When it comes to wiring solutions, the choice between tinned copper wire and bare copper wire can significantly impact performance, durability, and cost. Have you ever wondered why some applications opt for tinned copper wire despite its higher price tag? This comprehensive guide will unravel the mysteries behind these two types of copper wire, delving into their unique advantages and potential drawbacks. You’ll discover why tinned copper wire is the preferred choice in certain environments, such as marine and industrial settings, and how it stands up to bare copper in terms of corrosion resistance, heat tolerance, and overall longevity. Join us as we explore the key factors that influence wire selection and provide practical insights to help you make an informed decision. Ready to dive into the world of copper wiring? Let’s get started!
Overview of Tinned vs. Bare Copper Wire
Definition of Tinned Copper Wire
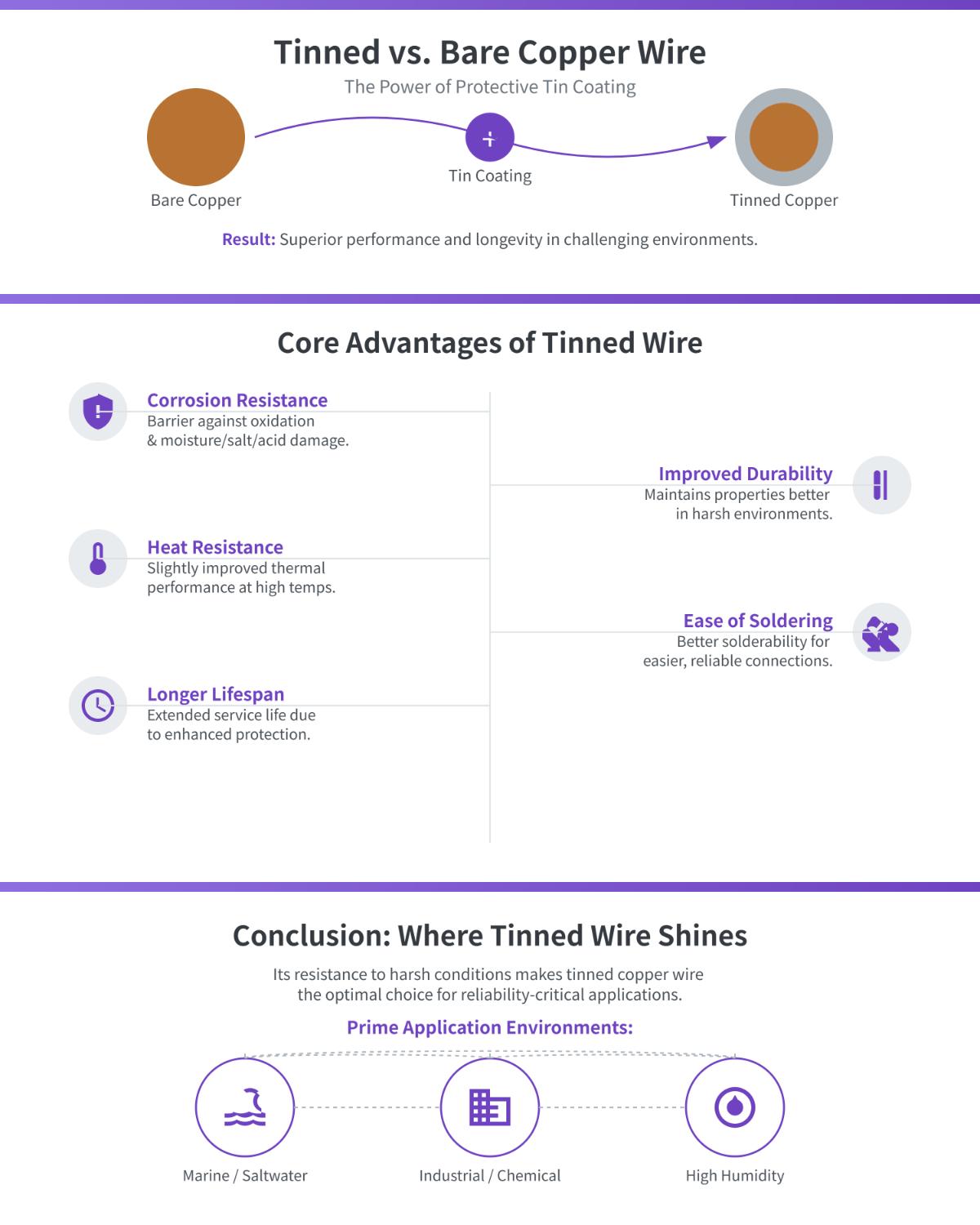
Tinned copper wire is a type of copper wire that has a thin layer of tin coating. This tin coating protects the copper from oxidation and corrosion, making the wire more durable in environments with moisture and chemicals, and also improves the wire’s solderability for creating strong connections.
Definition of Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire is simply copper wire without any coating or plating. This wire is highly conductive and flexible, making it suitable for a wide range of electrical applications. While it does develop a natural oxide layer over time, bare copper wire generally resists corrosion well in many environments, especially indoors or in dry conditions.
Key Differences
Conductivity
Bare copper wire has slightly higher electrical conductivity compared to tinned copper wire. The uncoated copper surface allows for rapid current flow with minimal resistance, making it ideal for applications where maximum efficiency is required. Tinned copper wire, although slightly less conductive due to the tin coating, still offers excellent performance for most electrical uses.
Corrosion Resistance
One of the primary advantages of tinned copper wire is its superior corrosion resistance. The tin coating acts as a barrier against oxidation and corrosion, making tinned copper wire suitable for use in harsh environments such as marine and industrial applications. In contrast, bare copper wire develops an oxide layer that can offer some protection, but it is less effective in environments with high moisture or chemical exposure.
Durability and Lifespan
Tinned copper wire generally has a longer lifespan than bare copper wire due to its resistance to corrosion and oxidation. The tin coating helps maintain the integrity of the wire over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. Bare copper wire, while durable, may require more upkeep in environments where corrosion is a concern.
Heat Resistance
Both tinned and bare copper wires exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, allowing them to dissipate heat efficiently. However, the tin coating on tinned copper wire can enhance its performance in high-temperature applications, providing additional protection against heat-induced damage.
Flexibility and Strength
Bare copper wire is known for its high ductility and malleability, allowing it to be easily shaped and bent without breaking. This makes it highly versatile for various installation configurations. Tinned copper wire, while still flexible, may be slightly less so due to the added coating.
Performance in Various Environments
Tinned copper wire is ideal for outdoor, marine, and corrosive environments where the risk of oxidation and corrosion is high. Its protective tin coating ensures reliable performance in such conditions. Bare copper wire, on the other hand, is best used in indoor, dry, or protected environments where exposure to harsh elements is limited.
Detailed Advantages of Tinned Copper Wire
Corrosion Resistance
Tinned copper wire stands out for its excellent corrosion resistance, thanks to its protective tin coating. This coating acts as a barrier, preventing the copper core from oxidizing when exposed to moisture and corrosive environments, making it ideal for marine environments, industrial settings, and areas with high humidity.
Improved Durability
Tinned copper wire offers enhanced durability compared to bare copper wire. The tin layer not only offers corrosion resistance but also adds mechanical protection, making it ideal for environments with physical wear and tear, such as underground installations or industrial machinery. This added durability ensures the wire maintains its integrity and functionality over a longer period.
Heat Resistance
The tin coating helps the wire endure high temperatures without degrading, making it reliable for industrial and commercial applications with temperature fluctuations. This heat resistance ensures that the wire remains safe and functional in various demanding environments.
Ease of Soldering
Tinned copper wire is easier to solder, resulting in stronger and more consistent joints, which reduces assembly time and improves connection quality. The tin layer allows for better wetting of the solder, enhancing the overall quality of electrical connections.
Longer Lifespan
Due to its resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and heat, tinned copper wire generally has a longer lifespan than bare copper wire. The protective tin coating helps preserve the wire’s conductive properties and structural integrity over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements, particularly in challenging or costly maintenance environments.
Resistance to Chemicals and Sulfur Compounds
In industrial settings where chemicals and sulfur compounds are present, tinned copper wire is more resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for chemical plants and refineries. The tin coating protects the copper from reacting with these substances, ensuring longevity and reliability in harsh industrial environments.
Performance in High-Humidity Environments
Tinned copper wire performs exceptionally well in high-humidity environments, where bare copper wires would typically suffer from accelerated corrosion. The tin coating provides a reliable barrier against moisture, making it suitable for outdoor applications, such as solar power systems, and wet indoor environments like basements and tunnels. This reliability in high-humidity conditions ensures consistent electrical performance and safety.
Comparative Analysis of Tinned and Bare Copper Wire
Conductivity Differences
Both wires have a pure copper core, which ensures excellent electrical current flow. However, bare copper wire has a slight advantage because it doesn’t have the additional tin layer that might introduce minimal resistance.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
A key difference between tinned and bare copper wire is corrosion resistance. Tinned copper wire, with its protective tin coating, offers enhanced resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for environments with high moisture, such as marine or industrial settings. In contrast, bare copper wire can develop an oxide layer over time, which provides some level of protection but is less effective in harsh or corrosive environments.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
The tin coating shields the copper core from environmental damage, extending its lifespan, particularly in tough conditions. Bare copper wire, while durable and robust, may require more frequent maintenance or replacement in environments where corrosion is a concern.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Both tinned and bare copper wires exhibit high thermal conductivity, which is essential for dissipating heat in electrical systems. The tin coating on tinned copper wire can enhance its performance in high-temperature applications by providing an additional layer of protection against heat-induced damage. Bare copper wire also performs well in such environments but does not have the extra safeguard provided by the tin layer.
Flexibility and Strength
Bare copper wire is known for its excellent ductility and malleability, making it easy to shape and install in various configurations. Tinned copper wire, while still flexible, may exhibit slightly less flexibility due to the added tin coating. However, this difference is generally minor and both types of wire can be used effectively in a range of applications.
Performance in Various Environments
Choosing between tinned and bare copper wire often depends on the environment. Tinned copper wire is ideal for outdoor, marine, and corrosive environments where the risk of oxidation and corrosion is high. Its protective tin coating ensures reliable performance and longevity in such conditions. Bare copper wire, on the other hand, is best suited for indoor, dry, or protected environments where exposure to harsh elements is minimal.
Cost Considerations
Bare copper wire is usually more affordable because it doesn’t require the extra tin coating process. This makes bare copper wire an attractive option for projects where budget constraints are a significant consideration and the environmental conditions do not demand the enhanced corrosion resistance offered by tinned copper wire.
Typical Usage Environments
| Feature | Bare Copper Wire | Tinned Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (best in dry conditions) | High (ideal for humid, marine, corrosive environments) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Very High | Very High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Grounding, power distribution, telecom, construction | Marine wiring, electronics, wastewater treatment, subway systems |
| Solderability | Good | Excellent |
Disadvantages and Cost Considerations
Higher Cost
One major drawback of tinned copper wire is its higher cost compared to bare copper wire. The tin-coating process adds extra manufacturing steps and material expenses, resulting in a higher overall price. This increased cost can be a critical factor for projects with tight budgets, particularly in non-corrosive environments where the benefits of tinned copper may not be necessary.
Additional Processing
Applying the tin coating involves cleaning the copper wire, adding the tin layer, and ensuring it adheres uniformly. This additional processing not only increases production time but also involves more complex equipment and quality control measures. Consequently, the manufacturing complexity of tinned copper wire contributes to its higher cost and can affect the supply chain dynamics.
Potential Environmental Impact
Producing tinned copper wire uses tin, which can have environmental consequences. The mining and processing of tin can lead to ecological disturbances, including habitat destruction and pollution. Moreover, the tin coating process itself may involve chemicals that need to be managed carefully to minimize environmental impact. While tinned copper wire offers long-term durability and corrosion resistance, its production can have a more substantial environmental footprint compared to bare copper wire.
Reduced Conductivity
Although the tin coating offers benefits, it slightly reduces the copper wire’s electrical conductivity. The tin layer introduces a minimal resistance, which, although often negligible, can be a concern in high-precision applications where optimal conductivity is crucial. Bare copper wire, with its uncoated surface, offers superior conductivity, making it preferable for applications requiring maximum efficiency.
Limited Use Cases
Tinned copper wire’s advantages are most pronounced in specialized environments, such as marine, high-humidity, or industrial settings. In general wiring applications, the benefits of tinned copper do not justify its higher cost. Bare copper wire is often sufficient for standard indoor or dry environments, providing reliable performance without the additional expense associated with tinned copper.
Soldering Trade-offs
While tinned copper wire is easier to solder due to its pre-coated surface, this advantage comes with trade-offs. Improper soldering techniques can degrade the performance of tinned copper wire, leading to potential issues with solder joints. Bare copper wire requires more skill to solder but avoids the risks associated with the tin coating, providing more consistent results if handled correctly.
Budget Impact
In non-corrosive environments, the higher cost of tinned copper wire can greatly affect the budget. Bare copper wire offers a cost-effective solution, providing adequate performance without the added expense of the tin coating. Therefore, selecting bare copper wire for indoor wiring and other non-corrosive applications can help minimize costs while still achieving reliable results.
Comparative Analysis
| Factor | Bare Copper Wire | Tinned Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Conductivity | Higher | Slightly Lower |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Lifespan | Shorter in harsh conditions | Longer in extreme environments |
| Application Scope | General wiring, grounding | Marine, outdoor, industrial |
Recommendations
- Prioritize Bare Copper for cost-sensitive, indoor, or dry environments where oxidation risks are minimal.
- Use Tinned Copper exclusively for high-moisture, saline, or chemically aggressive settings to maximize longevity.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: While tinned copper has higher upfront costs, its extended lifespan in harsh conditions may reduce long-term replacement expenses.
Environmental Conditions Affecting Wire Choice
Temperature
Temperature variations can significantly affect the performance and durability of both tinned and bare copper wires.
Tinned Copper Wire
Tinned copper wires generally offer superior resistance to high temperatures due to the protective tin coating. This layer acts as a barrier against oxidation, which can be exacerbated by heat, thereby preserving the wire’s integrity. However, at extremely high temperatures, the tin itself can melt or degrade, potentially compromising the wire’s effectiveness.
Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire, lacking a protective coating, is more vulnerable to oxidation when exposed to temperature fluctuations. This can lead to a reduction in conductivity over time. Without the tin layer, bare copper may soften or become brittle depending on the temperature extremes, affecting its mechanical properties and lifespan.
Moisture
Moisture is a critical factor in determining the appropriate wire type for various environments, as it can lead to corrosion and electrical failures.
Tinned Copper Wire
The tin coating on tinned copper wire provides a significant advantage in moist environments by preventing direct exposure of the copper to water. This barrier reduces the risk of corrosion and ensures the wire remains functional and safe. Prolonged exposure to moisture, however, can still pose challenges, but the tin layer offers a much-needed defense.
Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire is highly susceptible to moisture-induced corrosion. When exposed to water or high humidity, the copper can oxidize and corrode quickly, leading to degraded performance and potential safety hazards. This makes bare copper less suitable for wet or marine environments.
UV Radiation
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can degrade wire insulation, affecting both tinned and bare copper wires.
Tinned Copper Wire
While the tin coating does not directly protect against UV radiation, tinned copper wire is often used with UV-resistant insulation materials, ensuring the wire’s durability in outdoor applications.
Bare Copper Wire
Similarly, bare copper wire is not directly affected by UV radiation, but its insulation can degrade over time if not UV-stabilized. The choice of insulation material is crucial for maintaining the wire’s performance in UV-exposed environments.
Chemical Presence
Chemical exposure can significantly impact the longevity and functionality of copper wires.
Tinned Copper Wire
Tinned copper wire is better suited for environments with mild chemical exposure due to the protective tin layer. This coating acts as a barrier against many corrosive substances, ensuring the wire remains intact and functional. However, in highly aggressive chemical environments, the tin coating may eventually degrade.
Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire is more vulnerable to corrosion from chemicals since it lacks a protective coating. Direct exposure to corrosive chemicals can lead to rapid degradation, making it less ideal for industrial settings where chemical exposure is common.
Mechanical Stress
Mechanical stress, including bending, stretching, or vibration, can lead to wire fatigue and failure.
Tinned Copper Wire
The tin coating provides a slight increase in durability against mechanical stress. This added tensile strength helps the wire withstand physical wear and tear better than bare copper in some conditions, making it suitable for installations subject to frequent movement or vibration.
Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire, while flexible and ductile, may show earlier signs of fatigue under mechanical stress compared to tinned copper. Without the protective tin layer, it is more prone to damage and may require more frequent maintenance or replacement in high-stress environments.
Soldering Properties and Practical Tips
Soldering Properties
Tinned Copper Wire
Tinned copper wire is favored for its excellent soldering properties, primarily due to the thin layer of tin that coats the copper. This tin coating, a key element in most solder materials, improves the solder’s adhesion to the wire. The presence of tin ensures better wetting of the solder, making the process smoother and more efficient. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for less-experienced solderers or in applications where reliable and strong solder joints are crucial.
Bare Copper Wire
Bare copper wire, lacking any coating, presents a slightly more challenging surface for soldering. The absence of a tin layer means that the solder must bond directly to the copper, which can be impeded by oxidation on the wire’s surface. For a reliable solder joint with bare copper wire, thoroughly clean the wire to eliminate oxidation and contaminants. Despite the initial challenge, once properly soldered, bare copper wire maintains excellent conductivity and performance.
Practical Tips for Soldering
Selecting the Appropriate Wire
- Environment Considerations:
- Tinned Copper Wire: Choose tinned copper wire for environments with high humidity, saltwater exposure, or corrosive conditions. The tin coating not only facilitates easier soldering but also provides enhanced corrosion resistance.
- Bare Copper Wire: Choose bare copper wire for cost-sensitive projects or in environments where corrosion is not a significant concern, such as indoor or dry settings.
- Project Requirements:
- Ease of Soldering: Tinned copper wire is preferable for projects requiring quick and efficient soldering, especially for large-scale or time-sensitive applications.
- Maximum Conductivity: For applications where superior conductivity is critical, bare copper wire may be the better choice due to its slightly higher conductivity.
Soldering Techniques
- Preparation:
- Tinned Copper Wire: Ensure the tin coating is intact and clean. This preparation is usually minimal since the tin layer inherently provides a solder-friendly surface.
- Bare Copper Wire: Thoroughly clean the wire to remove any oxidation. Use fine sandpaper, a wire brush, or a chemical cleaner to achieve this. Proper cleaning is crucial to ensure a reliable solder joint.
- Solder Application:
- Tinned Copper Wire: Apply heat evenly to the wire and the soldering point, allowing the solder to flow smoothly over the tin-coated surface.
- Bare Copper Wire: Apply heat to the cleaned wire and the connection point, ensuring the solder flows directly onto the copper. It may require more precise temperature control to achieve a strong bond.
Maintenance and Inspection
- Regular Checks:
- Tinned Copper Wire: Periodically inspect the wire for any signs of wear or damage to the tin coating, which could compromise its corrosion resistance and solderability.
- Bare Copper Wire: Regularly check for oxidation or corrosion, especially in environments with variable humidity or temperature. Clean and re-solder as needed to ensure optimal performance.
- Protective Measures:
- Tinned Copper Wire: Utilize heat shrink tubing or electrical tape to provide additional protection at solder joints, particularly in harsh environments.
- Bare Copper Wire: Apply protective coatings or use insulating materials to shield the wire from environmental exposure, thereby prolonging its lifespan and maintaining electrical integrity.
Application Case Studies
Marine Applications
In marine environments, the choice of wire is critical due to the high exposure to moisture and saltwater. Tinned copper wire is highly favored in these settings because of its superior corrosion resistance. The tin coating protects against harsh marine conditions, preventing oxidation and preserving electrical integrity.
- Use Case: Wiring for boats, docks, and marine electronics.
- Benefits: Extended lifespan, reduced maintenance costs, and reliable performance in salty and humid conditions.
- Example: A marine electrician uses tinned copper wire for boat wiring to ensure that electrical systems remain operational despite constant exposure to seawater.
Industrial Machinery
Industrial environments often involve exposure to chemicals, vibrations, and high temperatures, making tinned copper wire the preferred choice due to its enhanced durability and resistance.
- Use Case: Wiring in manufacturing plants, chemical processing units, and heavy machinery.
- Benefits: Increased durability, longer lifespan, and resistance to chemical exposure.
- Example: A factory uses tinned copper wire for its conveyor belt systems to withstand the constant mechanical stress and occasional chemical spills.
Electronics Assembly
Solderability and reliability are crucial in electronics manufacturing. Tinned copper wire is often used because the tin coating simplifies the soldering process, resulting in stronger and more consistent joints. This is particularly important in applications requiring frequent connections and disconnections.
- Use Case: Circuit boards, connectors, and electronic devices.
- Benefits: Ease of soldering, reduced risk of corrosion, and better performance in repetitive assembly processes.
- Example: An electronics company opts for tinned copper wire in the production of circuit boards to ensure that the solder joints are robust and reliable, enhancing the overall quality of the final products.
High-Temperature Applications
High-temperature environments, like industrial processes or automotive applications, require wires that withstand thermal stress. Tinned copper wire is suitable for these applications due to its ability to resist oxidation at elevated temperatures, ensuring consistent electrical performance.
- Use Case: Automotive wiring, furnace controls, and high-temperature industrial processes.
- Benefits: Enhanced durability and reliability under thermal stress.
- Example: An automotive manufacturer uses tinned copper wire for engine compartment wiring to ensure that the wires do not degrade due to the high temperatures generated by the engine.
Indoor and Dry Environments
In indoor and dry environments, bare copper wire is often sufficient. It offers higher conductivity and is cost-effective for installations where the risk of corrosion is minimal. Bare copper wire is suitable for residential wiring, telecommunications, and applications where moisture or chemical exposure is minimal.
- Use Case: Residential wiring, telecommunications, and dry industrial settings.
- Benefits: Higher conductivity, lower cost, and adequate performance in controlled environments.
- Example: A residential electrician installs bare copper wire for home electrical systems, taking advantage of its high conductivity and cost-effectiveness in an environment where corrosion is not a significant issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the main advantages of tinned copper wire over bare copper wire?
Tinned copper wire offers several advantages over bare copper wire due to the protective tin coating applied to the copper. This tin coating significantly enhances the wire’s performance in challenging environments. The primary advantages include:
- Corrosion Resistance: The tin coating acts as a barrier against oxidation and corrosion, which bare copper is susceptible to when exposed to moisture, humidity, saltwater, or acidic environments. This resistance prolongs the wire’s lifespan in such conditions.
- Improved Durability: Tinned copper wire maintains its mechanical and electrical properties longer than bare copper, especially in high humidity, saltwater, contaminated soils, or chemical exposure environments.
- Heat Resistance: The tin plating can slightly enhance the thermal resistance of the wire, allowing it to perform better in elevated temperature conditions without degrading prematurely.
- Ease of Soldering: The tin coating improves solderability, making it easier to form secure electrical connections during assembly and repair. This results in better workmanship and more reliable joints.
- Longer Lifespan: Due to its resistance to corrosion and oxidation, tinned copper wire generally has a longer lifespan compared to bare copper, particularly in harsh environments.
These advantages make tinned copper wire a preferred choice for applications in marine, industrial, and high-humidity environments, where durability and reliability are critical.
What are the disadvantages or drawbacks of using tinned copper wire?
Tinned copper wire, while offering enhanced corrosion resistance and improved durability, has several disadvantages compared to bare copper wire. Firstly, tinned copper wire exhibits slightly lower electrical conductivity due to the tin coating, which introduces minimal additional resistance. This reduction, though minor, can impact applications where maximum conductivity is critical. Secondly, tinned copper wire is more expensive than bare copper wire because of the added material and extra manufacturing processes required to apply the tin coating. For projects where corrosion resistance is not essential, this added expense may not be justified. Additionally, tinned copper wire is typically reserved for specialized environments, such as marine or high-humidity industrial settings, limiting its general utility and availability for common wiring applications. Finally, handling and processing tinned copper wire can be more complex, as damage to the tin coating can expose the copper underneath, making it susceptible to corrosion and negating the benefits of the tin layer. Therefore, while tinned copper wire has distinct advantages, these drawbacks should be carefully considered based on the specific needs and conditions of the application.
In what environments is tinned copper wire preferable to bare copper wire?
Tinned copper wire is preferable to bare copper wire in several specific environments due to its enhanced properties. In humid and high-moisture environments, such as wastewater treatment facilities and underground subway systems, tinned copper wire’s tin coating provides protection against oxidation and corrosion, ensuring reliable electrical performance over time. In marine environments, the wire’s resistance to saltwater corrosion makes it an ideal choice, as the tin layer prevents the formation of copper oxide, which can compromise the wire’s integrity. Additionally, tinned copper wire is well-suited for industrial and corrosive environments, where it resists degradation from sulfur compounds and acidic conditions. Its superior thermal resistance also makes it a better option for high-temperature applications, such as industrial machinery. These characteristics collectively make tinned copper wire a reliable choice in challenging environments, offering improved durability and a longer lifespan compared to bare copper wire.
How does tinned copper wire affect soldering compared to bare copper?
Tinned copper wire significantly enhances the soldering process compared to bare copper wire. The tin coating on tinned copper wire provides a clean, smooth surface that promotes better solder flow, resulting in stronger and more reliable joints. This coating also prevents oxidation during soldering, which can impair the solderability of bare copper wire. Consequently, soldering tinned copper wire is generally quicker and more efficient as it does not require additional cleaning or tinning steps, unlike bare copper wire. These features make tinned copper wire especially advantageous in applications requiring reliable electrical connections, such as in high-temperature or corrosive environments, outdoor and underground installations, and electrical grounding systems.
Is the higher cost of tinned copper wire justified by its benefits?
Yes, the higher cost of tinned copper wire is justified by its benefits. Tinned copper wire features a thin coating of tin, which provides significant advantages over bare copper wire, particularly in challenging environments. Firstly, the tin coating offers superior corrosion resistance, protecting the wire from oxidation in humid, wet, or salty conditions, which is crucial for marine and industrial applications. Secondly, tinned copper wire has an extended lifespan due to this corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, thus offering long-term cost savings. Additionally, it withstands higher temperatures better than bare copper, making it suitable for high-heat environments. Its enhanced solderability also ensures more secure electrical connections. These benefits make tinned copper wire a valuable investment for applications exposed to moisture, corrosive chemicals, or high temperatures, where reliability and durability are paramount.
How do the lifespan and maintenance needs of tinned copper wire compare to bare copper wire?
Tinned copper wire generally has a longer lifespan and requires less maintenance compared to bare copper wire, primarily due to its enhanced resistance to corrosion and oxidation. The tin coating on tinned copper wire acts as a protective barrier, preventing the underlying copper from degrading when exposed to moist, humid, or chemically aggressive environments. This makes tinned copper particularly suitable for marine, outdoor, and industrial applications where it can significantly outlast bare copper wire.
On the other hand, bare copper wire, while naturally resistant to corrosion, is more susceptible to oxidation over time, especially in the presence of air and moisture. This oxidation can form a patina that may degrade electrical performance, necessitating more frequent maintenance checks and potential replacements. Bare copper wire is best suited for dry, indoor environments where exposure to corrosive elements is minimal, allowing it to maintain its performance with less upkeep.
