Imagine a world where the intricate web of pipelines transporting essential fluids and gases could be disrupted by something as simple as thermal expansion. This is where pipe expansion joints come into play, acting as unsung heroes that accommodate movement and prevent system failures. But what makes one type of expansion joint more suitable than another? How do these marvels of engineering work, and where are they most effectively applied?
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fascinating world of pipe expansion joints, offering a comparative analysis of their various types and applications. You’ll discover the critical role these components play in maintaining the integrity of piping systems, from the resilient rubber joints to the versatile gimbal joints used in complex industrial setups. By the end, you’ll not only understand how these joints function but also gain insights into selecting the right type for your specific needs. Ready to explore the intricacies of pipe expansion joints and their indispensable applications? Let’s dive in.
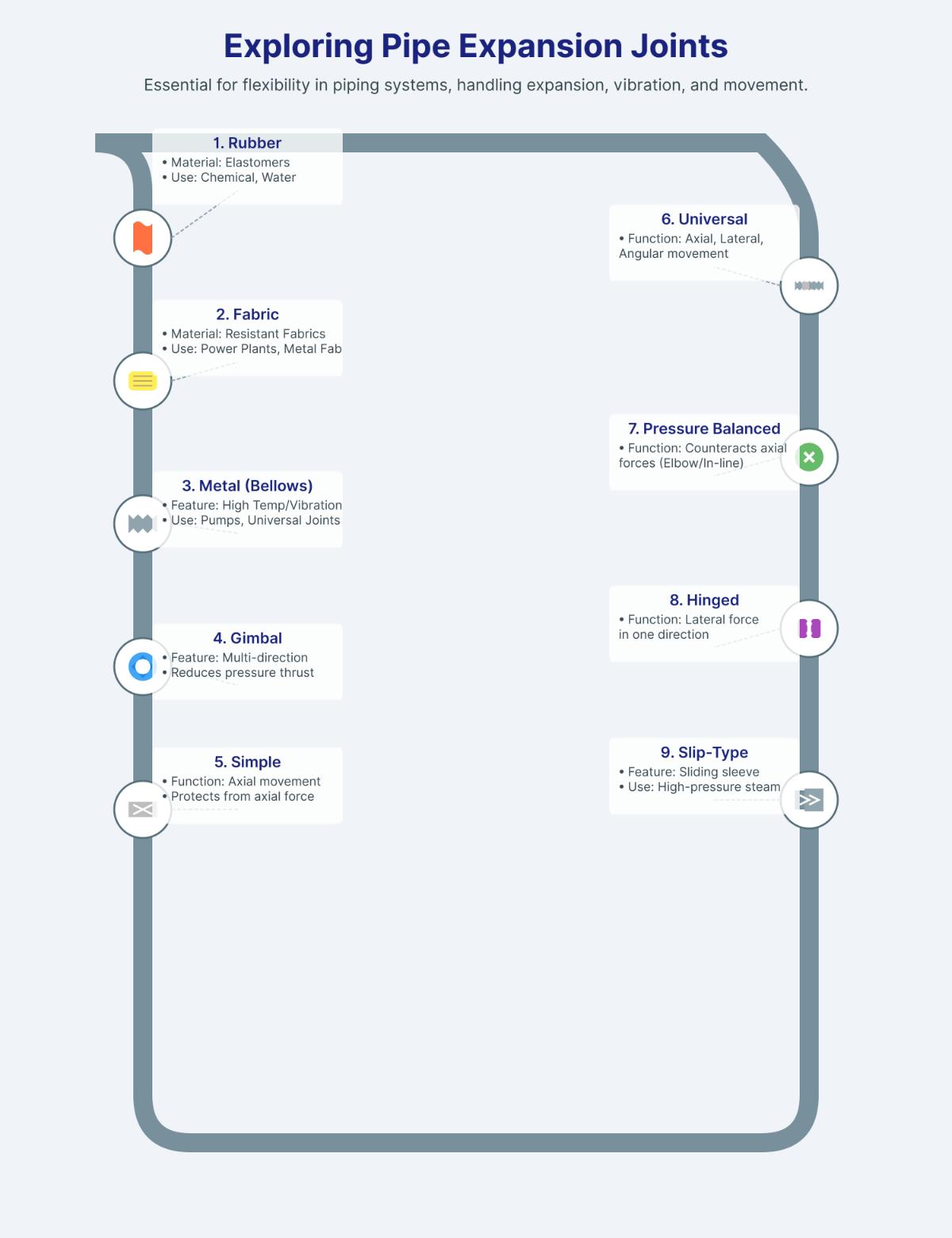
Overview of Pipe Expansion Joints
How Expansion Joints Work in Piping Systems
Mechanism of Action
Expansion joints create a flexible section in an otherwise rigid piping system. This flexibility allows the joint to absorb movements and vibrations, which would otherwise be transferred to the pipes and connected equipment. The specific design and materials used in an expansion joint determine its ability to handle various types of stress and movement.
Types of Movements
- Absorb Axial Movement: Manage lengthwise expansion or contraction.
- Flex Laterally: Handle side-to-side displacement.
- Adjust to Angular Movement: Accommodate bending or angular shifts.
Types of Pipe Expansion Joints
Metal Bellows Expansion Joints
Constructed from corrugated stainless steel or high-performance alloys, metal bellows expansion joints are designed for high-temperature and high-pressure applications. They offer excellent durability and flexibility, making them suitable for industries such as power generation and petrochemical processing.
Rubber Expansion Joints
Made from elastomers like EPDM, neoprene, or nitrile, rubber expansion joints are reinforced with materials like nylon or steel. These joints are ideal for systems with lower pressure and temperature requirements, providing superior vibration absorption and flexibility.
Fabric Expansion Joints
Fabric expansion joints, made from heat-resistant materials like PTFE, fiberglass, or silicone, are typically used in low-pressure, high-temperature environments such as exhaust systems and ducting applications.
Slip-Type Expansion Joints
These joints allow axial movement by sliding one pipe section inside another. They are suitable for compact systems with limited space but require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation.
Pressure-Balanced Expansion Joints
Pressure-balanced expansion joints use multiple bellows to counterbalance internal pressure, ensuring system stability. These joints are essential for unanchored systems, as they absorb axial forces without transferring pressure thrust.
Hinged and Gimbal Expansion Joints
Hinged expansion joints limit motion to a single plane, absorbing angular displacement. In contrast, gimbal expansion joints offer multi-directional flexibility, eliminating pressure thrust and making them suitable for complex piping layouts.
Universal Expansion Joints
Comprising two bellows connected by a central pipe, universal expansion joints are adaptable to various movement requirements, offering versatility in numerous applications.
Applications of Pipe Expansion Joints
Expansion joints are employed across various industries to manage thermal growth, reduce mechanical vibrations, and accommodate misalignment in piping systems. Common applications include:
- Energy Sector: Power plants, nuclear power plants, and district heating systems.
- Petrochemical and Chemical Industries: Oil refineries, pumping stations, and high-temperature systems.
- Process Industries: Sugar factories and pulp and paper industries.
- Construction and HVAC: Managing thermal growth in heating systems.
- Oil and Natural Gas: Refining and distribution lines.
- Wastewater Treatment: Managing corrosive conditions.
- Steel Plants: Controlling mechanical stress.
- LNG/LPG Carriers: Ensuring operational safety and efficiency.
Advantages and Considerations
Advantages
- Absorb Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Prevent excessive stress and potential damage to pipes.
- Reduce Mechanical Vibrations: Mitigate vibration-induced stress and ensure system stability.
- Accommodate Misalignment: Manage movement caused by seismic activity or building settlement.
- Minimize Maintenance Needs: Prolong the lifespan of piping systems by reducing material strain and installation space requirements.
- Cost-Efficiency: Enhance system reliability by mitigating flow turbulence and pressure drops.
Considerations
- Proper Selection and Installation: Crucial for preventing operational downtime, environmental hazards, and significant repair costs.
- Regular Inspections: Essential for detecting visible damage and ensuring safety and efficiency.
Selection Criteria
When choosing an expansion joint, consider factors such as the pipe size, operating temperature, application specifics, movement requirements, and pressure conditions, summarized by the STAMP acronym: Size, Temperature, Application, Movement, and Pressure. Ensuring the right expansion joint is chosen based on these criteria can significantly enhance the reliability, safety, and longevity of piping systems.
Types of Expansion Joints
Selecting the right expansion joint is essential for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of industrial piping systems.
Metal Expansion Joints
Metal expansion joints, often referred to as metal bellows, are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding industries like power generation and petrochemical processing. The different types include:
- Single Unrestrained: Handles axial movement and some lateral deflection.
- Universal: Two bellows connected by a central pipe, accommodating various movements.
- Single Tied: Includes tie rods to limit axial movement while allowing lateral displacement.
- Tied Universal: Combines universal and single tied features for complex movement patterns.
- Pressure-Balanced Elbow: Counterbalances internal pressure to maintain system stability without transferring thrust.
- Gimbal: Allows angular movement in any plane, ideal for complex piping systems.
- Hinged: Restricts motion to a single plane, effectively absorbing angular displacement.
Rubber Expansion Joints
Rubber expansion joints are made from natural or synthetic elastomers and are reinforced with metal or fabric. They are flexible and capable of absorbing vibrations and movements, making them suitable for systems with lower pressure and temperature requirements. Types include:
- Offset: Accommodates misalignment between piping sections.
- Filled Arch: Enhances flexibility and vibration absorption.
- Concentric/Eccentric Reducer: Connects pipes of different diameters.
- Sleeve Type: Simplifies installation and maintenance.
- Spool Type: Provides a broad range of motion and flexibility.
- Wide Arch: Maximizes movement absorption capabilities.
- Bellows: Handles axial movements.
- Spherical: Offers multi-directional flexibility and movement absorption.
Fabric Expansion Joints
Fabric expansion joints are flexible connections made from heat-resistant materials such as PTFE, fiberglass, or silicone, typically used in low-pressure, high-temperature environments. Key characteristics include:
- Single-Layer Designs: Suitable for less demanding applications.
- Multi-Layer Designs: Enhanced resistance to chemicals, heat, and mechanical stress.
- Customizable: Tailored to specific application needs.
Key Considerations for Choosing Expansion Joints
Application Area
Determine the specific industry or application requirements to select the most suitable expansion joint.
Material and Design
Choose materials and designs that can handle the required pressures, temperatures, and movements for the intended application.
Installation and Support
Ensure proper anchoring and support to maintain the efficiency and performance of the expansion joints in the piping system.
In-depth Analysis of Fabric Expansion Joints
Fabric expansion joints are essential for providing flexibility and resilience in industrial piping systems. Constructed from non-metallic materials such as PTFE, silicone, and fiberglass, they are designed to handle a variety of thermal and mechanical stresses.
Flexibility and Temperature Resistance
Fabric expansion joints can absorb movements in multiple directions, including axial, lateral, and angular displacements, accommodating thermal expansion, contraction, and mechanical vibrations. These joints can endure temperatures up to 1300℃, depending on their materials. High-temperature joints are specifically engineered for environments with extreme heat, such as power plants and metallurgical facilities.
Corrosion Resistance
The materials used in fabric expansion joints, such as PTFE and silicone, offer excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals. Their ability to resist corrosive substances makes them ideal for harsh chemical environments, including chemical plants and refineries.
Customization
Fabric expansion joints can be tailored to meet specific requirements in terms of size, shape, and material composition, ensuring optimal performance for unique applications.
Advantages
-
Lightweight and Flexible: Fabric expansion joints are lighter and more flexible than their metallic counterparts, making them easier to install and maintain.
-
Cost-Effective: They typically have lower initial costs and can reduce maintenance expenses due to their durability and ease of replacement.
-
Noise and Vibration Damping: These joints help dampen noise and vibrations, reducing stress on connected equipment and enhancing system performance and longevity.
Disadvantages
-
Limited Pressure Capacity: Fabric expansion joints are generally not suitable for high-pressure applications, as their non-metallic materials may not withstand extreme pressures.
-
Lower Mechanical Strength: Compared to metal expansion joints, fabric joints have lower mechanical strength and may not be suitable for applications requiring high structural integrity.
-
Temperature Limitations: While high-temperature fabric joints exist, they may not perform as well as metal joints in extremely high-temperature environments over extended periods.
Use Cases and Performance Metrics
Fabric expansion joints are utilized in various industries due to their unique properties, including power plants, chemical plants, and refineries. In power plants, they are used in gas, oil, steam, and coal operations to manage thermal expansion and vibrations. In chemical plants, fabric joints handle corrosive chemicals, providing durability and resistance in harsh environments. In refineries, these joints accommodate thermal movements and reduce stress on the piping systems. They are also used in waste incineration plants to manage high-temperature gases and in metallurgical plants to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress during metal processing.
Performance metrics for fabric expansion joints include:
- Temperature Range: The maximum temperature the joint can withstand without degradation.
- Pressure Rating: The maximum operating pressure the joint can handle.
- Movement Capability: The extent of axial, lateral, and angular movements the joint can accommodate.
- Durability: The lifespan of the joint under specific operating conditions, including exposure to chemicals and thermal cycles.
- Installation and Maintenance Ease: How easily the joint can be installed, inspected, and replaced, affecting
Applications of Expansion Joints
Industrial Applications
Expansion joints play a crucial role in various industries by managing thermal expansion, vibrations, and misalignment in piping systems.
Power Generation
In power plants, expansion joints are essential for handling thermal expansion and contraction in high-temperature settings. They are used in steam and gas turbines, boilers, and heat exchangers, ensuring the integrity and efficiency of the power generation process.
Chemical Processing
The chemical industry uses expansion joints to manage corrosive substances and high temperatures. These joints are essential in reactors, heat exchangers, and pipelines transporting aggressive chemicals, providing durability and resistance to chemical attack.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas industry, expansion joints are used in pipelines, refineries, and offshore platforms to manage thermal expansion and vibrations. They ensure the safe transportation of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products, reducing the risk of leaks and system failures.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing plants utilize expansion joints in various processes involving high temperatures and mechanical vibrations. These joints protect equipment and piping systems in steel mills, pulp and paper plants, and automotive manufacturing facilities, enhancing operational efficiency and longevity.
HVAC Systems
HVAC systems greatly benefit from using expansion joints. These components help manage thermal expansion and contraction due to temperature changes, ensuring the proper functioning of air ducts, boilers, and chillers. They also reduce noise and vibrations, contributing to a more comfortable and stable environment.
Piping Systems
Expansion joints are vital in maintaining the integrity of various piping systems. They absorb movements caused by thermal expansion, vibrations, and structural shifts, preventing damage to pipes and connected equipment.
Water and Wastewater Treatment
In water and wastewater treatment facilities, expansion joints accommodate the thermal and mechanical stresses in pipelines, ensuring the efficient transport of water and sewage. They also help manage the corrosive conditions often present in these environments.
Fire Protection Systems
Fire protection systems use expansion joints to handle the thermal expansion of pipes exposed to high temperatures during a fire. These joints ensure the reliability and effectiveness of the system, maintaining the safety of buildings and infrastructure.
Case Studies of Successful Expansion Joint Implementations
Power Plant Efficiency
A case study in a coal-fired power plant demonstrated the effectiveness of metal expansion joints in managing thermal expansion in steam lines. The installation of these joints resulted in reduced maintenance costs and improved system reliability.
Chemical Plant Durability
In a chemical processing facility, PTFE-lined fabric expansion joints provided excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals, leading to a longer lifespan for the piping system and reduced downtime for repairs.
Oil Refinery Safety
An oil refinery implemented rubber expansion joints to absorb vibrations and thermal movements in its pipeline system. This solution enhanced the safety and efficiency of the refinery operations, preventing leaks and reducing maintenance needs.
These examples highlight the diverse applications and benefits of expansion joints across various industries, demonstrating their critical role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of piping systems.
Advanced Applications of Gimbal Expansion Joints
Design and Functionality
Gimbal expansion joints are engineered to absorb angular movements in multiple planes, providing significant flexibility and stress reduction in piping systems. These joints feature two pairs of hinges connected to a floating ring, enabling rotation in all directions. This capability allows gimbal expansion joints to manage complex motion patterns and absorb angular movements common in dynamic piping systems, without imposing excessive stress on the infrastructure.
The hinges and floating ring let these joints rotate freely, handling movements from thermal expansion, seismic activity, or equipment vibrations. This design ensures that the stresses induced by these movements are not transferred to the connected pipes or equipment, thereby enhancing the
Unlike hinged expansion joints that are restricted to single-plane movements, gimbal expansion joints can handle movements in multiple directions. This multi-plane flexibility makes them ideal for complex piping configurations, where movements in various directions must be absorbed simultaneously. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where space constraints or intricate piping layouts necessitate a high degree of movement absorption.
Gimbal expansion joints are often made from durable alloys like stainless steel or nickel-based materials to endure high-pressure and high-temperature environments. These materials provide excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, ensuring the joints perform reliably under extreme conditions. The choice of material is critical to the joint’s ability to handle specific industrial applications, such as those found in power plants and chemical processing facilities.
Key Applications
Power Plants
Gimbal expansion joints are essential in power plant steam lines, where they must endure extreme temperatures and pressures. These joints manage the thermal expansion and contraction cycles that occur during plant operation, preventing stress on the piping system and ensuring continuous, efficient operation. Materials like Inconel and stainless steel are commonly used due to their high-temperature resistance and strength.
Chemical Processing
In the chemical processing industry, gimbal expansion joints must resist corrosive substances while maintaining structural integrity. The joints’ material selection is crucial to ensure compatibility with the chemicals being processed. These joints effectively manage thermal and mechanical stresses, maintaining system integrity and reducing the risk of leaks or failures.
Offshore Platforms
Offshore platforms present harsh marine environments where gimbal expansion joints offer superior flexibility and stress reduction. These joints accommodate the dynamic movements caused by waves, currents, and temperature variations, enhancing the longevity and reliability of the piping systems used in oil and gas extraction and processing.
High-Temperature Gas Turbines
High-temperature gas turbines require expansion joints that can withstand extreme temperatures and multi-axial movements. Gimbal expansion joints made from nickel-based alloys and advanced ceramics are often employed in these applications to ensure durability and performance under the strenuous conditions of turbine operation.
Benefits and Considerations
Gimbal expansion joints significantly reduce the stress on connected piping systems by absorbing angular movements and preventing the transfer of these stresses to the pipes and equipment. This stress reduction contributes to the
By eliminating the need for costly anchors and minimizing installation expenses, gimbal expansion joints provide a cost-effective solution compared to traditional expansion joint types. Their ability to manage complex movements without additional support structures reduces both material and labor costs.
These joints effectively manage thermal growth and contraction, reducing reaction forces within the piping system. This capability is crucial for maintaining system stability and preventing damage due to thermal stresses.
Recent Developments and Trends
Recent advancements in gimbal expansion joint technology focus on optimizing materials and designs to enhance durability and performance in extreme conditions. Innovations such as advanced bellows designs and multi-ply configurations are being adopted to improve flexibility and fatigue resistance in high-pressure applications. The integration of new materials and technologies continues to expand the capabilities of gimbal expansion joints, making them suitable for an even broader range of critical industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Expansion Joint for Specific Piping Systems
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right expansion joint for a piping system involves evaluating key factors to ensure it performs optimally and lasts long.
Media Being Conveyed
The type of fluid or gas passing through the piping system significantly influences the choice of expansion joint. Abrasive or corrosive media may require expansion joints with specific linings or materials that can withstand such conditions. PTFE-lined joints suit highly corrosive environments, while rubber joints are flexible and absorb vibrations, ideal for less aggressive media.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Expansion joints must be capable of handling the system’s pressure and temperature requirements. Metal joints, like those made from stainless steel or Inconel, handle high pressure and temperature due to their durability, while rubber or fabric joints are flexible and easier to install, suited for lower pressure and temperature.
Movement Type and Range
The type and range of movements the expansion joint needs to accommodate is a crucial consideration. These movements can include axial, lateral, and angular displacements. Metal bellows joints are good for axial and lateral movements, while gimbal joints handle multi-directional angular movements. Rubber expansion joints are highly effective in absorbing vibrations and minor misalignments, making them ideal for dynamic systems.
Installation and Environmental Conditions
Space Constraints
The available space for installing the expansion joint can dictate the type of joint selected. For instance, pipe expansion loops require more space but offer long-term reliability and low maintenance. In contrast, slip-type expansion joints are compact but necessitate regular maintenance to prevent leakage.
Environmental Exposure
Consideration of environmental factors, such as exposure to UV rays, chemicals, or mechanical wear, is essential. For outdoor installations exposed to sunlight, UV-resistant materials should be chosen to prevent degradation. In chemical plants, joints made from materials resistant to specific chemicals are necessary to ensure durability and safety.
Standards Compliance
Ensuring that the selected expansion joint complies with industry standards and regulations is vital for safety and performance. Standards such as the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code or the EJMA (Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association) guidelines provide benchmarks for design, manufacturing, and testing of expansion joints. Compliance with these standards ensures that the joints can withstand the specified operating conditions and meet safety requirements.
Efficiency and Durability
Maintenance Requirements
The maintenance needs of different expansion joints vary significantly. Metal expansion joints generally require minimal maintenance but must be monitored for signs of fatigue or corrosion. Rubber expansion joints might need more frequent inspections due to their susceptibility to wear and tear. Opting for a joint that needs less maintenance can cut long-term costs and minimize downtime.
Lifecycle Costs
Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase, installation, and maintenance expenses, is critical. While metal expansion joints may have higher upfront costs, their durability and low maintenance can make them more cost-effective over time. Rubber and fabric expansion joints may be less expensive initially but might incur higher maintenance and replacement costs.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can select the most suitable expansion joint for their specific piping systems, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
Interactive Tools for Expansion Joint Selection
Online Selection Tools
Online selection tools make it easy to find the right expansion joint for your needs. These tools typically feature interactive interfaces where users can input various parameters related to their piping systems, such as size, pressure, temperature, and movement requirements. Based on these inputs, the tool provides recommendations for the type and specifications of expansion joints that best meet the system’s needs. For example, Bellows Design Software assists in designing metal bellows expansion joints by allowing users to input detailed parameters such as axial, lateral, and angular movements, pressure, and temperature.
Example Tools
-
Bellows Design Software: This software aids in designing metal bellows expansion joints by letting users input detailed parameters, including axial, lateral, and angular movements, pressure, and temperature. The software then calculates the appropriate bellows design, considering factors like material selection and fatigue life.
-
Rubber Joint Configurators: These tools help users choose rubber expansion joints by asking questions about the environment, such as media type, pressure, and temperature. The tool then recommends suitable products with technical specs and installation advice.
User Guides and Tutorials
Comprehensive user guides and tutorials are invaluable for selecting and installing expansion joints. These materials often provide step-by-step instructions, detailed explanations of different types of expansion joints, and best practices for installation and maintenance.
Notable Resources
-
Manufacturer Manuals: Manufacturers provide detailed manuals covering product selection, installation, and maintenance. These guides often include troubleshooting tips and diagrams to help users install and maintain expansion joints correctly.
-
Video Tutorials: Online video tutorials offer visual and practical guidance on the selection and installation of expansion joints. These videos can demonstrate proper handling techniques, show real-world application examples, and provide insights into common issues and solutions.
Accessing Professional Assistance
For more complex or critical applications, consulting with experienced engineers or industry experts ensures that the selected expansion joint meets all operational requirements. Professional assistance can provide tailored solutions that account for unique system specifications and potential challenges.
Consultation Services
-
Technical Support Lines: Many manufacturers and suppliers offer technical support services where users can speak directly with engineers to discuss their specific needs and receive recommendations.
-
On-Site Evaluations: Some companies offer on-site evaluations where experts assess the system’s conditions and needs, providing tailored solutions and ensuring proper installation of expansion joints.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the different types of pipe expansion joints?
Pipe expansion joints are critical components in piping systems, designed to accommodate thermal expansion, vibrations, and other movements that could otherwise damage the pipes. There are several types of pipe expansion joints, each suited for specific applications and conditions:
- Rubber Expansion Joints: Made from elastomers like EPDM and Neoprene, these joints are flexible and durable, ideal for applications in chemical processing, water waste, and mining.
- Fabric Expansion Joints: Constructed from materials that resist chemical, thermal, and mechanical stresses, these are used in power plants and metal fabrication.
- Metal Expansion Joints (Metal Bellows): Suitable for high-temperature and vibration environments, such as in pump connectors and universal joints.
- Gimbal Expansion Joints: Allow movement in multiple directions, reducing pressure thrust and providing extensive flexibility.
- Simple Expansion Joints: Absorb axial forces to protect pipes from axial movement.
- Universal Expansion Joints: Comprising two bellows and a center pipe, they handle axial, lateral, and angular movements.
- Pressure Balanced Expansion Joints: Designed to counteract axial forces, available in elbow or in-line configurations.
- Hinged Expansion Joints: Address lateral forces in one direction with a hinge near the bellows.
- Slip-Type Expansion Joints: Feature a sliding sleeve to manage axial movements in high-pressure steam systems.
Each type is designed to address specific needs within a piping system, ensuring efficiency and durability.
How do expansion joints work in piping systems?
Expansion joints in piping systems are designed to manage and absorb movements caused by thermal expansion, contraction, vibrations, and other mechanical stresses. These movements can occur due to temperature fluctuations, shifting foundations, or external forces. Expansion joints provide a flexible interface between adjacent pipe sections or between pipes and other components, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the system.
When temperature changes cause pipes to expand or contract, the expansion joints accommodate this movement, preventing potential damage such as pipe rupture or joint separation. They absorb and distribute mechanical stresses, which helps maintain the system’s When temperature changes cause pipes to expand or contract, the expansion joints accommodate this movement, preventing potential damage such as pipe rupture or joint separation. They absorb and distribute mechanical stresses, which helps maintain the system’s integrity and prolong its lifespan.
What are the applications of gimbal expansion joints?
Gimbal expansion joints are specialized components designed to absorb angular movements in multiple planes within piping systems. They are particularly suited for applications where multidirectional movement compensation is necessary.
Common applications of gimbal expansion joints include industrial piping networks, such as those found in shipbuilding and large-scale industrial environments, where their ability to handle complex movements helps maintain system integrity.
Additionally, they are used in power plants and refineries for specific movement requirements and in chemical processing facilities where they can manage the demands of complex movement while ensuring system stability. Gimbal expansion joints help mitigate stress on pipelines and effectively dampen vibrations, thus protecting the pipeline and associated equipment from potential damage.
What are the benefits of using fabric expansion joints?
Fabric expansion joints offer several benefits, making them highly valuable in various industrial applications. Their primary advantage lies in their flexibility and versatility. These joints can absorb movements in multiple directions, accommodating thermal expansions and contractions due to temperature fluctuations. Additionally, they can be customized to fit specific size requirements, which is particularly useful in tight installations.
Another significant benefit is their thermal and chemical resistance. Fabric expansion joints are constructed from high-quality, reinforced materials that withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals, thus ensuring longevity and durability. They also excel in noise reduction and vibration isolation, mitigating the impact of vibrations and reducing noise levels, which helps extend the lifespan of connected equipment.
Moreover, fabric expansion joints require less maintenance compared to their metal counterparts, as they do not need regular lubrication or tightening. This contributes to their cost-effectiveness, offering a budget-friendly solution with a longer functional lifespan. Their easy installation and inspection further enhance their practicality, allowing for quick identification and resolution of potential issues.
How can I choose the right expansion joint for my system?
To choose the right expansion joint for your system, you must consider several key factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity. First, determine the size and movement requirements by assessing the nominal bore size and the types of movements (axial, lateral, angular) the joint needs to accommodate. Next, evaluate the pressure conditions, including operating, design, surge, and test pressures, and select materials that can handle these pressures, especially at high temperatures.
Consider the medium that will flow through the joint, ensuring compatibility with the fluid or gas. Abrasive materials may necessitate special linings or thicker tubes. Temperature range is another critical factor; select materials suitable for the system’s minimum and maximum temperatures. Installation and environmental conditions also play a role; account for space constraints, accessibility, UV exposure, chemical exposure, and mechanical wear.
Ensure material compatibility with both the conveyed medium and environmental conditions, and comply with relevant regulatory standards, such as the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) in the EU. Additional hardware, like limiting rods or control units, can help prevent overextension and stabilize joints in high-pressure or vibrating systems. Consulting with experts and using online selection tools can further aid in making the right choice for your specific piping system needs.
Are there any tools available to help with expansion joint selection?
Yes, several tools are available to assist with expansion joint selection. One notable example is the BelMaker Light software developed by Belman. This free tool provides advanced features to select expansion joints based on multiple parameters, including searchable resistance tables and flange tables, ensuring precise calculations.
Additionally, selection criteria such as the acronym STAMPED (Size, Temperature, Application, Movement, Pressure/Vacuum, End Fittings, Delivery) can help gather detailed application information to choose the appropriate joint.
Expert consultation is also valuable, as technical experts can provide insights, conduct pipe stress analyses, and ensure compliance with industry standards like ASME and EJMA. These resources and guidelines help optimize system performance and extend the life of the components.
