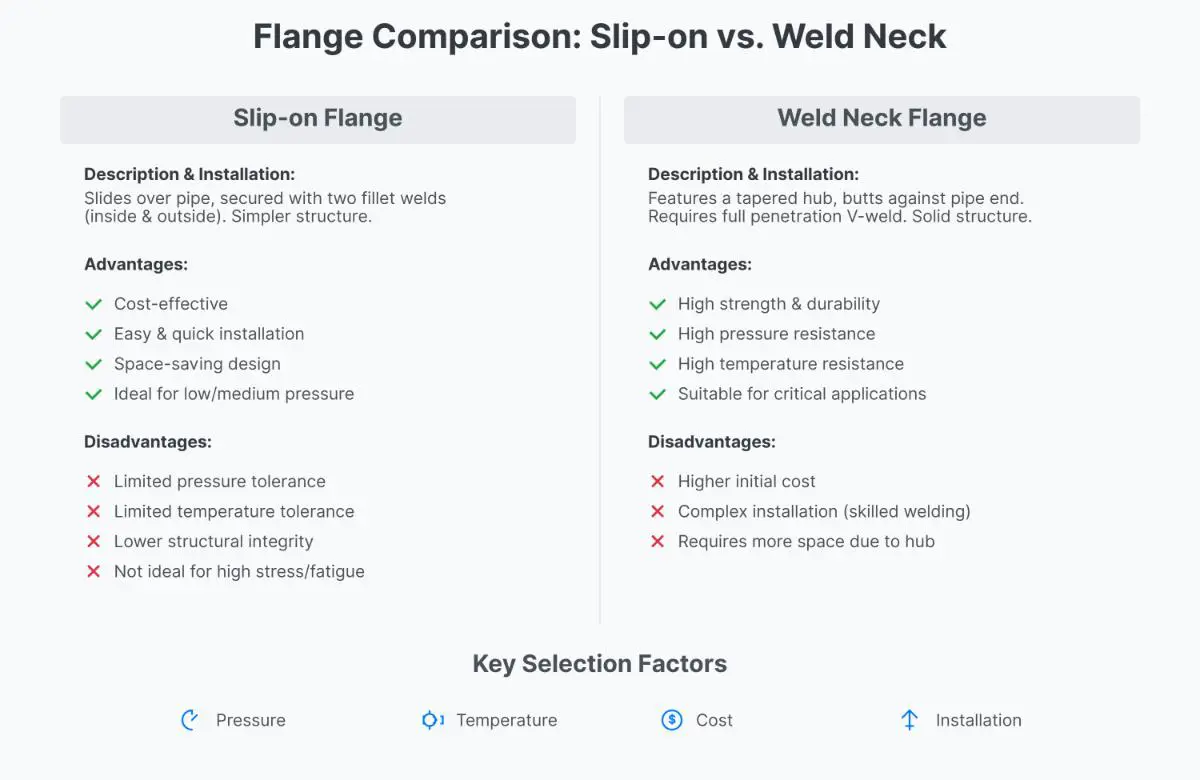
- Slip-On Flanges: Slip-on flanges slide over pipes and are welded on both sides, making them suitable for low-pressure applications due to their easy installation.
- Weld Neck Flanges: Weld neck flanges, with their tapered hub, are butt-welded to pipes, providing strength for high-pressure systems.
Selection Criteria Based on System Requirements
Choosing the right flange depends on factors like pressure, temperature, ease of installation, cost, strength, and maintenance needs.
Understanding the distinctions between slip-on and weld neck flanges, along with their benefits and drawbacks, is vital for selecting the optimal flange type for any piping system.
Comparing Slip-On and Weld Neck Flanges
Overview of Slip-On Flanges
Slip-on flanges are pipe fittings that slide over the end of a pipe and are secured with welds on both the inside and outside.
Definition and Structure
Slip-on flanges are designed with a bore slightly larger than the outer diameter of the pipe, allowing the pipe to be inserted before welding. They generally feature:
- A flat face or raised face for sealing.
- Two fillet welds, one on the outside and one on the inside of the flange.
Key Features and Benefits
- Ease of Installation: Slip-on flanges are easier and quicker to install compared to other types because they do not require precise cutting of the pipe.
- Cost-Effective: They are cost-effective and ideal for low-pressure applications where frequent disassembly is needed.
- Flexibility: Ideal for low-pressure applications where frequent disassembly is required.
Overview of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are designed to be butt-welded to the pipe, providing a smooth transition from the flange to the pipe and reducing stress concentrations.
Definition and Structure
Weld neck flanges have a long, tapered hub that smoothly transitions to the pipe’s wall thickness. This design includes:
- A neck that is welded to the pipe, allowing for full penetration welding.
- A smooth bore that matches the pipe’s internal diameter.
Key Features and Benefits
- Structural Integrity: The tapered hub offers strong structural integrity, making these flanges suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
- Leak Resistance: Full penetration welding reduces the risk of leaks, making them ideal for critical services.
- Durability: Better suited for systems subjected to high stress, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
Comparative Analysis
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
Slip-On Flanges
Advantages:
- Easier and faster installation.
- Cost-effective and ideal for low-pressure applications where frequent disassembly is needed.
Disadvantages:
- Weaker structural integrity due to the fillet welds.
- Higher risk of leaks compared to weld neck flanges.
- Not ideal for high-stress environments.
Weld Neck Flanges
Advantages:
- Superior strength and durability.
- Excellent leak resistance due to full penetration welding.
- Ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Disadvantages:
- They are more expensive due to higher material and labor costs and require skilled welding, leading to longer installation times.
Performance Differences in Specific Applications
Structural Design and Integrity
- Weld Neck Flanges: Feature a tapered hub that ensures a smooth stress transition and uniform load distribution, reducing crack risks in high-pressure systems.
- Slip-On Flanges: Lack a tapered hub and are secured via external fillet welds, resulting in weaker structural integrity and higher susceptibility to stress at connections.
Pressure and Temperature Performance
- Weld Neck: Excel in extreme conditions such as oil and gas pipelines and chemical plants due to robust construction and full-penetration welds.
- Slip-On: Best suited for low to medium pressure applications like HVAC and water supply systems, where the lower structural strength is less critical.
Leak Resistance and Longevity
- Weld Neck: Precision welding creates leak-resistant joints, and the design facilitates radiographic testing to ensure integrity. This extends the service life and enhances corrosion and erosion resistance.
- Slip-On: Higher risk of leaks due to external welds and potential misalignment. They often require more frequent maintenance in demanding environments.
Cost and Installation Complexity
- Weld Neck: Higher material costs and skilled labor increase initial expenses. The installation process is more complex and time-consuming.
- Slip-On: More cost-effective for budget projects, with simpler and quicker installation that does not require internal welding.
Application Suitability
| Parameter | Weld Neck Flanges | Slip-On Flanges |
|---|---|---|
| Industries | Oil/gas, chemical processing, power generation | Water supply, HVAC, low-pressure systems |
| Pressure Range | High (ASME 600+) | Low/Medium (ASME 150-300) |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate |
| Lifespan | 15-30+ years | 10-20 years |
Key Trade-Off Considerations
- Choose Weld Neck: For critical high-pressure and high-temperature systems where safety and durability outweigh cost.
- Opt for Slip-On: In temporary setups or non-critical low-pressure pipelines to reduce capital expenditure.
Pipe Welding and Flange Selection
The choice of flange type for pipe connections is significantly influenced by the welding method used, as different techniques affect the strength, flexibility, and durability of the system.
Flange Types Overview
Slip-On Flanges
Slip-on flanges are designed to slide over the pipe and are secured using two fillet welds. These welds, simpler in nature, join the flange to the pipe and are suitable for low to moderate pressure applications. Slip-on flanges are favored for their ease of installation and flexibility, making them ideal for systems that may require frequent disassembly or where precise cutting of pipes is not critical.
Key Considerations:
- Fillet Welds: Provide adequate strength for low to moderate pressure applications.
- Ease of Installation: Simplifies the welding process, reducing labor costs and installation time.
- Flexibility: Suitable for systems needing frequent disassembly.
Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges feature a long tapered hub and are attached using a full penetration butt weld. This welding method creates a seamless and strong connection, enhancing the structural integrity of the piping system. Weld neck flanges are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to their superior performance and durability.
Key Considerations:
- Butt Welds: Create a seamless, high-strength connection that reduces stress concentrations.
- Strength and Durability: Suitable for environments with high stress, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
- Leak Resistance: Minimizes the risk of leaks, ideal for critical applications.
Installation Considerations
- Slip-On Flanges: Pipes must be cut to the proper length, allowing the flange to slide over before being secured with fillet welds. This method is straightforward and cost-effective.
- Weld Neck Flanges: Require precise cutting and beveling of pipes to match the flange’s neck for a full penetration butt weld. This process demands skilled labor and careful alignment to ensure a seamless connection.
Considerations for Specific Applications
- Structural Integrity:
- Slip-On Flanges: Best for low to moderate pressure applications due to simpler welds.
- Weld Neck Flanges: Preferred for high-pressure systems, offering superior strength.
- Cost and Installation Complexity:
- Slip-On Flanges: More cost-effective with easier installation, ideal for budget-conscious projects.
- Weld Neck Flanges: Higher initial cost due to complex welding, providing long-term reliability.
- Leak Resistance and Maintenance:
- Slip-On Flanges: Higher risk of leaks, requiring more frequent maintenance.
- Weld Neck Flanges: Superior leak resistance, reducing maintenance needs.
Standards Compliance
Standards compliance is crucial for selecting and using pipe flanges in industrial applications, ensuring they meet strict criteria for safety and performance. This is particularly important in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment, where the integrity of piping systems is paramount.
Governing Standards
ASME Standards
ASME standards, like ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47, provide specifications for flanges used in high-pressure settings. These guidelines cover dimensions, materials, pressure ratings, and testing procedures, ensuring flanges can withstand specified pressure and temperature conditions without failure.
ANSI Standards
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) complements ASME standards by focusing on compatibility and interoperability within piping systems. ANSI standards promote uniformity across various components, facilitating seamless integration and reducing the risk of operational issues.
Compliance Requirements
Compliance involves adhering to specific material and design specifications while ensuring rigorous testing and certification. Slip-on and weld neck flanges must meet material requirements that resist environmental stressors such as corrosion and mechanical stress. Design specifications ensure that each flange type is suited to its intended pressure range, with weld neck flanges typically favored for higher-pressure environments due to their robust design. Testing, including hydrostatic and radiographic tests, verifies performance criteria, while certification confirms safety for critical applications.
Comparative Standards Implications
Slip-On Flanges
Slip-on flanges are commonly used in low-pressure applications and must comply with standards to ensure they provide adequate sealing and support. Their design allows for easier installation, but compliance guarantees system integrity even in less demanding environments.
Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges, suited for high-pressure and high-stress applications, face stricter compliance requirements. Their design and material specifications are more rigorous, as they must provide superior leak resistance and structural integrity, ensuring they can handle extreme conditions without risk of failure.
Selection Based on Standards
When choosing between slip-on and weld neck flanges, engineers must consider the system’s pressure and temperature needs, along with material properties and certifications, to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Installation and Cost Considerations
Installing weld neck flanges is more complex than slip-on flanges because they need a full penetration butt weld. This method requires precise alignment to ensure a seamless connection, and the tapered hub design helps distribute stress effectively, making weld neck flanges suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
The welding process for weld neck flanges demands skilled labor to perform precise alignment and welding, typically requiring advanced inspection techniques like radiographic testing to ensure weld integrity. Conversely, slip-on flanges require two fillet welds, which, while less skill-intensive, increase the welding time and inspection efforts. Slip-on flanges slide over the pipe and are secured with two fillet welds—one on the inner side and another on the outer side of the flange. This simpler method makes slip-on flanges more suitable for low-pressure applications where rapid assembly is beneficial.
Weld neck flanges generally have higher initial costs due to their complex design and the quality of materials required. Their robust construction and welding complexity contribute to the higher price, making them a significant investment at the outset. Slip-on flanges are typically less expensive initially. Their straightforward design and simpler welding requirements result in lower purchase costs, appealing to projects with budget constraints.
Weld neck flanges are strong and durable, which means they need less maintenance over time. Their ability to withstand higher pressures and temperatures makes them a reliable choice for critical applications. Slip-on flanges are cheaper at first but might cost more in the long run. They are less resistant to fatigue and more likely to leak, which may necessitate frequent maintenance and inspections, especially in demanding environments.
Choosing between weld neck and slip-on flanges involves weighing the upfront costs against the long-term benefits and maintenance requirements. Weld neck flanges provide excellent strength and fatigue life, making them ideal for environments with significant pressure variations and stresses. Meanwhile, slip-on flanges, with their lower strength and fatigue resistance, are more suited for less critical applications.
Application Areas for Slip-On and Weld Neck Flanges
Industry Use Cases
Choosing between slip-on and weld neck flanges depends on the specific needs of each industry, as each type offers distinct advantages for different applications.
Oil and Gas Applications
In the oil and gas sector, weld neck flanges are preferred for their high strength and ability to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for upstream and downstream operations, such as drilling rigs, production platforms, and refineries. The complete weld connection ensures strong, leak-proof joints, reducing the risk of leaks and failures.
Slip-on flanges, while less common in high-pressure scenarios, may be used in auxiliary systems within oil and gas facilities, such as low-pressure water and air lines. Their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness make them suitable for non-critical applications where frequent disassembly might be required.
Water Treatment Systems
In water treatment plants, weld neck flanges are ideal for high-pressure pipelines that transport treated water or chemicals. Their durability and leak resistance are crucial in ensuring the integrity of the system, especially in areas dealing with high flow rates and pressures.
Slip-on flanges are widely used in water treatment systems for low to medium pressure applications, such as distribution lines and connections to tanks and pumps. The simplicity of installation and lower initial cost make slip-on flanges a practical choice for these applications.
Chemical Processing Environments
In chemical facilities, weld neck flanges are essential for handling aggressive chemicals and high-pressure steam due to their superior strength and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for reactors, heat exchangers, and hazardous fluid pipelines.
In chemical plants, slip-on flanges are typically utilized in non-critical systems such as cooling water lines and low-pressure chemical distribution networks. Their lower cost and ease of installation are advantageous in these less demanding applications.
Selecting the Right Flange for Your Application
Choosing between slip-on and weld neck flanges depends on several factors, including pressure requirements, temperature conditions, and the need for maintenance and disassembly.
Pressure and Temperature Considerations
Weld neck flanges are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications where structural integrity and leak resistance are paramount. They are the preferred choice in environments with fluctuating temperatures and pressures, ensuring long-term reliability and safety.
Slip-on flanges are ideal for low to medium pressure systems where ease of installation and cost savings are more critical than maximum strength. They perform well in stable temperature conditions and are used in applications where frequent maintenance or disassembly is expected.
Maintenance and Longevity
Weld neck flanges are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements, offering extended service life in demanding environments. Their robust construction minimizes the need for frequent inspections and repairs.
Although slip-on flanges are budget-friendly at first, they might need more regular maintenance because of a higher risk of leaks and fatigue. They are suitable for applications where ease of replacement and lower initial investment are prioritized.
Application Guidance and Standards Compliance
When selecting flanges, it is essential to adhere to industry standards to ensure safety and performance. Both ASME and API standards provide guidelines on flange dimensions, materials, and pressure ratings.
Weld neck flanges must comply with stringent standards due to their use in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Ensuring compliance with ASME B16.5 and API specifications guarantees the flanges can withstand the demanding conditions.
Slip-on flanges also need to meet industry standards, though the requirements are less rigorous compared to weld neck flanges. Compliance with relevant ASME and ANSI standards ensures they provide adequate sealing and support in lower pressure applications.
Interactive Tools and Resources
Selecting the right flange type for your piping system is easier with interactive tools and resources designed for engineers and technicians. These tools streamline the decision-making process and enhance accuracy and efficiency.
Online calculators help determine the most suitable flange type based on parameters like pressure, temperature, and pipe dimensions. These calculators allow users to input data points and receive tailored recommendations, ensuring compatibility with operational demands.
Advanced piping design software provides comprehensive solutions for flange selection, integrating simulations and analyses to optimize systems. These programs allow users to create detailed 3D models of piping systems, ensuring precise placement and integration of flanges. Stress analysis tools predict how different flange types will behave under various loads, aiding in the selection of durable and strong components. Compatibility checks ensure all components, including flanges, meet relevant standards and specifications, reducing the risk of system failure.
Industry-specific resources such as technical manuals and guides from ASME and API provide detailed information on flange types, material specifications, and installation procedures. Reviewing case studies can offer insights into the practical application of slip-on and weld neck flanges in real-world scenarios.
Interactive selection tools further aid in choosing the best flange type for specific applications. Decision trees guide users through questions about system requirements to suggest appropriate flange types. Comparison charts allow side-by-side evaluations of key attributes like cost, installation complexity, and performance under specific conditions.
Mobile applications provide on-the-go access to flange selection tools, making it easier for field engineers and technicians to make informed decisions. Flange finder apps offer quick reference guides and calculators for immediate project needs, while installation guides ensure correct and efficient installation, even in remote locations. By utilizing these interactive tools and resources, engineers and technicians can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of flange selection, ensuring that their piping systems are both reliable and cost-effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the advantages and disadvantages of slip-on flanges compared to weld neck flanges?
Slip-on flanges and weld neck flanges each have distinct advantages and disadvantages that influence their suitability for different applications. Slip-on flanges are cost-effective and straightforward to install, as they slide over the pipe and are secured with fillet welds. This makes them ideal for low to medium pressure applications where ease of installation and space-saving are priorities. However, they offer limited pressure and temperature tolerance due to their simpler weld structure, which results in less structural integrity.
In contrast, weld neck flanges provide high strength and pressure resistance, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. They feature a solid hub and require full penetration welds, which contribute to their superior durability and reliability. The main drawbacks of weld neck flanges are their higher cost and the complexity of installation, which demands skilled welding techniques. The choice between these flanges depends on system requirements, including pressure, temperature, cost, and installation considerations.
In which applications are slip-on flanges preferred over weld neck flanges?
Slip-on flanges are preferred over weld neck flanges in applications where lower pressure and simpler installation are key considerations. Specifically, they are well-suited for low to medium pressure systems such as water supply networks, HVAC systems, and general-purpose pipelines. Their straightforward design, which allows them to slip over the pipe and be welded both inside and outside, makes them easier and quicker to install compared to weld neck flanges. This ease of installation can be particularly advantageous in projects where time and labor costs are critical factors. Additionally, slip-on flanges are generally more cost-effective, making them an attractive option for budget-constrained projects without compromising essential functionality. However, it is important to note that slip-on flanges may not provide the same level of structural integrity and resistance to high pressure and thermal stress as weld neck flanges, which are preferred for more demanding applications.
How does pipe welding impact flange selection?
Pipe welding significantly impacts the selection of flanges, particularly when choosing between Slip-On Flanges and Weld Neck Flanges. The primary consideration is the strength and durability required for the application. Weld Neck Flanges are preferred in high-pressure and critical situations because they offer robust weld joints that effectively distribute stress and provide reinforcement through their tapered hub. This makes them suitable for applications where strong, durable connections are essential.
On the other hand, Slip-On Flanges are easier and less costly to install but provide lower strength, making them suitable for lower-pressure applications where ease of installation and cost are prioritized over strength. The welding process itself dictates the compatibility of flange materials with the pipe, ensuring that both components can be securely joined. In summary, the choice of flange in pipe welding depends on pressure requirements, material compatibility, and the specific demands of the piping system, emphasizing the need for strong connections in demanding environments.
What standards should be considered when selecting flanges?
When selecting flanges, particularly when comparing Slip-On Flanges and Weld Neck Flanges, adherence to specific standards is crucial to ensure safety, performance, and compatibility. The primary standards to consider are ANSI/ASME B16.5 and ANSI/ASME B16.47, which cover the dimensions, pressure classes, and tolerances for flanges. These standards ensure interchangeability and are essential for both slip-on and weld neck flanges. They specify flange face types and thickness based on pressure class, which influences the selection for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
Additionally, pressure and temperature ratings, often indicated by classes like 150, 300, and 600, dictate the maximum allowable working conditions. Weld Neck Flanges are generally preferred for high-pressure environments due to their robust design, while Slip-On Flanges are suitable for lower pressure scenarios. Material standards, such as ASTM A105 for carbon steel and ASTM A182 for stainless steel, also play a significant role, ensuring the flange material aligns with the fluid type and system conditions. These standards collectively guide the appropriate flange choice, ensuring system integrity and safety.
Are there interactive tools available for flange selection?
Yes, there are several interactive tools available for flange selection that can assist engineers and technicians in choosing the appropriate flange types, such as Slip-On and Weld Neck Flanges. These tools offer detailed calculations and component recommendations based on standards and application requirements. Notable examples include KRAJ SELEKTOR, which calculates flange-bolt connections according to EN PN and ASME standards, and Enerpac’s Flange Tool Guru, which guides users through tool selection based on flange specifications. Additionally, HYTORC’s Flange Pattern Calculator provides torque values and bolting patterns, while GF Piping Systems’ Perfect Flange Connection Tool calculates bolt size and tightening torque. These tools enhance design accuracy and installation efficiency, making them invaluable for optimizing flange connections in various applications.
