In the intricate world of piping systems, the selection of the right flange type can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of operations. Two common yet often misunderstood components are spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges. While both play critical roles in pipeline isolation and flow control, their designs and applications differ in ways that can influence your choice. What sets these two apart? How do their unique features and functionalities serve specific industrial needs? Join us as we delve into the distinctions between spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges, exploring their designs, operational advantages, and the scenarios where each excels. Are you ready to discover which flange is the perfect fit for your system? Let’s get started.
Introduction
Flanges are essential components in piping systems, connecting pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment. They provide easy access for cleaning, inspection, and modification, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the piping system. Various types of flanges are available, each designed to meet specific needs and operational conditions. Among these, spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges are notable for their specialized roles in flow control and pipeline isolation.
Importance of Choosing the Correct Flange Type
Selecting the appropriate flange type is crucial for ensuring the efficiency, safety, and longevity of a piping system. This choice affects several factors, including:
- Operational Efficiency: The right flange ensures smooth operation, reducing the likelihood of leaks and other issues that can disrupt flow and pressure.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Flanges that facilitate easy switching between open and closed states can significantly reduce downtime during maintenance and inspections.
- Safety: Proper flange selection is vital for maintaining safe operations, especially in high-pressure or hazardous environments where leaks or failures can have serious consequences.
- Cost-effectiveness: Using the correct flange type can help avoid unnecessary expenses related to repairs, replacements, and operational disruptions.
Comparative Analysis
Understanding the differences between various flange types, such as spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges, is essential for making informed decisions. These flanges, while serving similar functions, have distinct designs and operational characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. A comparative analysis can help in selecting the right flange based on factors like:
- Design and Functionality: The structural differences between spectacle blind and spacer blind flanges influence their suitability for specific tasks, such as isolating sections of a pipeline or maintaining precise spacing.
- Application: Different industries and operational environments may have unique requirements, making one type of flange more appropriate than another.
- Material and Pressure Ratings: The choice of material and the flange’s ability to withstand specific pressure and temperature conditions are critical considerations.
Key Considerations for Selection
When selecting a flange type, it is important to evaluate the following aspects:
- System Requirements: Evaluate the specific needs of the piping system, including pressure, temperature, and flow control.
- Operational Conditions: Consider the operational environment, such as exposure to corrosive substances, high temperatures, or high pressure.
- Maintenance Practices: Determine the ease of maintenance and the need for quick isolation or flow control during inspections and repairs.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the selected flange meets relevant industry standards and regulations, such as ASME, ANSI, and API.
Definition and Design of Spectacle Blind Flanges
Overview of Spectacle Blind Flange
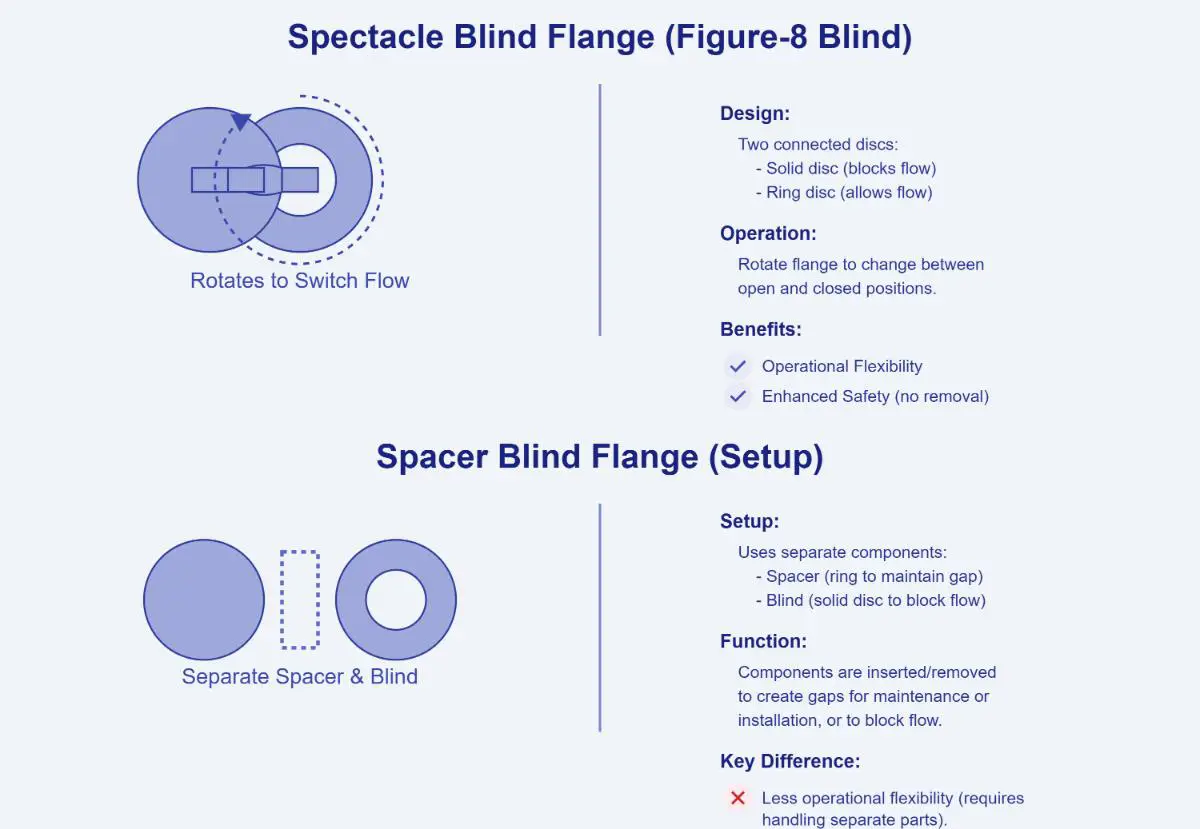
A spectacle blind flange is a specialized component used in pipeline systems to control and isolate fluid flow. Its design resembles a pair of spectacles, consisting of two interconnected discs—one solid and the other with an open hole—joined by a central web or bar. This unique figure-8 structure allows the flange to perform dual functions by providing reliable methods for either isolating or allowing flow within a pipeline system.
Function and Design
Structure and Components
The spectacle blind flange is composed of the following elements:
- Solid Disc (Blind Side): This part of the flange is used to completely block the flow of fluid within the pipeline.
- Open Disc (Spacer Side): This part has an open hole that allows the fluid to pass through when aligned with the pipeline.
- Connecting Web: The central web connects the solid and open discs, allowing for easy rotation and switching between flow states.
Dual Operation
The solid disc blocks the fluid flow when aligned with the pipeline, crucial for maintenance or safety isolation, while the open disc allows normal flow when aligned, making it easy to switch between states.
Common Applications in Piping Systems
Spectacle blind flanges are widely used across various industries due to their functionality and reliability. Some common applications include:
- In the oil and gas industry, they isolate high-pressure pipelines during maintenance.
- Chemical processing systems use them for easy inspection and cleaning.
- Power plants rely on them for safe turbine shutdowns.
- Water treatment facilities use them to prevent contamination during repairs.
Importance in Pipeline Isolation and Flow Control
Spectacle blind flanges enhance safety by reliably isolating pipeline sections, ensuring maintenance personnel safety. Their quick-switch capability minimizes downtime, making them versatile for various applications. Designed to meet industry standards like ASME B16.48, they withstand different pressures and temperatures, making them essential for modern piping systems.
Definition and Design of Spacer Blind Flanges
Spacer blind flanges are essential components in piping systems, designed to separate pipe sections without interrupting fluid flow.
Function and Design
Structure and Components
Spacer blind flanges, often called pipe spacers or blind flanges, consist of a flat, ring-shaped plate that fits between two standard flanges. Their thickness matches that of a standard flange gasket, ensuring compatibility. These flanges are made from durable materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys to withstand high pressure.
Operational Mechanism
Spacer blind flanges maintain the necessary gap between flanges without restricting fluid flow, making them ideal for continuous operation and easy maintenance.
Common Applications in Piping Systems
Spacer blind flanges are widely used in various industries because they are versatile and easy to use. Typical applications include:
- Power Plants: They are used in high-pressure systems to maintain the flow while allowing for periodic maintenance and inspection.
- Refineries: Spacer blind flanges facilitate the separation of pipeline sections, ensuring uninterrupted operations during maintenance.
- Chemical Processing: These flanges are essential for systems requiring frequent adjustments and isolation without disrupting the flow.
Role in Flow Allowance and Isolation
Spacer blind flanges play a crucial role in maintaining flow allowance while providing a simple yet effective means of isolating sections of a pipeline. This capability is vital in environments where continuous operation is necessary, but periodic maintenance is required.
- Flow Allowance: By maintaining the gap between flanges, these components ensure that the fluid flow remains uninterrupted.
- Isolation: Spacer blind flanges allow for easy isolation of pipeline sections without halting the entire system, which is beneficial during maintenance and repairs.
Compliance and Standards
Spacer blind flanges adhere to industry standards such as ASME B16.48, ensuring their reliability and safety. These standards cover dimensions, specifications, and pressure classes, making spacer blind flanges suitable for various industrial applications.
Structural and Operational Differences
Structural Differences
Spectacle Blind Flanges
Spectacle blind flanges have a distinctive figure-8 shape, consisting of two discs connected by a small metal section. One disc is a solid plate designed to completely block the flow within the pipeline, while the other is a ring-shaped plate that allows fluid to pass through. This configuration enables easy switching between open and closed states. The thickness of the discs aligns with the pressure class of the flange, ensuring proper sealing and mechanical strength. Typically, these flanges are made from robust materials like carbon steel or stainless steel, adhering to standards such as ASME B16.48. The design ensures the sealing surface diameter is slightly larger than the raised face of the mating flange to prevent bolt interference during assembly.
Spacer Blind Flanges
Spacer blind flanges, also known as spacer rings, have a simpler design compared to spectacle blind flanges. They consist of a flat, ring-shaped component that maintains a fixed space between two flanges without obstructing the flow. Unlike spectacle blinds, spacer flanges do not include a solid disc and are not dual-disc designs. They are generally made from the same durable materials as spectacle blinds, such as carbon steel and stainless steel, and comply with ASME B16.48 standards. The thickness of spacer flanges is typically equivalent to or slightly greater than that of a standard flange gasket, facilitating easy installation and removal.
Operational Differences
Flow Control and Isolation with Spectacle Blind Flanges
Spectacle blind flanges are mainly used for isolating flow during maintenance or testing. By rotating the flange, operators can position either the solid disc or the ring side between the flanges, allowing for complete isolation of the pipeline or permitting flow. This dual functionality provides a reliable physical barrier that can be visually verified, making spectacle blinds a preferred choice for permanent or semi-permanent isolation solutions in various piping systems.
Spacer Flanges in Maintaining Flow
Spacer blind flanges are used to keep a fixed space between flanges without blocking the flow. They are ideal for applications requiring frequent removal and reinstallation of components without disrupting the pipeline’s operation. Spacers provide the necessary flexibility in piping systems, accommodating equipment such as flow meters or valves, and offering room for maintenance activities without halting the flow. Unlike spectacle blinds, spacer flanges do not function as isolation devices but rather as simple spacers.
Applications and Use Cases
| Aspect | Spectacle Blind Flange | Spacer Blind Flange |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Flow isolation (on/off) | Maintain spacing without flow restriction |
| Design | Two discs connected by a metal piece (solid + ring) | Single flat ring-shaped flange |
| Installation | Rotated between open/close positions | Installed as a fixed spacer between flanges |
| Common Uses | Maintenance isolation in power plants, refineries | Systems requiring frequent access or equipment spacing |
| Pressure Class & Size | Wide range, from NPS 1/2 to 24, various pressure classes | Similar range, matching flange specifications |
| Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel, etc. | Carbon steel, stainless steel, etc. |
| Standards Compliance | ASME B16.48 | ASME B16.48 |
| Visibility & Safety | Solid disc provides positive visual confirmation of closure | Less visible, usually marked for identification |
Understanding these structural and operational distinctions aids in selecting the appropriate flange type for specific industrial applications. Spectacle blinds focus on isolation and safety, while spacer blinds ensure spacing and maintain flow continuity.
Material and Pressure Rating Comparisons
Material Comparisons
Common Materials Used
Spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges are generally made from strong, durable materials that resist corrosion. The most commonly used materials include:
- Carbon Steel: Known for its strength and affordability, carbon steel is widely used in industrial applications. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for both spectacle and spacer blind flanges.
- Stainless Steel: Offering superior corrosion resistance, stainless steel is ideal for environments where the piping system is exposed to corrosive substances or high temperatures. Its durability makes it a preferred choice for both types of flanges.
- Alloys: Various alloy compositions are used to enhance specific properties such as resistance to wear, corrosion, and extreme temperatures. These materials are selected based on the specific requirements of the piping system.
Impact of Material Selection on Performance
The choice of material significantly influences the performance and longevity of spectacle and spacer blind flanges. For instance:
- Strength and Durability: Carbon steel and stainless steel provide the necessary mechanical strength to withstand high pressures and mechanical stresses. This is crucial for ensuring the reliability of the flanges in demanding applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel and certain alloys are preferred in environments where corrosion is a concern. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the flanges over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Temperature Resistance: Materials like stainless steel and high-temperature alloys can withstand extreme temperatures, making them suitable for applications involving high heat.
Pressure Rating Comparisons
Pressure Ratings of Spectacle Blind Flanges
Spectacle blind flanges are designed to handle a wide range of pressure classes, which are defined under standards such as ASME B16.48. The pressure ratings for spectacle blind flanges typically include:
- Class 150
- Class 300
- Class 600
- Class 900
- Class 1500
- Class 2500
These classes show the highest pressure the flange can handle at specific temperatures. The high-pressure ratings make spectacle blind flanges suitable for applications where complete isolation of the pipeline is required, especially in high-pressure or hazardous environments.
Pressure Ratings of Spacer Blind Flanges
Spacer blind flanges, also known as spacer rings, are designed to match the pressure ratings of the standard flanges they complement. Even though spacer blind flanges don’t isolate flow, they must meet the same pressure class standards for compatibility and safety. The pressure ratings for spacer blind flanges include:
- Class 150
- Class 300
- Class 600
- Class 900
- Class 1500
- Class 2500
Since spacer blind flanges do not block fluid flow, their pressure role is less critical compared to spectacle blinds. They are primarily used to maintain spacing between flanges without being subjected to differential pressure.
Functional Differences Affecting Material and Pressure Requirements
| Feature | Spectacle Blind Flanges | Spacer Blind Flanges (Spacer Rings) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Can block or allow flow by rotating the flange | Maintain space between flanges without flow restriction |
| Design | Two connected discs – one solid, one ring-shaped (figure-8 design) | Simple flat ring matching flange thickness |
| Material Requirements | High-grade carbon or stainless steel, meeting ASME B16.48 standards for full pressure isolation | Durable carbon or stainless steel, compliant with ASME B16.48 but less stringent due to non-isolation role |
| Pressure Ratings | Wide range including Class 150 to 2500, designed to withstand full line pressure when closed | Pressure rating consistent with pipeline class but no isolation pressure requirements |
| Applications | Isolation during maintenance, testing, or emergencies in hazardous or high-pressure pipelines | Maintain space for maintenance, system adjustments, or installing equipment without restricting flow |
The functional differences between spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges dictate their respective material and pressure requirements. Spectacle blind flanges, being dual-purpose isolation devices, require robust materials and high-pressure ratings to safely block flow under demanding conditions. Spacer blind flanges, serving a non-isolating role, have simpler design requirements and do not need to withstand isolation pressures, focusing instead on maintaining the integrity of the spacing within the pipeline system.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Spectacle blind flanges are widely used in various industries for pipeline isolation and flow control. Their versatile design allows easy switching between blocking and allowing fluid flow, making them critical in the oil and gas sector for isolating pipeline sections during maintenance, testing, and repair. They ensure safety by preventing the flow of hazardous substances, thereby protecting workers and equipment, particularly in high-pressure environments where reliable isolation is essential.
In the chemical and petrochemical industries, spectacle blind flanges enable safe isolation of pipeline sections during cleaning, inspection, and maintenance. They provide a clear barrier, essential for safely handling reactive or hazardous chemicals.
Power plants, especially those with steam lines, rely on spectacle blind flanges to isolate sections of piping systems during maintenance. With high-temperature tolerance and robust construction, these flanges are ideal for the tough conditions in power generation facilities.
Water treatment facilities use spectacle blind flanges to isolate sections of the piping system during maintenance and repairs, ensuring water quality is maintained and contamination is prevented. The ease of switching between open and closed states reduces downtime and operational disruptions.
Though not as versatile as spectacle blind flanges, spacer blind flanges are beneficial in specific applications. These flanges are primarily used to maintain spacing between flanges without obstructing fluid flow.
In power plants, spacer blind flanges help maintain the necessary spacing in high-pressure systems, allowing for periodic maintenance and inspection without interrupting the flow of steam or other fluids. This ensures continuous operation and reduces the need for complete system shutdowns.
Refineries utilize spacer blind flanges to separate sections of piping systems, facilitating maintenance and adjustments while keeping the flow uninterrupted. This is particularly important in processes that require constant operation to maintain efficiency and safety.
Chemical processing facilities depend on spacer blind flanges for systems requiring frequent isolation and reconfiguration. They allow easy insertion and removal of equipment such as flow meters or valves, providing flexibility in the system’s operation.
In manufacturing, both spectacle and spacer blind flanges are used to manage the flow of various fluids and gases. Spectacle blinds are preferred for applications requiring frequent isolation for maintenance and safety checks, while spacer blinds are used in systems where maintaining a fixed distance between components is necessary.
In the oil and gas industry, spectacle blind flanges provide reliable isolation in high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Spacer blind flanges are used where maintaining spacing without flow restriction is critical, such as in the installation of instrumentation or control devices.
In construction, especially in large-scale projects involving complex piping systems, spectacle blind flanges ensure sections of the pipeline can be safely isolated during various phases of construction and testing. Spacer blind flanges help maintain the structural integrity of the piping system by providing necessary spacing.
Safety is a primary concern when using spectacle blind flanges. Their ability to provide a clear visual indication of whether a section of the pipeline is open or closed enhances safety during maintenance and operation. Adhering to industry standards such as ASME B16.48 ensures that these flanges perform reliably under specified pressure and temperature conditions.
While spacer blind flanges do not isolate flow, their role in maintaining spacing is crucial for the safe operation of piping systems. Ensuring they are made from materials that can withstand the operational environment and pressure ratings of the system is essential for maintaining overall system integrity and safety.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Design and Functional Differences Impacting Installation
Spectacle Blind Flanges
Spectacle blind flanges feature a figure-8 design with two connected discs: one solid and one ring-shaped. These flanges are permanently installed between two pipe flanges and can be rotated to switch between blocking and allowing flow. Their dual-disc construction means they are heavier and require precise alignment during installation. This ensures the correct side faces the flow, making the process more labor-intensive but effective for flow control.
Spacer Blind Flanges
Spacer blind flanges, or spacer rings, have a simpler design. Unlike spectacle blinds, they are flat and ring-shaped, designed to maintain a fixed gap between two flanges without restricting flow. Their lightweight and straightforward shape make them easier to install, especially in large diameter pipes. The installation process involves inserting the spacer ring between the flanges to create the necessary space for maintenance or pipeline adjustments. Spacer blind flanges do not provide flow isolation but facilitate system configuration flexibility.
Maintenance Considerations
Spectacle Blind Flanges
Spectacle blind flanges are used for complete isolation during maintenance or testing, allowing quick switching between open and closed states without disassembling the pipeline. This ensures safety during maintenance operations. However, installing and removing them can be labor-intensive due to their weight and alignment needs. They require periodic inspection for wear and corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
Spacer Blind Flanges
Spacer blind flanges are designed for systems where frequent maintenance or adjustments occur, but full flow isolation is not necessary. They reduce the weight load on flange connections compared to spectacle blinds, which is advantageous in large pipe sizes. Spacer blind flanges are easier to handle and replace since they are simple rings without a blocking disc. Maintenance primarily involves checking for wear and ensuring the spacer maintains proper spacing to avoid flange misalignment.
Application and Safety Implications
Spectacle blind flanges are preferred in high-pressure or hazardous systems where complete isolation is crucial for safety. They conform to ASME B16.48 standards, ensuring reliable performance under specified pressure and temperature conditions. Spectacle blind flanges reduce the risk of accidental flow during maintenance, providing a robust solution for blocking flow.
Spacer blind flanges are suitable for pipelines that require spacing and ease of access but do not need to completely block flow. They offer convenience but no assurance of isolation, making them less suitable for critical safety applications. However, they facilitate maintenance and adjustments in systems where continuous operation is essential, without the need for full flow isolation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What is the difference between spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges?
Spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges serve distinct purposes in piping systems, differing primarily in design and functionality.
Spectacle blind flanges, also known as figure-8 blinds, consist of two connected metal discs—one solid for blocking flow and one with a hole for allowing flow. This design allows easy switching between blocking and permitting flow by rotating the flange without removing it, providing operational flexibility and enhancing safety during maintenance.
Spacer blind flanges, on the other hand, typically refer to setups where separate spacers and blinds are used in conjunction to create gaps for maintenance or installation. Unlike spectacle blinds, they do not combine blocking and spacing functions into one unit, resulting in less operational flexibility.
How do spectacle blind flanges function in pipeline isolation?
Spectacle blind flanges function in pipeline isolation by providing a physical barrier that can easily switch between allowing and preventing flow in a piping system. They consist of two metal discs connected by a small section, resembling a figure-8. One disc is a solid plate (blind) and the other is a ring (spacer). When the solid plate is positioned to face the pipeline, it blocks the flow, isolating the section of the pipeline. Conversely, when the ring is aligned with the pipe, it allows flow to continue, essentially acting as part of the pipeline during normal operations.
The design allows for quick and easy changeover between the open and closed positions by rotating the spectacle blind without needing to remove it from the flange. This minimizes downtime during maintenance and operational changes. Spectacle blind flanges are particularly useful in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and petrochemicals where they enhance safety and cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for separate shut-off valves and simplifying maintenance procedures.
What materials are used to make spectacle and spacer blind flanges?
Spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges are essential components in piping systems, primarily used for isolation and maintenance. These flanges are manufactured from various materials to meet specific application requirements such as pressure, temperature, and the nature of the conveyed fluid.
Common materials used for both spectacle and spacer blind flanges include:
- Carbon Steel: Known for its strength and durability, carbon steel is cost-effective and capable of withstanding high pressures and temperatures. It is widely used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power plants.
- Stainless Steel: Offering excellent corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel is suitable for environments where corrosion and heat resistance are critical, such as chemical processing and food industries. Common grades include ASTM A182.
- Alloy Steel: Incorporating elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, alloy steel enhances strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Specialty materials may also be used for specific applications, including super alloys like Inconel and non-ferrous metals like aluminum and brass.
In what applications are spectacle blind flanges preferred over spacer blind flanges?
Spectacle blind flanges are preferred over spacer blind flanges in applications where versatility, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness are critical. These flanges feature a figure-8 design that combines a solid disk and a ring spacer, allowing for quick rotation between isolation and operational modes without the need for complete removal. This reduces downtime and simplifies maintenance, making them ideal for environments where frequent maintenance or testing is required.
Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation commonly use spectacle blind flanges due to their ability to handle high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. They offer a reliable solution for pipeline isolation during maintenance, testing, and repairs, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Additionally, spectacle blind flanges are more cost-effective as they eliminate the need for separate shut-off valves, saving space and reducing installation costs.
In contrast, spacer blind flanges are typically used for permanent separation and do not offer the same level of versatility, making them less suitable for applications requiring frequent adjustments or high-pressure conditions.
What are the environmental considerations when selecting flange materials?
When selecting flange materials for spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges, environmental considerations are crucial. These considerations include the sustainability of the materials, their environmental impact, and the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
Firstly, using recycled materials, such as recycled steel, helps reduce the environmental footprint by minimizing the need for raw material extraction and processing, which are energy-intensive. Compliance with environmental regulations also necessitates the use of eco-friendly materials and processes.
The environmental impact of materials like stainless steel and carbon steel must be considered. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance and strength, but its production is energy-intensive. Carbon steel, while strong and durable, requires proper coating to prevent corrosion, which can pose environmental risks if not managed properly.
Energy efficiency in manufacturing is another key factor. Optimizing production to minimize waste and energy consumption is essential. Effective waste management strategies ensure that any waste generated during manufacturing is handled responsibly.
How do pressure and temperature ratings affect flange selection?
Pressure and temperature ratings are crucial factors in the selection of spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges, as they ensure the flanges can withstand the specific operating conditions of a piping system.
Pressure ratings, defined by standards such as ASME B16.5, indicate the maximum allowable pressure a flange can handle at a given temperature. These ratings are categorized into classes (e.g., 150, 300, 600, etc.), with higher classes indicating the ability to withstand higher pressures. The choice of a pressure class depends on the system’s operating pressure; for instance, a Class 300 flange can handle higher pressures than a Class 150 flange.
Temperature ratings affect the pressure capacity of a flange. As temperature increases, the pressure rating typically decreases. For example, a Class 150 flange can handle approximately 270 PSIG at ambient temperature but only about 75 PSIG at 800°F. Therefore, the material of the flange must be suitable for the operating temperatures to maintain structural integrity and safety.
In the context of spectacle blind flanges and spacer blind flanges, selecting the appropriate flange involves matching the pressure class and temperature rating to the system’s requirements. This ensures the flanges can perform reliably under the specified conditions, preventing failures and ensuring safe operation in industrial applications.
