Imagine the inner workings of machinery held together by a small yet powerful component, ensuring stability and preventing loosening under stress. This is the essence of the prevailing torque lock nut, a critical element in engineering and construction. In this technical deep dive, we’ll explore how these specialized nuts function, the distinctions between all-metal and nylon insert types, and their prominent role across various industries. By understanding their properties and uses, you’ll gain insight into why prevailing torque lock nuts are indispensable in maintaining the integrity of mechanical assemblies. Ready to uncover the mechanics and advantages of these versatile fasteners? Let’s dive in.
What is a Prevailing Torque Lock Nut?
Introduction to Prevailing Torque Lock Nuts
Prevailing torque lock nuts are essential in mechanical assemblies that require secure fastening under dynamic conditions. These specialized nuts are designed to resist loosening when subjected to vibrations or rotational forces, ensuring the stability and integrity of the assembly.
Design and Mechanism
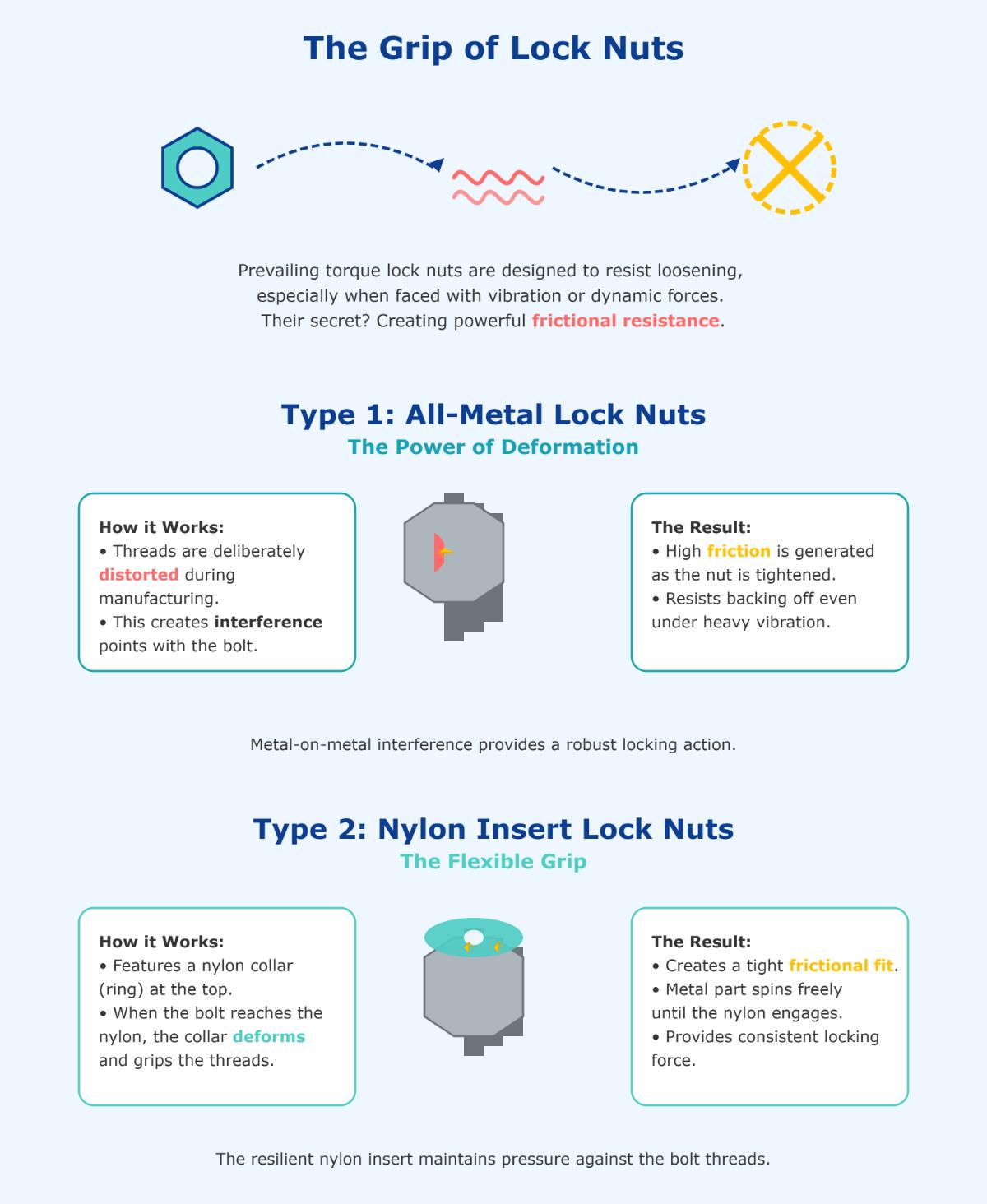
Prevailing torque lock nuts achieve their locking capability through the creation of a consistent frictional force. This is accomplished by either deforming the threads of the nut or using an insert that creates interference with the bolt threads. The friction generated by these methods prevents the nut from backing off, even under significant vibration or dynamic loads.
Thread Distortion
In all-metal lock nuts, thread distortion is a common technique where the threads are intentionally deformed to create an interference fit with the bolt threads, increasing the frictional force needed to rotate the nut. This method is particularly effective in high-temperature applications where materials like nylon might not perform well.
Nylon Insert
Nylon insert lock nuts use a slightly undersized nylon collar that creates a tight, frictional fit with the bolt threads when tightened. This type of lock nut is especially useful in applications where vibration is a concern, as the nylon insert provides a consistent locking force over repeated installations.
Key Characteristics
Prevailing torque lock nuts exhibit several important characteristics:
- Vibration Resistance: These nuts are specifically engineered to withstand high levels of vibration, making them ideal for use in environments where equipment is subject to dynamic forces.
- Reusable: While not intended for indefinite reuse, prevailing torque lock nuts can often be used multiple times without significant loss of their locking ability, provided they are not subjected to excessive wear or damage.
- Corrosion Resistance: Many prevailing torque lock nuts are manufactured from materials like stainless steel or coated with corrosion-resistant finishes, ensuring durability in harsh environments.
- Ease of Installation: These nuts can be installed with standard tools, making them a convenient choice for a wide range of applications.
Applications
Prevailing torque lock nuts are used in various industries due to their reliable performance under challenging conditions. They are essential in the automotive industry for engine mounts and suspension systems, in the aerospace industry for securing aircraft parts, in construction for structural elements, and in agricultural equipment for consistent performance under vibration.
By understanding the design, mechanism, and applications of prevailing torque lock nuts, engineers and technicians can make informed decisions about their use in various mechanical assemblies. These nuts play a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of connections in numerous demanding environments.
How Do Prevailing Torque Lock Nuts Work?
Mechanism of Operation
Prevailing torque lock nuts work by creating frictional resistance that prevents them from loosening due to vibrations and dynamic loads. This resistance is achieved either by distorting the threads of the nut or using inserts that generate frictional interference with the bolt threads.
Localized Plastic Deformation and Interference Fit
All-metal lock nuts often employ localized plastic deformation and interference fit to create frictional resistance. In localized plastic deformation, the threads of the nut are intentionally distorted to create points of interference with the bolt threads. This deformation results in increased friction as the nut is threaded onto the bolt, generating a prevailing torque that resists rotation. The interference fit is achieved by designing the threads of the lock nut with negative clearance relative to the bolt threads, ensuring continuous contact and deflection during installation. This tight grip prevents the nut from loosening under vibration.
Continuous Sliding
As the nut is installed, the thread surfaces slide across each other, smoothing out minuscule asperities and contributing to the frictional forces that maintain the locking effect. This continuous sliding action helps maintain a stable connection, ensuring the prevailing torque remains effective over time. The sliding also aids in distributing the load evenly across the threads, reducing the risk of localized wear and tear.
Types of Prevailing Torque Lock Nuts
Prevailing torque lock nuts come in various designs, each utilizing different mechanisms to achieve the desired locking effect. The two primary types are nylon insert lock nuts and all-metal lock nuts.
Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
Nylon insert lock nuts have a nylon collar that deforms when the bolt threads engage, creating a tight fit that prevents loosening. The metal part of the nut remains free-spinning until the nylon ring engages, providing a consistent locking force over repeated installations. Nylon insert lock nuts are particularly effective in applications where vibration is a concern, as the nylon material maintains its integrity and frictional properties over multiple uses.
All-Metal Lock Nuts
All-metal lock nuts achieve their locking capability through mechanical interference, often utilizing thread deformation or serrations. These nuts are designed to create a secure lock by distorting the threads or using serrated surfaces that interfere with the bolt threads. All-metal lock nuts are ideal for high-temperature applications where nylon inserts might not perform well. They offer high resistance to vibration and are suitable for critical assemblies requiring robust connections.
Prevailing Torque Decay and Variation
Over time, repeated tightening and loosening of prevailing torque lock nuts can lead to prevailing torque decay. This occurs as the thread surfaces smooth out, reducing the interference fit and causing the prevailing torque to decrease. The rate of decay depends on factors such as material hardness and the extent of interference.
Variations in manufacturing tolerances and material properties can also affect the prevailing torque levels. These variations must be considered during the design and assembly processes to ensure reliable performance. Engineers must account for potential torque variation to maintain the integrity of the assembly.
Applications and Benefits
Prevailing torque lock nuts are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing due to their exceptional vibration resistance and secure fastening capabilities.
- Resistance to loosening: Reliable against vibration-induced loosening.
- Ease of installation: Can be installed with standard tools.
- Corrosion resistance: Made from materials like stainless steel for harsh environments.
Technical Considerations for Installation and Maintenance
When installing prevailing torque lock nuts, it is essential to ensure clean threads and use the correct lock nut for the application. Avoid over-tightening to prevent damage to the threads and maintain the effectiveness of the lock nut. For all-metal types, consider their reusability, as their locking capability may decline with repeated use. Proper installation and maintenance practices are crucial for maximizing the performance and longevity of prevailing torque lock nuts in various applications.
Types of Lock Nuts
Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
Nylon insert lock nuts incorporate a nylon ring within the top section of the nut. The nylon ring is slightly undersized compared to the nut’s inner diameter, ensuring a tight and frictional fit when threaded onto a bolt. The primary advantages of nylon insert lock nuts include:
- Vibration Resistance: The nylon insert provides a consistent locking force, preventing the nut from loosening under vibrations.
- Reusability: These nuts can be reused multiple times, although the nylon insert may wear out after repeated installations.
- Chemical and Temperature Sensitivity: Nylon insert lock nuts are not suitable for high-temperature environments or applications where they might be exposed to chemicals that could degrade the nylon material.
All-Metal Lock Nuts
All-metal lock nuts achieve their locking mechanism through metal-to-metal interference. These nuts, which do not rely on additional materials like nylon, are suitable for high-temperature and chemically challenging environments. Key features include:
- Thread Deformation: The nut’s threads are designed to deform slightly, creating a tight fit that increases friction and prevents loosening.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Since they are entirely metal, these nuts can withstand extreme temperatures without losing their locking capability.
- Durability: All-metal lock nuts are highly durable and can be used in harsh environments where other types of lock nuts might fail.
Serrated Flange Lock Nuts
Serrated flange lock nuts feature a serrated flange on one side, which bites into the mating surface to provide additional resistance to loosening. This design eliminates the need for a separate lock washer and distributes the bearing load over a larger area. The main benefits include:
- Increased Surface Area: The flange increases the contact area with the mating surface, reducing the risk of damage and ensuring a more secure connection.
- Vibration Resistance: The serrations bite into the surface, preventing the nut from loosening due to vibrations.
- Ease of Installation: These nuts can be installed using standard tools, simplifying the assembly process.
Tension-Induced Lock Nuts (Free-Spinning Lock Nuts)
Tension-induced lock nuts, or free-spinning lock nuts, secure themselves through a wedging action once fully seated. Before reaching this point, they spin freely, making them easy to install on long threaded assemblies. The key characteristics include:
- Free-Spinning Nature: These nuts do not create significant resistance until they are fully seated, allowing for easy and quick installation.
- Wedging Action: Once seated, the nuts lock into place through a wedging action, providing a secure connection.
- Ideal for Long Assemblies: Their free-spinning nature makes them particularly suitable for applications involving long threaded rods or bolts.
Choosing the Right Lock Nut
Selecting the appropriate lock nut depends on various factors, including the operating environment, the length of the threaded assembly, and specific application requirements. Nylon insert lock nuts are excellent for applications with moderate temperatures and vibrations, while all-metal lock nuts are better suited for high-temperature and chemically harsh environments. Serrated flange lock nuts are ideal for applications requiring increased surface contact and resistance to loosening, and tension-induced lock nuts offer ease of installation for long threaded assemblies.
Comparison: All-metal vs. Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
Design and Material Composition
All-metal lock nuts and nylon insert lock nuts differ significantly in their design and material composition, which impacts their functionality and suitability for various applications.
All-Metal Lock Nuts
All-metal lock nuts are made entirely from metal, providing high resistance to temperature and corrosion. The locking mechanism often involves thread deformation or serrations that create frictional interference with the bolt threads. This design is particularly effective in high-temperature environments and corrosive conditions, making all-metal lock nuts ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to extreme conditions.
Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
Nylon insert lock nuts have a metal body with a nylon ring embedded within, which grips the bolt threads when tightened. This design provides a reliable locking mechanism that is effective in preventing loosening due to vibration. However, the nylon material is sensitive to high temperatures and chemicals, which can degrade its effectiveness over time.
Temperature and Corrosion Resistance
The ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion is a critical factor when choosing between all-metal and nylon insert lock nuts.
Temperature Resistance
All-metal lock nuts can withstand temperatures above 350°F, making them suitable for high-temperature applications where nylon insert lock nuts, limited to around 350°F, would fail.
Corrosion Resistance
All-metal lock nuts offer excellent resistance to corrosion and environmental factors such as UV exposure and salt, which makes them ideal for harsh environments. Nylon insert lock nuts are less resistant to chemicals and UV exposure, and prolonged exposure can degrade the nylon insert, reducing the nut’s effectiveness.
Reusability
The reusability of lock nuts is an important consideration for applications that require multiple installations and removals.
All-Metal Lock Nuts
Due to the potential for thread wear caused by frictional interference, all-metal lock nuts are less likely to be reused multiple times without losing their locking effectiveness. The thread deformation that provides the locking mechanism can wear out over repeated use, making these nuts less suitable for applications requiring frequent disassembly and reassembly.
Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
Nylon insert lock nuts can be reused several times because the nylon ring deforms instead of the metal threads. This makes them more suitable for applications where repeated installations are necessary. However, the nylon insert may wear out over time, especially under high-stress conditions.
Sealing Properties
The ability to provide a moisture and gas seal can be a deciding factor in choosing the right lock nut for specific applications.
All-Metal Lock Nuts
All-metal lock nuts do not provide sealing against moisture or gases. Their design focuses on creating a secure lock through thread deformation, which does not offer any sealing properties.
Nylon Insert Lock Nuts
Nylon insert lock nuts have the advantage of providing a gas and moisture seal due to the nylon ring. This can be beneficial in applications where preventing rust and corrosion within the assembly is important, adding an extra layer of protection to the connection.
Mechanism of Locking
The mechanism by which lock nuts achieve their locking capability varies between all-metal and nylon insert types.
Frictional Interference (All-Metal Lock Nuts)
All-metal lock nuts create frictional interference through thread deformation or serrations. This interference increases the friction between the nut and bolt threads, preventing the nut from backing off under vibration and dynamic loads. This mechanism is robust and effective in high-temperature applications.
Nylon Insert Engagement (Nylon Insert Lock Nuts)
Nylon insert lock nuts use a nylon ring that engages with the bolt threads to create prevailing torque. The nylon material bites into the threads, providing a consistent locking force over repeated installations. This makes them particularly effective in applications where vibration is a concern.
Technical Specifications of Prevailing Torque Lock Nuts
Key Features and Specifications
Prevailing torque lock nuts are engineered to prevent loosening in mechanical assemblies subjected to vibrations and dynamic forces. Their design and specifications ensure optimal performance in various applications.
Mechanism
Prevailing torque lock nuts lock in place using two main mechanisms: thread distortion and coatings or inserts. The threads of the nut are deliberately deformed to create an interference fit with the bolt threads, generating a consistent frictional force that prevents loosening. Some lock nuts also use coatings or inserts, such as nylon, to enhance friction. All-metal prevailing torque lock nuts rely solely on thread distortion, while nylon insert lock nuts use a nylon collar to create frictional resistance.
Materials and Grades
Materials for prevailing torque lock nuts are chosen based on their suitability for various applications and environments. Commonly used materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and occasionally copper, offering varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. These nuts are available in various grades, such as 4.8, 6.8, 8.8, and 10.9, indicating the nut’s tensile strength and compatibility with specific bolt strengths. For example:
- Grade A: Suitable for bolts with tensile strength not greater than 90 ksi.
- Grades B and F: Suitable for bolts with tensile strength not greater than 120 ksi.
- Grade C: Suitable for bolts with tensile strength between 105 and 150 ksi.
- Grade G: Suitable for bolts with tensile strength between 120 and 150 ksi.
Compatibility
Ensuring the lock nut and bolt are compatible is essential for a secure assembly. Each grade of nut is recommended for use with bolts of specific minimum tensile strengths. Using bolts of equal or higher grade than the nut minimizes the risk of thread damage and ensures a secure connection. Proper matching of the nut and bolt grades is crucial to maintaining the assembly’s strength and durability.
Applications
Prevailing torque lock nuts are widely used across various industries due to their ability to withstand vibration-induced loosening. They are commonly found in aerospace, automotive, industrial, and electronics sectors, where vibration resistance is critical. These nuts are ideal for shorter assemblies that require immediate resistance to loosening, though they are not recommended for long assemblies as extended use can damage the locking feature.
Surface Treatments
To enhance the performance and longevity of prevailing torque lock nuts, various surface treatments are applied. Options include zinc plating, nickel plating, passivation, and other coatings, which improve corrosion resistance and appearance, making the nuts suitable for harsh environments.
Torque Requirements
The torque required for tightening and loosening prevailing torque lock nuts is a key consideration. These nuts need significant torque for both installation and removal, so care must be taken to avoid damaging the threads. The break-loose torque, the torque needed to start loosening the nut when it’s fully tightened, ensures the nut stays secure under dynamic conditions.
Choosing the Right Prevailing Torque Lock Nut
Selecting the appropriate prevailing torque lock nut involves considering several factors, including the specific needs of the application, such as bolt strength, assembly length, and environmental conditions. Understanding the technical specifications ensures that the selected lock nut provides optimal performance and durability for the mechanical assembly.
Applications and Uses of Prevailing Torque Lock Nuts
Automotive Industry
Prevailing torque lock nuts are integral to the automotive industry, where they are used to secure components that experience significant vibration and dynamic loads. They are crucial for securing engine mounts, suspension systems, and steering mechanisms. Their ability to maintain a tight grip under high-stress conditions makes them invaluable in ensuring vehicle stability and safety. Additionally, they are widely used in trucks and semi-trucks, providing the necessary stability in high-vibration environments.
Aerospace Sector
In the aerospace industry, prevailing torque lock nuts are critical for maintaining the structural integrity of aircraft. They are used to secure various components, including fuselage sections, landing gear, and engine mounts. Their vibration resistance and high strength help them withstand extreme flight conditions, such as rapid changes in pressure and temperature.
Construction Industry
The construction industry relies on prevailing torque lock nuts to stabilize structural elements and metal frameworks. These nuts offer the durability and reliability needed to support heavy loads and resist loosening from machinery vibrations and environmental factors. They are commonly used in the assembly of steel structures, bridges, and heavy equipment.
Agricultural Sector
In the agricultural sector, machinery and equipment are often subjected to dynamic conditions and vibrations. They enhance machine reliability by securing critical components. Prevailing torque lock nuts are used in tractors, harvesters, and other agricultural equipment to ensure consistent performance and minimize the risk of mechanical failures in the field.
Metalworking and Manufacturing
Manufacturing and metalworking industries benefit from the use of prevailing torque lock nuts in securing equipment and machinery components. These nuts provide the necessary vibration resistance to maintain the integrity of assemblies, even under the high-speed operations of manufacturing processes. They are essential in applications such as conveyor systems, presses, and robotic assemblies.
Electrical Installations
In electrical installations, prevailing torque lock nuts are used to secure various components and prevent loosening due to vibrations. This is particularly important in environments where electrical systems are subject to mechanical vibrations, such as in industrial facilities and transportation systems. The secure fastening provided by these nuts ensures the reliability and safety of electrical connections.
Furniture Industry
The furniture industry utilizes prevailing torque lock nuts to enhance the stability and durability of furniture, especially in heavy or dynamic uses. These nuts are used in the assembly of office furniture, seating systems, and other structures that require robust connections to withstand repeated use and movement.
Marine Applications
Marine environments require fasteners that resist corrosion and maintain secure connections despite constant exposure to water and salt. Prevailing torque lock nuts, often made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel, are ideal for marine applications. They are used in boat construction, dock assemblies, and other marine equipment to ensure long-lasting, reliable fastening.
Road and Highway Signage
Prevailing torque lock nuts are crucial for securing road and highway signage, which must withstand wind and vibration from passing traffic. These nuts provide the necessary stability to ensure that signs remain securely fastened, contributing to road safety and effective traffic management.
Heavy Machinery
In heavy machinery applications, prevailing torque lock nuts are used to secure components that experience significant vibration and dynamic loads. They are found in construction equipment, mining machinery, and industrial machines, where their ability to resist loosening under harsh conditions is essential for operational safety and efficiency.
Case Studies
Loosening Under Combined Loads
Prevailing torque lock nuts are engineered to resist loosening in dynamic conditions. However, studies have shown that these nuts can fail under combined axial and transverse loads, as revealed by research from Bolt Science and the University of Central Lancashire. When the axial load exceeds the preload of the nut, it generates a loosening torque. This torque can keep turning the nut until it eventually comes off. This phenomenon underscores the importance of considering the combined effects of different load types when designing assemblies that use prevailing torque lock nuts.
Wear-Out of Prevailing Torque Lock Nuts
The longevity of the locking feature in prevailing torque lock nuts is a critical factor for their performance. A study by Adam Zimandy examined how long these nuts last, focusing on both all-metal and nylon insert types. The research indicated that nylon insert lock nuts generally have a longer reuse life compared to their all-metal counterparts.
However, the study also found that the performance of nylon insert lock nuts can be adversely affected by lubrication, which reduces the frictional resistance created by the nylon collar. This insight is crucial for applications where repeated use and lubrication are common, as it affects the overall reliability and safety of the fastening system. Engineers and maintenance professionals must consider these findings when selecting the appropriate type of lock nut for their specific applications.
Vibration-Induced Loosening
Prevailing torque lock nuts are specifically designed to prevent loosening due to vibrations. Despite this, practical applications have demonstrated that these nuts are not entirely foolproof. A detailed study on vibration-induced loosening showed that prevailing torque lock nuts could still experience nut-bolt separation under certain conditions. The standard tests, such as the DIN 65151 test, do not always capture the unforeseen factors that contribute to this loosening. Real-world conditions often present variables that standard tests cannot replicate, making it essential to consider additional testing and design measures to ensure the reliability of these lock nuts in critical applications.
Safety-Critical Applications
Prevailing torque lock nuts are commonly used in safety-critical applications across various industries. Despite their widespread use, the failure to prevent nut-bolt separation under certain conditions poses significant risks. In industries like automotive and aerospace, the loosening of these nuts can lead to dangerous failures, putting lives at risk and causing significant financial damage. The importance of understanding the limitations and potential failure modes of prevailing torque lock nuts cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the safety and reliability of the assemblies in which they are used.
Improvement Measures
To enhance the performance and reliability of prevailing torque lock nuts, researchers suggest several improvement measures. One approach is to develop more robust testing standards that better simulate real-world conditions. This could involve creating new test protocols that account for the combined effects of axial and transverse loads, as well as more realistic vibration profiles. Additionally, modifications to fastener finishes and lubrication practices can help reduce the variability in friction, thereby improving the consistency and integrity of the bolted joints. Implementing these improvements can significantly enhance the effectiveness of prevailing torque lock nuts in various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
How do prevailing torque lock nuts work?
Prevailing torque lock nuts work by creating frictional resistance that prevents them from loosening under conditions of vibration and dynamic forces. This is achieved through two primary mechanisms: localized plastic deformation and interference fits. In all-metal lock nuts, the threads are intentionally distorted to create interference points with the mating part, such as a bolt, generating frictional resistance as the nut is threaded on.
In nylon insert lock nuts, the resistance is created by a nylon collar that deforms when the bolt threads engage it, producing a frictional fit. This design ensures that the metal part of the nut remains free-spinning until the nylon ring is engaged. These mechanisms ensure that the nuts maintain a secure connection even in demanding applications.
What are the advantages of using all-metal versus nylon insert lock nuts?
All-metal lock nuts and nylon insert lock nuts each have distinct advantages based on their design and material properties. All-metal lock nuts offer high temperature resistance, making them suitable for applications exceeding 350°F where nylon would degrade. They also provide excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as UV and salt exposure, making them ideal for marine or outdoor use.
On the other hand, nylon insert lock nuts are beneficial for their sealing properties, providing a gas and moisture seal that helps prevent rust and simplifies disassembly. They are generally more cost-effective and offer good vibration resistance, as the nylon creates friction to prevent loosening.
Additionally, nylon insert nuts can be reused more than all-metal nuts, which typically become unusable after a single use due to thread deformation. The choice between these types depends on specific application requirements, including temperature, corrosion resistance, reusability, and cost considerations.
In which industries are prevailing torque lock nuts commonly used?
Prevailing torque lock nuts are commonly used in various industries where securing components under high vibration and dynamic forces is essential. In the automotive industry, they are used in engine assemblies, suspension systems, and steering mechanisms to ensure components remain fastened despite constant vibrations. The aerospace sector relies on these nuts for critical parts like fuselage and landing gear due to their ability to withstand high stresses. In construction, they maintain the stability of structural elements and metal frameworks. Agricultural machinery also benefits from their vibration resistance.
Additionally, these nuts are vital in manufacturing, metalworking, electrical installations, furniture, marine applications, heavy machinery, and military sectors due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and reliable locking capabilities.
What are the technical specifications of prevailing torque lock nuts?
Prevailing torque lock nuts are designed to resist loosening under vibration and dynamic loads. They achieve their locking capability through an internal design that generates friction by distorting the top threads, typically ovalizing them to grip the bolt threads firmly.
Technical specifications of prevailing torque lock nuts include:
-
Grades and Compatibility: These nuts are available in various grades:
-
Grade A: For bolts with tensile strengths up to 90 ksi.
-
Grades B and F: For bolts with tensile strengths up to 120 ksi.
-
Grade C: For bolts with tensile strengths between 105 ksi and 150 ksi.
-
Grade G: For bolts with tensile strengths between 120 ksi and 150 ksi.
-
Material and Mechanical Properties: They are made from materials like stainless steel (e.g., 18-8). The hardness can vary, with some grades specifying a maximum Rockwell hardness of C28. Proof load stress ranges from 90,000 psi to 150,000 psi depending on size and grade.
These specifications ensure that prevailing torque lock nuts are suitable for applications requiring reliable resistance to loosening in shorter threaded assemblies and fragile components.
How do I choose the right type of lock nut for my application?
Choosing the right type of lock nut for your application involves evaluating several critical factors to ensure optimal performance, stability, and longevity of the mechanical assembly. First, consider the application environment, including exposure to high temperatures, chemicals, or vibrations, and select a lock nut material that can withstand these conditions. Common materials include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and nylon for vibration dampening.
Next, assess the locking mechanism suitable for your needs. Prevailing torque lock nuts provide immediate resistance to loosening and are ideal for short assemblies, while nylon insert lock nuts offer excellent vibration resistance but are less reusable. For long threaded assemblies, tension-induced lock nuts may be more appropriate due to their free-spinning nature.
Additionally, ensure the thread type and size match the mating component to avoid incompatibility issues. Evaluate the mechanical load requirements and select a lock nut that can handle the necessary strength. Consider the need for reusability, as some lock nuts, like nylon inserts, are not suitable for repeated use.
Can you provide examples of prevailing torque lock nuts in use?
Prevailing torque lock nuts are used in various industries where resistance to loosening due to vibrations is crucial. In the automotive industry, they are employed in engine mounts, suspension systems, and wheel hubs to ensure components remain secure under dynamic conditions.
In aerospace, these lock nuts are vital for maintaining the integrity of aircraft components such as the fuselage and landing gear, where reliability under high-stress conditions is essential. The construction industry uses them to stabilize structural frameworks, while agricultural machinery benefits from their ability to withstand vibrations.
Additionally, they are used in metalworking, manufacturing, electrical installations, and marine applications, where secure and reliable fastening is necessary.
