Steel, a backbone of modern infrastructure and industries, has a dynamic market influenced by a myriad of factors. As we move through 2023, understanding the fluctuating prices and emerging market trends becomes crucial for stakeholders. Have you ever wondered how the global demand for steel impacts its price, or what the forecasts suggest for steel production in the near future? This article delves into the current steel price trends, analyzing data to uncover the key drivers and economic influences shaping the market. From regional demand variations to the impact of new technologies on production, we provide a comprehensive overview to help you navigate the complexities of the steel industry. Ready to unravel the intricacies behind these trends and their implications? Let’s dive in.
Current Steel Price Trends
Steel price is the market cost of steel, an essential economic indicator affecting industries like construction, manufacturing, and automotive. It influences the cost of production for companies using steel as a raw material, thereby impacting overall market competitiveness, profitability, and economic growth.
Several factors influence steel price, including supply and demand dynamics, raw material costs, production capacity, economic conditions, trade policies, energy costs, and technological advancements. Raw material costs, such as iron ore, coal, and scrap metal, directly impact steel production expenses. An increase in demand or a decrease in supply can lead to higher prices, while the opposite can reduce them.
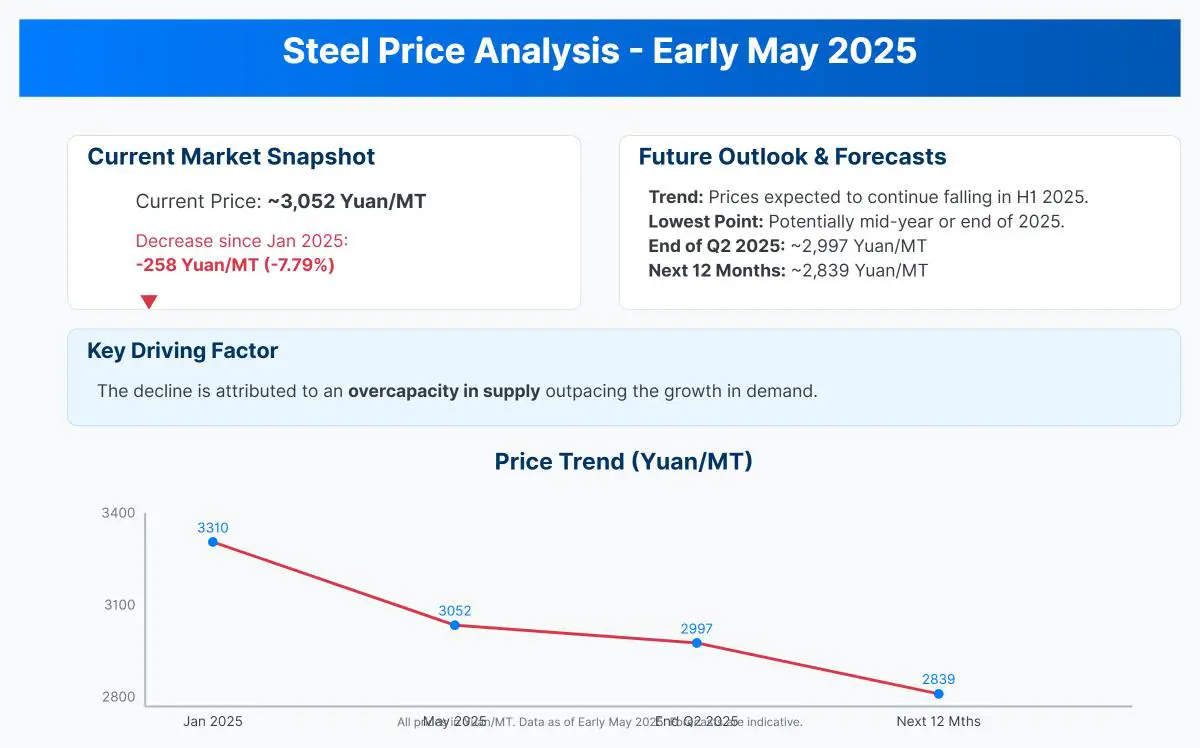
In early 2025, steel prices are notably declining. This trend is driven by global supply and demand factors. A 7.79% decrease at the beginning of the year highlights market dynamics, attributed to global overcapacity, economic slowdowns in various regions, and trade uncertainties.
Data-Driven Analysis of Steel Price Trends
Market forecasts indicate that steel prices will keep falling throughout the first half of 2025, potentially hitting their lowest point mid-year or by year’s end. The World Steel Association projects global steel demand to grow by 1.2% in 2025 compared to 2024, moving from approximately 1,751 million tonnes to 1,772 million tonnes of finished products. However, new steel capacity additions are expected to significantly outstrip demand growth.
Regional trends show a slight recovery in U.S. steel prices, with hot rolled coil prices reaching their highest levels since June 2024. This recovery is partly driven by efforts from steel mills to increase prices, alongside potential tariff impacts.
Stainless steel prices are influenced by the costs of raw materials, particularly nickel and chromium. Nickel prices are expected to stabilize between $15,000 and $20,000 per tonne in 2025, which can impact stainless steel pricing. Additionally, chromium prices play a significant role in determining the cost of stainless steel.
The steel market is anticipated to experience a gradual recovery starting from 2026. Factors such as the phasing out of free allowances under the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) may accelerate price increases in Europe. The overall trend suggests that after reaching a low in 2025, steel prices are likely to begin a cycle of recovery leading up to 2027.
Global Steel Market Trends
Overview of Steel Market Trends
The steel market is influenced by a variety of factors, including production levels, global demand, trade policies, and economic conditions. Understanding these trends is crucial for stakeholders in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive.
Key Drivers of Market Trends
Production and Supply-Demand Balance
Global crude steel production is expected to reach 1.846 billion tonnes in 2025, which is 34 million tonnes less than earlier estimates due to trade uncertainties and tariffs. Despite this reduction, apparent steel consumption is expected to grow by 1.2%, driven by steady demand in China and significant growth in India, although the addition of 50 million tonnes of new capacity in 2024 has pushed global overcapacity to approximately 573 million tonnes, far exceeding demand growth projections.
Trade Policies
Trade policies, such as reciprocal tariffs and geopolitical tensions, significantly impact the steel market. For instance, U.S. import tariffs have disrupted supply chains and weakened efforts to recover production. These policies create uncertainty, affecting market stability and prices.
Regional Dynamics
Regional production trends also play a crucial role in shaping the global steel market. China, having surpassed 1 billion tonnes in production in 2024, continues to influence global pricing through its export volumes. Meanwhile, strong output in countries like Vietnam, South Korea, and India supports regional demand in Asia. In the U.S., steel prices bottomed in mid-2024 but have shown modest recovery in the latter half of the year, boosting domestic output.
Cost Pressures
Increasing costs of scrap metal and energy, driven by investments in sustainability, are affecting profit margins across the steel industry. These rising costs are crucial considerations for market participants, influencing production decisions and pricing.
Sector-Specific Demand Trends
Construction and Infrastructure
The construction and infrastructure sector remains the primary driver of steel consumption. Urbanization and global infrastructure investments are fueling demand, making this sector a pivotal component of the steel market.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is transitioning towards electric vehicles (EVs), which increases the demand for high-strength, lightweight steel components. This shift is driving innovation and specialization within steel production to meet the evolving needs of automotive manufacturers.
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector, particularly wind turbines and solar infrastructure, requires specialized steel, creating niche demand within the market. As investments in renewable energy grow, this sector’s influence on steel consumption becomes more pronounced.
Transformative Industry Shifts
Sustainability Push
The steel industry is prioritizing sustainability through the adoption of Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) and low-carbon production methods. Green steel projects, focusing on hydrogen-based reduction, are gaining traction amid stricter environmental regulations. These initiatives are reshaping production practices and market dynamics.
Digitalization
The integration of IoT and AI technologies is improving operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and supply chain agility in the steel industry. Digitalization efforts are critical for enhancing competitiveness and adapting to market changes.
Market Consolidation
Mergers and partnerships within the steel industry are accelerating to enhance competitiveness and fund innovation. This trend towards consolidation is expected to drive efficiency and bolster the industry’s capacity to meet future demand.
Market Outlook
The global steel market, valued at $1.47 trillion in 2024, is projected to grow at a 4.6% CAGR through 2035. Despite short-term price declines due to oversupply and weaker capacity utilization, long-term growth is anticipated, supported by infrastructure spending and the adoption of green steel. However, risks such as trade disputes, energy price volatility, and slower-than-expected EV adoption could dampen growth prospects.
Analysis of Global Steel Demand
Definition and Importance of Global Steel Demand
Global steel demand represents the worldwide need for steel across various industries and regions. This metric is crucial as it drives production decisions, influences market prices, and impacts economic growth. Understanding global steel demand helps stakeholders make informed choices regarding investments, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Factors Affecting Global Steel Demand
Infrastructure and Construction
Infrastructure and construction projects are major consumers of steel. Urbanization, population growth, and government investments in public works drive demand in this sector. Steel is used extensively in buildings, bridges, roads, and other structures, making it indispensable for modern development.
Automotive Industry
Electric vehicles (EVs) increasingly rely on high-strength, lightweight steel for batteries and frames, boosting demand in the automotive sector. As the International Energy Agency predicts a rise in EV sales, the automotive industry’s need for specialized steel products is expected to grow.
Renewable Energy
Steel is crucial for renewable energy projects like wind turbines and solar panels, as it must endure harsh environmental conditions. With increasing investments in renewable energy infrastructure, steel consumption in this sector is set to rise.
Regional Demand Variations
Asia
Asia, particularly China and India, plays a pivotal role in global steel demand. China, the world’s largest steel consumer, is expected to maintain steady consumption levels. India’s steel demand is experiencing significant growth, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development.
Europe
Europe’s steel demand is influenced by economic policies and sustainability initiatives. The phasing out of free allowances under the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) may affect steel prices and demand. Investments in green steel technologies are also shaping the market dynamics in this region.
North America
In North America, steel demand is supported by construction projects and the automotive industry. The U.S. has seen a modest recovery in steel prices, which encourages domestic production and consumption. Trade policies and tariffs continue to impact the market, creating both opportunities and challenges for stakeholders.
Supply Dynamics
The global steel supply is expected to surpass demand in 2025, leading to overcapacity. New capacity additions have resulted in lower capacity utilization rates, which may decrease steel prices. This imbalance between supply and demand highlights the need for strategic adjustments in production and distribution to stabilize the market.
Impact of Global Steel Demand on Market Prices
Global steel demand directly influences market prices. When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise, whereas overcapacity can lead to price declines. With forecasts predicting moderate demand growth and supply overcapacity, stakeholders must monitor trends to adapt strategies and maintain competitiveness.
Steel Production and Demand
Overview of Steel Production Process
Steel production is a complex, multi-step process that involves converting raw materials into finished steel products. The primary methods of steel production are the Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) and the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF).
Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF)
BOF is a traditional method where molten iron from a blast furnace is converted into steel. In this process, oxygen is blown through molten iron to lower its carbon content and eliminate impurities. The BOF method is known for producing large volumes of steel efficiently.
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
EAF is a more flexible and environmentally friendly method that uses electric arcs to melt scrap steel or direct reduced iron (DRI). This method is gaining popularity due to its lower carbon footprint and ability to use recycled materials.
Factors Influencing Steel Production
Several factors affect steel production, including raw material availability, energy costs, technological advancements, and regulatory policies.
Raw Material Availability
The availability and cost of raw materials like iron ore, coal, and scrap metal significantly impact steel production. Changes in raw material prices can affect production costs and output levels.
Energy Costs
Steel production is energy-intensive, and energy costs play a crucial role in determining production efficiency and profitability. Rising energy prices can increase production costs and affect the competitiveness of steel producers.
Technological Advancements
Innovations in steel production technologies, such as the development of more efficient furnaces and automation, can enhance production capacity and reduce costs. Emerging technologies like hydrogen-based steelmaking are also being explored to reduce carbon emissions.
Regulatory Policies
Environmental regulations and trade policies can influence steel production. Stricter emissions standards push producers to adopt cleaner technologies, while trade policies like tariffs can affect the global supply chain and market dynamics.
Forecasts for Steel Production in 2025
Global steel production is expected to face several challenges and opportunities in 2025. According to recent data, global crude steel production reached 1.878 billion tonnes in 2024. However, projections for 2025 indicate a decline to 1.846 billion tonnes due to weak demand and trade uncertainties.
Regional Production Trends
- China: China’s steel production exceeded 1 billion tonnes in 2024, driven by a late-year recovery. Despite efforts to curb overcapacity, China remains a dominant player in the global steel market.
- United States: US production increased in late 2024; however, ongoing tariffs and trade tensions may limit growth in 2025.
- Asia (Ex-China): Countries like India and Vietnam are expected to continue increasing their steel output, supported by strong domestic demand and infrastructure investments.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Steel Production
Emerging technologies are poised to transform the steel industry by improving efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing product quality.
Hydrogen-Based Steelmaking
Hydrogen-based steelmaking is a new method that uses hydrogen instead of carbon to process iron ore. This method significantly reduces CO2 emissions and aligns with global decarbonization goals. Several pilot projects are underway, and widespread adoption could reshape the industry’s future.
Digitalization and Automation
The integration of IoT, AI, and automation in steel production processes enhances operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. These technologies enable better resource management, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
Relationship Between Steel Production and Demand
Steel production and demand are closely interlinked. When demand for steel rises, production typically increases to meet market needs. Conversely, overcapacity can lead to lower prices and reduced production activity.
Supply-Demand Balance
In 2025, global steel supply is expected to surpass demand, leading to overcapacity. This imbalance may result in lower steel prices and necessitate strategic adjustments in production and distribution to stabilize the market.
Market Dynamics
Market dynamics such as economic growth, infrastructure investments, and industrial activities drive steel demand. As a result, production levels adjust to meet these demand trends, helping to maintain a balanced market.
Comparative Analysis of Steel Prices
Steel prices can vary widely based on the type, grade, and region, and understanding these differences is essential for businesses that rely on steel. This section delves into a comparative analysis of steel prices, providing insights into the factors that influence variations across different types and regions.
Types of Steel and Their Pricing
Steel is categorized into various types, each with distinct properties and applications, leading to differing price points. Carbon steel is the most widely used type due to its versatility and affordability. Prices for carbon steel vary based on its carbon content and grade, which influences its strength and ductility. Lower-grade carbon steels tend to be less expensive but offer limited performance in demanding applications.
Stainless steel is valued for its resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for industries like food processing and chemical manufacturing. Prices are generally higher than carbon steel due to the added cost of alloying elements like chromium and nickel. Variations in nickel pricing can significantly affect stainless steel costs.
Alloy steel contains elements such as manganese, molybdenum, and vanadium, providing enhanced mechanical properties. Prices for alloy steel can fluctuate based on the specific alloying elements used and their market availability. These steels are often used in high-stress applications, justifying their higher cost.
Regional Price Variations
Steel prices vary by region due to production costs, demand, and local economic policies. In North America, steel prices are influenced by domestic production capacities and trade policies. The U.S. market has seen fluctuations due to tariffs and import restrictions, which can lead to higher domestic prices compared to global averages.
European steel prices are affected by environmental regulations and the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS). The anticipated phasing out of free allowances under the ETS is expected to impact prices, potentially leading to an increase from 2026 as producers adapt to stricter emissions standards.
Asia, particularly China, plays a dominant role in global steel pricing. Chinese production capacity and export volumes have a direct impact on regional and global steel prices. In addition, economic conditions in major Asian economies can influence demand and thus pricing trends.
Impact of Global Events on Steel Prices
Global events such as geopolitical tensions, trade agreements, and economic shifts can significantly influence steel prices. Tensions between major steel-producing and consuming nations can lead to trade barriers, affecting supply chains and causing price volatility. These tensions often result in tariffs and quotas, which alter market dynamics and pricing structures.
Economic growth or recession in key regions can drive demand changes, impacting steel prices. For instance, infrastructure investments in developing countries can boost demand and elevate prices, while economic slowdowns may lead to reduced consumption and price declines.
Data-Driven Insights
Recent data shows a global trend of declining steel prices due to overcapacity and moderate demand growth. However, regional variations exist, with the U.S. experiencing price resilience and Europe preparing for potential price recovery linked to regulatory changes. Understanding these data-driven insights helps stakeholders make informed decisions regarding purchasing and investment strategies.
Key Considerations for Stakeholders
For businesses and investors, monitoring steel price trends is essential to optimize purchasing strategies and manage costs. Factors such as type-specific demand, regional economic policies, and global market dynamics must be considered to effectively navigate the complexities of steel pricing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are current steel prices?
As of early May 2025, steel prices have declined significantly since the beginning of the year. The current trading price is approximately 3,052 Yuan/MT, reflecting a decrease of 258 Yuan/MT or 7.79% since January 2025. Market predictions indicate that steel prices will continue to fall throughout the first half of 2025, potentially reaching their lowest point around mid-year or by the end of 2025. By the end of the current quarter, prices are expected to stabilize around 2,997 Yuan/MT, with a further decrease to approximately 2,839 Yuan/MT over the next 12 months. This decline is attributed to an overcapacity in supply outpacing the growth in demand.
How is global steel demand affecting market prices?
Global steel demand significantly impacts market prices. When demand for steel rises, prices typically increase due to the competition for available supply. Conversely, when demand decreases, prices tend to fall as surplus steel accumulates. Currently, global steel demand is projected to grow modestly by 1.2% in 2025, driven by steady demand in regions like China and an upturn in India. However, despite this growth, the market is facing an overcapacity issue, with supply expected to outstrip demand. This surplus is leading to a downward pressure on steel prices, which have already seen a decline of about 7.79% since early 2025. Analysts predict that steel prices may continue to fall in the first half of 2025, with a potential stabilization and gradual recovery anticipated in the following years.
What are the forecasts for steel production in 2025?
Steel production forecasts for 2025 indicate a slight recovery in the global steel sector. According to Fitch Ratings, the outlook is neutral, with a modest increase in production expected. The World Steel Association projects global steel demand to grow by 1.2%, reaching approximately 1,772 million tonnes of finished products. In January 2025, world crude steel production was 151.4 million tonnes, a 4.4% increase from January 2024. Regionally, China’s production in February 2025 decreased by 3.3%, while India’s production rose by 6.3%. However, the market faces challenges due to overcapacity, with additional capacity leading to an estimated overcapacity of 573 million tonnes. This may result in decreased capacity utilization and potential downward pressure on steel prices. Overall, while demand grows modestly, the imbalance between supply and demand will influence production and pricing trends.
How do emerging technologies impact steel production?
Emerging technologies are significantly impacting steel production, primarily focusing on sustainability, efficiency, and innovation. Hydrogen-based steelmaking is one of the most notable advancements, substituting traditional coal with hydrogen to reduce the carbon footprint. This method emits only water vapor as a byproduct, making it a cleaner alternative. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies are also gaining traction, capturing CO2 emissions from blast furnaces to align with global carbon reduction goals.
Additionally, 3D printing and smart manufacturing allow for the creation of complex steel structures with reduced waste and improved efficiency. Automation and robotics enhance production by handling tasks such as material handling and quality checks, thereby improving efficiency and safety. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) optimize production processes and enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and maximizing output.
Smart steel supply chains, integrating AI, IoT, and blockchain technologies, provide real-time visibility and optimization, reducing costs and improving delivery times. Advanced coating technologies and recycling are also enhancing the durability of steel products and minimizing environmental impacts.
These advancements collectively influence market trends and steel prices by potentially adding a sustainability premium for green steel, reducing operational costs through efficiency gains, and stabilizing prices via improved supply chain transparency.
What factors influence steel price changes?
Steel prices are influenced by several key factors, making them subject to fluctuations based on various economic, environmental, and geopolitical conditions. One primary factor is supply and demand dynamics, where economic activity significantly impacts steel prices. During periods of economic growth, increased demand from sectors such as construction and manufacturing can drive prices up, especially if supply cannot keep pace. Global production levels, particularly in major steel-producing countries like China, also play a crucial role in determining prices.
Raw material costs, including iron ore and scrap metal, are vital components in steel production. Variations in the prices and availability of these materials directly affect steel costs. Energy prices, given the energy-intensive nature of steel manufacturing, are another significant factor; fluctuations in coal, natural gas, and electricity prices impact production costs and thus steel prices.
Trade policies and tariffs can influence steel prices by affecting supply. For instance, tariffs on steel imports can reduce competition from cheaper foreign steel, leading to higher domestic prices. Conversely, trade agreements that ease restrictions can lower prices by increasing the availability of imported steel.
Geopolitical instability and environmental regulations also affect steel prices. Political tensions can disrupt supply chains, while stringent environmental policies may limit production and drive up costs. Additionally, global economic trends, such as currency exchange rates and inflation, impact steel prices by affecting production costs and international competitiveness.
Lastly, natural disasters and weather-related disruptions can affect transportation and supply chains, causing volatility in steel prices. Understanding these factors is essential for analyzing market trends and predicting future price changes in the steel industry.
How do trade policies affect the global steel market?
Trade policies significantly influence the global steel market by altering competitive dynamics and impacting pricing strategies. Protectionist measures, such as tariffs, are often implemented to protect domestic steel industries from foreign competition. For example, the U.S. has imposed a 25% tariff on steel imports, which initially boosts domestic production and utilization rates. However, these benefits can be short-lived, as they often lead to increased costs for downstream industries and retaliatory actions from trade partners, affecting international relations.
Moreover, tariffs can cause trade diversion, where steel exporters shift focus to other regions, leading to oversupply and price suppression in those markets. This can result in global price volatility and affect supply chains, as industries may restructure to mitigate costs or explore alternative materials. Additionally, trade policies can prompt legal disputes and regulatory uncertainty, further complicating market conditions. Overall, trade policies shape the global steel market by influencing production, pricing, and international trade flows, with both immediate and long-term effects on industry dynamics.
