Have you ever wondered how some screws can achieve faster and more efficient fastening than others? Enter double-threaded screws, a marvel in fastening technology. These screws feature two intertwined threads that enable quicker installation and removal compared to single-threaded counterparts. They play a crucial role in various industries, from automotive to aerospace. In this technical deep – dive, we’ll explore their definition, working mechanism, benefits, and how they stack up against other screw types. So, are you ready to uncover the intricacies of double – threaded screws?
Introduction to Double-Threaded Screws
Definition and Basic Concept
Double-threaded screws are specialized fasteners with two distinct threaded sections along their shank. Unlike traditional single-threaded screws with uniform threading, double-threaded screws offer enhanced functionality and versatility for various fastening applications. They provide precise control over clamping forces, which is crucial for complex assemblies requiring differential tension and load balancing.
Importance in Fastening Technology
Double-threaded screws are significant in modern fastening technology due to their unique design. The dual-thread configuration lets these screws perform multiple functions simultaneously, streamlining assembly processes and improving efficiency. This is especially valuable in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing where precision and reliability are essential.
Design and Structure
Threading
The threading on double-threaded screws is divided into two sections with different diameters or pitches. A larger diameter or a coarser pitch can create greater clamping force, while a smaller diameter or a finer pitch may result in less force. This difference in threading allows the screw to exert varying levels of clamping force on different components, adjustable for specific applications.
Headless Design
Many double-threaded screws are headless, consisting entirely of a threaded shank. They are inserted into pre-drilled holes in two separate components, creating a secure joint without visible fasteners. This makes them suitable for applications where aesthetics matter, such as furniture assembly or architectural installations.
Smooth Mid-Shank
A common feature of double-threaded screws is a smooth mid-section between the two threaded areas. This smooth section reduces friction during installation, enabling the screw to be driven in smoothly and securely while also helping align the components, resulting in a tighter and more stable connection.
Applications and Versatility
Double-threaded screws are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility. They are commonly found in industries that require robust and reliable fastening solutions, including automotive (used in suspension systems for precise adjustments), aerospace (employed in assemblies needing high precision and load – bearing capacity), and manufacturing (integrated into machinery for differential clamping forces).
Enhanced Functionality
The dual-thread design of these screws offers several key advantages. Firstly, it provides different levels of compression on various components, making them ideal for complex assemblies. Secondly, it simplifies assembly by reducing the number of components needed and minimizing installation errors as it combines two fastening operations into one. Thirdly, it allows for fine – tuning of component positions, ensuring secure and precise connections.
How Double-Threaded Screws Work
Detailed Explanation of Screw Threading
Double-threaded screws have two helical threads that run parallel to each other, usually spaced 180 degrees apart around the screw’s shaft. This dual-thread design is a significant departure from single-threaded screws. The threads start at different points along the screw’s shaft, which enhances the screw’s ability to move through materials more rapidly.
Understanding the lead and pitch is crucial: pitch is the distance between points on adjacent threads, while lead is the distance the screw travels in one full turn. In double-threaded screws, the lead is usually twice the pitch. For example, if the pitch is 2 mm, the lead would be 4 mm. This means that for each full turn of the screw, it advances twice as far as a single-threaded screw with the same pitch, enabling faster engagement with the material.
Mechanism and Operational Principles
In terms of operation, double-threaded screws work on the same fundamental principle as other screws: the threads dig into the surfaces they are being screwed into. However, the dual-thread design offers distinct advantages.
A key benefit is faster assembly and disassembly, as the multiple threads engage the material more quickly. When a double-threaded screw is turned, both threads start to bite into the material simultaneously, reducing the time needed to reach the desired depth compared to a single-threaded screw. This makes them ideal for applications where speed is crucial, such as high-volume manufacturing processes.
Another advantage is enhanced stability. The dual-thread configuration distributes the load more evenly across the threads and the material. This even load distribution reduces the risk of the screw loosening over time, providing a more secure connection. This stability is especially valuable in applications with vibrations, like automotive or heavy machinery.
Benefits and Applications
Advantages of Double-Threaded Screws
Double-threaded screws offer several significant advantages over their single-threaded counterparts, making them highly valuable in various industrial applications.
Enhanced Efficiency
The dual-thread design of double-threaded screws allows them to engage with materials more quickly, effectively covering more distance per turn. This higher engagement rate results in quicker assembly, especially useful for high-volume production. By reducing the time required for installation, these screws help improve overall operational efficiency and productivity.
Precision, Adjustability, Stability, and Torque
Double-threaded screws provide precise control over clamping forces, making them ideal for applications that require fine-tuning. The ability to adjust the tension and alignment of components with high precision is crucial in fields such as optical instruments and precision engineering. This adjustability ensures that the components are securely fastened while maintaining the necessary alignment and tension.
The design of double-threaded screws allows for enhanced torque and stability. The dual-thread configuration distributes the load more evenly across the screw and the material it is fastened into, reducing the risk of loosening over time. This even distribution of load is especially important in applications that experience significant vibrations, such as automotive and heavy machinery, ensuring a secure and stable connection.
Flexibility in Design
Double-threaded screws can be customized with different thread pitches and diameters for specific tension ratios in particular applications. This customization ensures optimal performance in critical applications, such as aerospace and high-performance engines, where precise tension control is essential. The ability to design screws with varying thread characteristics enhances their versatility and functionality in specialized engineering tasks.
Common Fastening Applications
Double-threaded screws are used across a wide range of applications due to their unique advantages.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, double-threaded screws are employed for the efficient installation and removal of components. Their ability to provide rapid assembly and disassembly helps enhance production speed and reduce labor costs. They are particularly useful in areas that require precise adjustments, such as suspension systems and engine assemblies.
Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering relies on double-threaded screws for their precision and reliability. These screws are crucial for rapid assembly and disassembly during aircraft maintenance and repairs, ensuring minimal downtime. Their ability to maintain secure connections under high stress and vibration conditions makes them indispensable in aerospace applications.
Precision Instruments
Double-threaded screws are commonly used in precision instruments, such as microscopes and camera lenses. The fine adjustments enabled by these screws facilitate smooth and precise focusing and alignment, which are essential for the accurate functioning of these instruments.
Construction and Heavy Machinery
In construction and heavy machinery, double-threaded screws are valued for their ability to withstand significant stress and vibrations. They are used in the assembly of heavy equipment and structural components, providing secure and durable connections that are crucial for the stability and safety of large machinery and structures.
Industry-Specific Uses
Optical Instruments
In the field of optical instruments, double-threaded screws play a vital role in ensuring precise adjustments and stable connections. Their ability to provide fine-tuning capabilities is essential for achieving the high levels of accuracy required in optical devices.
High-Performance Engines
Double-threaded screws are used in high-performance engines to provide precise clamping forces and secure connections. Their ability to distribute load evenly and maintain stability under high torque conditions is critical for the reliable performance of these engines.
Architectural Installations
In architectural installations, where aesthetics and functionality must go hand in hand, double-threaded screws offer a solution that provides secure fastening without visible fasteners. Their headless design creates clean, unobtrusive connections that improve the installation’s look.
Comparison with Other Screw Types
Double-Threaded Screws vs. Double-Ended Screws
Design and Purpose
Double-threaded screws have multiple threads that allow for rapid engagement and disengagement, making them ideal for quick assembly applications. This design is particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where efficient assembly is critical. In contrast, double-ended screws, also known as dowel screws, are crafted to create hidden joints between two surfaces. These screws have no heads and feature two pointed ends, allowing them to disappear from view once installed.
Application
Double-threaded screws are frequently used in high-volume production and structural assembly environments where speed and precision are crucial. They are indispensable in settings that demand both rapid and accurate assembly. On the other hand, double-ended screws are a staple in woodworking and furniture assembly, providing the discreet connections necessary for a clean, professional finish.
Double-Threaded Screws vs. Single-Threaded Screws
Speed and Efficiency
Double-threaded screws cover a greater distance per turn compared to single-threaded screws. This characteristic significantly reduces assembly time, making them a preferred choice in high-volume production scenarios. Single-threaded screws, however, are better suited for tasks that require slower and more precise fastening, offering greater control over the process.
Thread Engagement
Double-threaded screws provide better stability and grip because their threads engage more with the material, distributing the load evenly and reducing the risk of loosening over time. While single-threaded screws may not offer the same level of stability, they are more accessible and cost-effective for a wide range of applications.
Double-Threaded Screws vs. Double-Threaded Bolts
Design and Functionality
Double-threaded screws are designed for fast fastening with multiple threads, making them ideal for applications requiring quick and precise assembly. Double-threaded bolts, also known as differential thread bolts, feature two distinct threaded sections. These sections can apply different forces or tensions, making them suitable for complex assemblies and fine-tuning operations.
Application
Double-threaded screws are mainly used in construction and manufacturing for fast assembly. Double-threaded bolts are useful in automotive suspension systems, aerospace, and other areas that need precise adjustments and varying clamping forces.
Manufacturing and Construction
The Role of Double-Threaded Screws in Manufacturing
Double-threaded screws are a game-changer in the manufacturing industry due to their efficiency and reliability. Their unique design allows them to engage materials quickly and securely, which is crucial in high-volume production environments.
High-Volume Production
In manufacturing settings, time and precision are critical. Double-threaded screws enhance operational efficiency by significantly reducing assembly time. For instance, in the production of automotive components, their dual-thread design allows each turn of the screw to advance further into the material compared to single-threaded screws, speeding up the fastening process. This is particularly beneficial in assembly lines where thousands of components need to be secured quickly and reliably.
The precision offered by double-threaded screws is another significant advantage. The even load distribution provided by the dual threads ensures that the screws maintain a stable grip, which is essential in applications subject to vibrations, such as machinery and automotive components. This stability helps in preventing loosening over time, thereby enhancing the durability and reliability of the assembled products.
Use in Construction Projects
In the construction industry, double-threaded screws are valued for their strength and speed, which are critical for structural integrity and efficiency.
Structural Applications
Double-threaded screws are ideal for securing structural components such as beams, posts, and joists. Their ability to provide strong and fast connections makes them indispensable in constructing frameworks for buildings and other structures. They are particularly effective in timber construction, where their quick engagement and strong hold help in creating robust and stable assemblies. Additionally, the use of double-threaded screws enhances safety by ensuring that connections remain secure under various load conditions.
The quick installation capabilities of double-threaded screws are highly beneficial in construction projects. Faster assembly times translate to reduced labor costs and shorter project timelines, which are significant advantages in the construction industry. Their efficiency also minimizes the potential for errors during installation, ensuring that the construction process is both rapid and accurate.
Applications in Heavy Machinery Manufacturing
Heavy machinery manufacturing demands fasteners that can withstand significant stress and vibrations. Double-threaded screws are well-suited for these demanding applications.
The dual-thread design of these screws provides enhanced durability and strength, making them suitable for securing heavy machinery components. The even load distribution across the threads helps in maintaining tight connections, which is crucial for the stability and safety of heavy machinery.
In heavy machinery, vibrations are a common challenge that can lead to the loosening of fasteners. Double-threaded screws address this issue effectively by distributing the load more evenly, thereby reducing the risk of loosening. This characteristic is particularly important in industries such as mining, construction, and manufacturing, where machinery is subject to intense operational conditions.
Material and Design Considerations
Double-threaded screws are manufactured from various materials to suit different applications and environmental conditions. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, alloy steel, brass, and nickel. To enhance their performance and longevity, these screws often undergo surface treatments such as zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, or passivation. These treatments improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance, making the screws suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Technical Specifications
Standards Compliance
Double-threaded screws must meet industry standards to ensure quality, reliability, and safety. These standards specify the dimensions, mechanical properties, and testing methods for screws, and the dual – thread design, which increases the pitch for faster engagement and disengagement, is critical for applications requiring quick assembly or disassembly while ensuring the screws meet the required performance criteria.
Material and Design Considerations
Materials
Double-threaded screws are made from different materials, each with properties suited to specific uses:
- Stainless Steel: Provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications.
- Carbon Steel: Offers high strength and durability, commonly used in construction and heavy machinery.
- Alloy Steel: Enhanced mechanical properties, suitable for high-stress applications.
- Brass: Good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, used in electrical and decorative applications.
- Nickel: Exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, used in aerospace and chemical industries.
Design Features
- Thread Design: The dual-thread design increases the pitch, allowing for faster engagement and disengagement.
- Head Type: Various head types, such as flat, pan, or hex, are available to suit different installation methods and aesthetic requirements.
- Coating and Finishes: Coatings such as zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and passivation improve corrosion resistance and extend the screw’s life.
Technical Diagrams and Images
Technical diagrams and images are essential for understanding the precise dimensions and features of double-threaded screws. These diagrams typically include:
- Thread Pitch and Lead: Detailed measurements of the distance between threads and the screw’s advancement per turn.
- Head Dimensions: Specifications of the head type, including diameter and height.
- Shank Length: The length of the threaded and unthreaded portions of the screw.
- Material Specifications: Indications of the material composition and any surface treatments applied.
Durability and Strength Metrics
The durability and strength of double-threaded screws are critical for their performance in various applications. Key metrics include:
- Tensile Strength: The maximum load the screw can withstand while being pulled apart.
- Shear Strength: The load the screw can endure perpendicular to its axis before failing.
- Hardness: Resistance to deformation, typically measured using the Rockwell or Vickers hardness tests.
- Corrosion Resistance: The ability of the screw to withstand environmental factors without degrading, often assessed through salt spray tests.
Installation Guidelines
Installing double-threaded screws correctly is crucial for their performance and durability:
- Pre-Drilling: For certain materials, pre-drilling pilot holes may be necessary to prevent splitting and ensure precise alignment.
- Torque Specifications: Follow recommended torque settings to avoid over-tightening, which can damage the screw or the material.
- Lubrication: In some cases, applying a suitable lubricant can reduce friction and facilitate smoother installation.
Surface Treatments and Finishes
Surface treatments and finishes enhance the performance of double-threaded screws by providing additional protection and improving aesthetics:
- Zinc Plating: Offers moderate corrosion resistance and is commonly used for indoor applications.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Provides a thick, durable coating suitable for harsh outdoor environments.
- Passivation: A chemical treatment that increases the corrosion resistance of stainless steel.
- Powder Coating: Adds a durable, decorative finish available in various colors, suitable for visible installations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What is a double-threaded screw and how does it work?
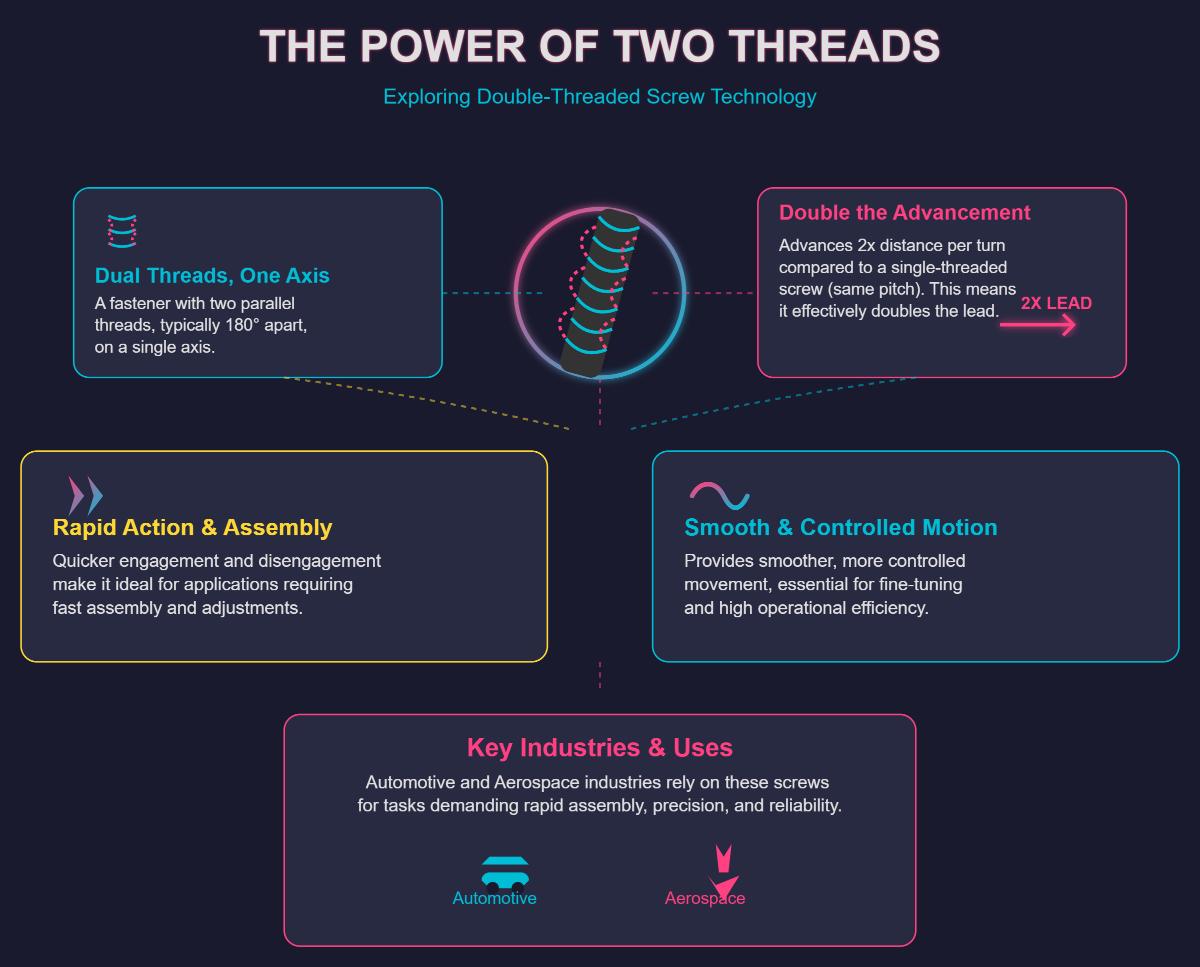
A double-threaded screw is a type of fastener that features two parallel threads running around the same axis. This configuration allows the screw to advance twice the distance per rotation compared to a single-threaded screw with the same pitch. The two helical threads are typically positioned 180 degrees apart, effectively doubling the lead, which is the distance the screw advances with each turn.
The working principle of a double-threaded screw involves its dual-thread design, which increases the lead without changing the pitch. This design enables quicker engagement and disengagement, making the screw ideal for applications requiring rapid assembly and precision, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. The increased lead also allows for smoother and more controlled movement, essential for tasks needing fine adjustments and high operational efficiency.
What are the advantages of using double-threaded screws?
Double-threaded screws offer several advantages that make them superior in certain applications compared to single-threaded screws. Firstly, their dual-thread design enables faster engagement, allowing the screw to advance twice as far with each turn, which significantly reduces assembly and disassembly time. This increased efficiency is particularly beneficial in high-volume production environments, such as automotive and electronics manufacturing, where time savings translate to higher productivity.
Secondly, double-threaded screws provide improved stability and grip. The dual-thread configuration ensures even load distribution, reducing the likelihood of loosening over time and ensuring secure, long-lasting connections. This stability is essential in applications like heavy machinery assembly where strong and reliable fastening is critical.
Additionally, double-threaded screws are versatile in their applications, suitable for both structural and precision engineering tasks. Their ability to handle higher torque without damaging materials makes them ideal for construction and industrial equipment. Moreover, specialized thread configurations, such as dual-thread directions, cater to specific needs where components require precise adjustments.
How do double-threaded screws compare to other fastening methods?
Double-threaded screws, featuring two parallel helical threads, offer significant advantages over other fastening methods. Their dual-thread design allows them to engage with materials more quickly, reducing fastening time and enhancing efficiency. This makes them ideal for high-volume production environments, such as automotive and aerospace industries, where speed and precision are paramount.
Compared to single-threaded screws, double-threaded screws provide faster assembly and disassembly due to their increased thread engagement, which distributes the load more evenly and reduces the risk of loosening. This results in greater stability and grip. However, double-threaded screws are more complex and costly to manufacture, which can limit their accessibility for smaller projects or DIY tasks.
In contrast to double-ended screws, which are designed for creating hidden joints in woodworking and furniture assembly, double-threaded screws are more suited for applications where visible, strong, and efficient fastening is required.
What are the common applications of double-threaded screws?
Double-threaded screws are commonly utilized in various applications due to their enhanced efficiency and reliability. In automotive manufacturing, they facilitate quick installation and removal of components on assembly lines, improving production speed. Aerospace engineering benefits from their ability to secure and release parts rapidly during maintenance, minimizing aircraft downtime. Precision instruments, such as camera lenses and microscopes, use these screws for smooth and precise movement. The electronics industry relies on them for assembling devices that need accurate and stable fastening. In industrial machinery, double-threaded screws enhance material handling efficiency in feed screws and conveyors. They are also used in structural wood connections, such as beam-to-post or roof-to-wall, where a secure and low-profile connection is required. These applications highlight the versatility and importance of double-threaded screws in various high-performance and precision tasks.
What industries benefit most from using double-threaded screws?
Double-threaded screws, with two sets of threads on the screw shaft, benefit several industries. In construction and woodworking, they’re used for structural connections due to their strength and low-profile design. Automotive manufacturing uses them for rapid assembly and disassembly on production lines, cutting labor costs. Aerospace engineering benefits from their high-torque and quick – fastening abilities, reducing aircraft downtime. Precision instruments and electronics rely on them for smooth adjustments and component alignment. Industrial machinery and manufacturing use them for efficient material handling and robust connections.
What are the technical standards for double-threaded screws?
Double-threaded screws adhere to specific technical standards to ensure their performance and reliability in various applications. These standards are established by organizations such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), which provide guidelines on aspects like material composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances.
Typically, double-threaded screws are made from materials like carbon steel or stainless steel, and they often feature coatings such as zinc for corrosion resistance. The threading design includes two distinct sets of threads: one coarse for quick entry and one finer for enhanced holding power. Compliance with standards like ASTM ensures that these screws meet the necessary requirements for strength, durability, and safety in structural applications. Additionally, adherence to DIN standards ensures compatibility and reliability in metric fastening systems.
These technical standards help in maintaining the consistency and quality of double-threaded screws, making them suitable for demanding uses in industries such as construction, automotive, and aerospace.
