Imagine you’re tasked with choosing the right plating for a critical component in your project. Should you opt for the gleaming resilience of chrome or the robust protection of zinc? These two plating options often seem interchangeable, yet they serve distinct purposes and offer unique advantages. In this article, we’ll dive into the fundamental differences between zinc and chrome plating, examining their corrosion resistance, wear resistance, aesthetic appeal, cost implications, and industrial applications. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of which plating is best suited for your needs, ensuring your choice aligns perfectly with your project’s demands. So, which one will stand the test of time and elements? Let’s find out.
Overview of Zinc and Chrome Plating
Definition and Basics of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is a process where a thin layer of zinc is electrochemically applied to a metal surface. This involves immersing the object in a solution containing zinc ions and then using an electric current to deposit the zinc onto the substrate. The primary purpose of zinc plating is to provide corrosion resistance, as zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, protecting the underlying metal from rust and other forms of corrosion.
Definition and Basics of Chrome Plating
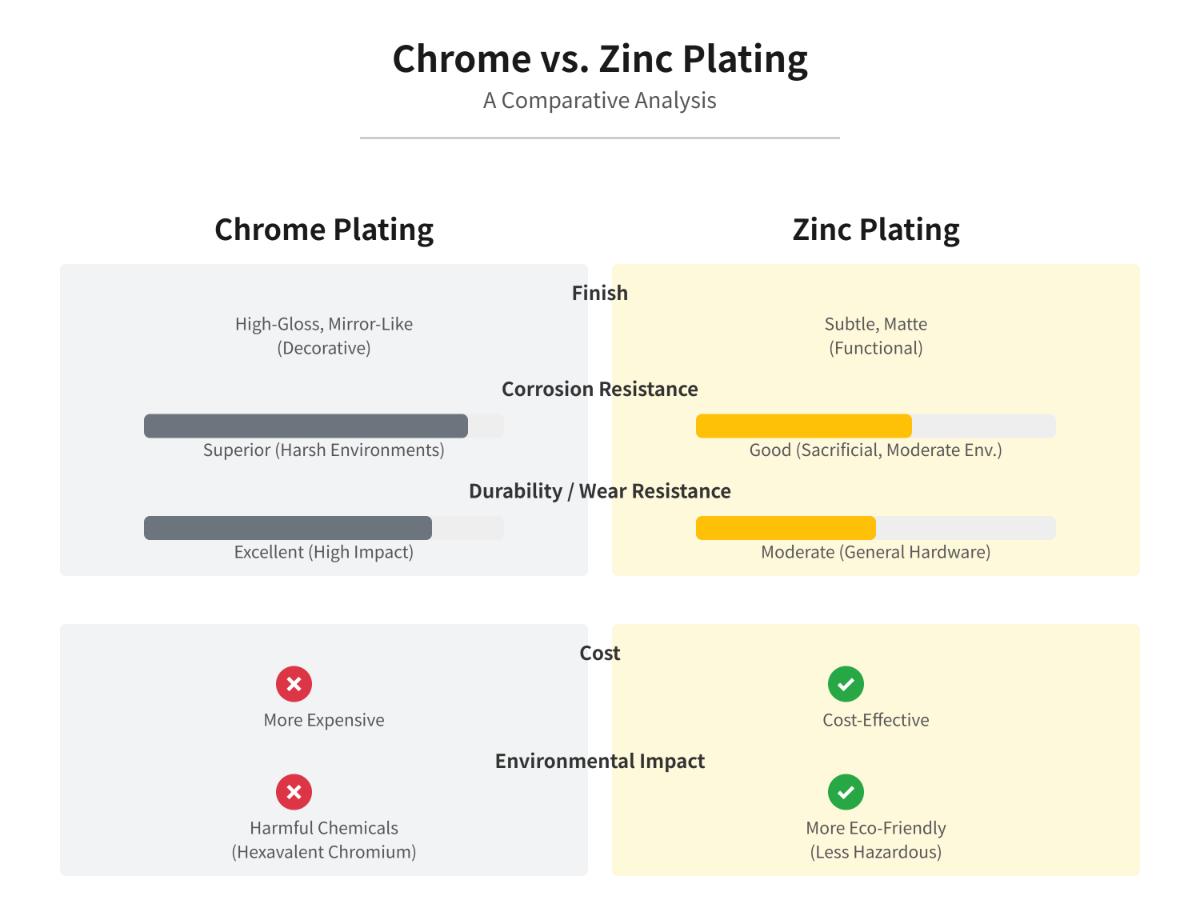
Chrome plating, also known as chromium plating, involves depositing a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object through electroplating, enhancing both its appearance and durability. The process provides a high-gloss, mirror-like finish and excellent resistance to corrosion and wear. Different types of chrome plating, such as decorative chrome, hard chrome, and thin dense chrome, cater to specific applications and requirements.
Introduction to Electroplating Process
Electroplating is a process that coats a metal object with a thin layer of another metal using an electric current. The object to be plated (cathode) is submerged in an electrolyte solution containing the metal ions to be deposited. An electric current is applied, causing the metal ions to move towards and deposit onto the surface of the object, enhancing its appearance and physical properties, such as corrosion resistance and hardness.
Comparative Analysis: Zinc vs. Chrome Plating
Corrosion Resistance
Zinc plating protects the underlying metal by corroding first, making it effective in less aggressive environments. This sacrificial layer ensures that the base metal remains intact, even as the zinc layer itself deteriorates over time.
Chrome plating offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments like those involving saltwater and industrial chemicals. The chromium layer forms a passive film of chromium oxide, which protects the underlying metal from further corrosion, making it ideal for applications where high corrosion resistance is essential.
Wear Resistance
Zinc plating provides moderate wear resistance, suitable for general hardware and fasteners where extreme wear is not a primary concern. The zinc layer can withstand some degree of abrasion but may wear off over time under high friction conditions.
Chrome plating excels in wear resistance, particularly in its hard chrome variant. Known for its high hardness, hard chrome plating can withstand significant mechanical stress and abrasion, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and wear resistance, such as hydraulic cylinders, pistons, and industrial machinery components.
Visual Appearance
Zinc plating typically results in a more subtle, matte finish that can be passivated with different colors, such as yellow, blue, or black, to enhance its appearance and corrosion resistance. It is often chosen for applications where aesthetics are less critical.
Chrome plating, especially decorative chrome, provides a high-gloss, mirror-like finish that is both visually appealing and easy to maintain. This shiny appearance makes chrome plating a popular choice for automotive trim, household fixtures, and other high-end consumer goods.
Cost and Environmental Impact
Zinc plating is usually cheaper and more environmentally friendly, using less expensive materials and generating less toxic waste. This process involves fewer hazardous chemicals and consumes less energy, making it a cost-effective option for many applications.
Chrome plating, while more expensive and energy-intensive, offers superior performance. However, it involves hazardous chemicals like hexavalent chromium, posing significant environmental challenges. Regulatory compliance and waste management for chrome plating operations can add to the overall cost and complexity of the process. Companies must invest in proper safety measures, waste treatment systems, and adhere to stringent environmental regulations to mitigate the risks associated with hexavalent chromium.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Corrosion Resistance of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating offers significant corrosion resistance because it acts sacrificially, meaning the zinc layer corrodes before the underlying metal. This protection is particularly effective in less aggressive environments with moderate exposure to corrosive elements. The zinc layer, even if scratched or damaged, continues to provide protection by sacrificing itself to prevent the base metal from rusting.
Zinc plating performs well in humid and hot conditions, providing a reliable barrier against atmospheric corrosion. However, its effectiveness diminishes in the presence of alkalis, sulfides, and acids, where the protective layer can degrade more rapidly. This makes zinc plating less suitable for highly corrosive environments such as industrial chemical exposure or marine applications.
Corrosion Resistance of Chrome Plating
Chrome plating, in contrast, provides excellent corrosion resistance in harsh conditions. The chromium layer forms a passive film of chromium oxide, which is highly stable and resistant to corrosion. This passive layer protects the underlying metal from further oxidation and corrosion, making chrome plating highly effective in aggressive environments such as saltwater exposure and industrial chemicals.
Additionally, chrome plating often involves multiple layers, including copper and nickel, which enhance its protective capabilities. These layers provide additional barriers to corrosion, further extending the lifespan of the coated metal. Chrome’s excellent resistance to a wide range of corrosive agents makes it ideal for applications where high durability and long-term protection are critical.
Comparative Analysis: Zinc vs. Chrome Plating for Corrosion Protection
When comparing zinc and chrome plating for corrosion protection, several factors need to be considered, including environmental suitability and maintenance requirements:
-
Environmental Suitability:
-
Zinc Plating: Best suited for general hardware, automotive components, and environments with moderate exposure to corrosive elements. Its sacrificial nature means it continues to protect even if the zinc layer is damaged.
-
Chrome Plating: Ideal for harsh environments, including marine and industrial settings, due to its superior resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand aggressive chemicals and saltwater exposure.
-
Durability and Maintenance:
-
Zinc Plating: Offers decent protection at a lower cost, making it a practical choice for many applications. However, it may require more frequent maintenance and replacement in highly corrosive environments.
-
Chrome Plating: Although more expensive, chrome plating provides long-term durability and less frequent maintenance, making it a cost-effective solution for critical applications where maximum corrosion resistance is essential.
Wear Resistance Comparison
Wear Resistance of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating provides moderate wear resistance, making it suitable for applications where extreme wear is not a primary concern. The zinc layer can withstand some abrasion but may not perform well in high-friction environments due to its relative softness compared to other metals, which limits its ability to endure significant mechanical stress and abrasion over time.
Zinc plating is typically used in low to moderate wear applications such as:
- Household fixtures
- General hardware
- Certain automotive parts
In these settings, the primary role of zinc plating is often to provide corrosion resistance, with wear resistance being a secondary benefit.
Wear Resistance of Chrome Plating
Hard chrome plating is known for its excellent wear resistance. The chromium layer provides a hard surface with a Rockwell C hardness typically between 68 and 72, which is significantly higher than that of zinc plating. This high hardness allows chrome-plated surfaces to withstand substantial mechanical stress and abrasion, making them ideal for high-impact applications.
Common applications of chrome plating include:
- Automotive exteriors
- Heavy machinery
- Aerospace components
Chrome plating’s high wear resistance ensures durability and performance in demanding environments with constant friction and stress.
Comparative Analysis: Zinc vs Chrome Plating for Wear Resistance
When comparing the wear resistance of zinc and chrome plating, several key differences emerge:
- Hardness: Chrome plating offers a much harder surface compared to zinc plating, which translates to higher wear resistance. This makes chrome plating suitable for high-impact and high-friction applications.
- Durability: Due to its higher hardness, chrome plating provides longer-lasting protection against wear and tear, whereas zinc plating may wear off more quickly under similar conditions.
- Application Suitability: Zinc plating is suitable for low to moderate wear environments where corrosion resistance is key, while chrome plating is ideal for applications needing high wear resistance and durability.
Key Differences
| Feature | Chrome Plating | Zinc Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | High, suitable for high-impact applications | Moderate, more suitable for low to moderate wear |
| Hardness | Rockwell C hardness of 68-72 | Relatively softer |
| Durability | Long-lasting, excellent under abrasion | Moderate, may wear off under high friction |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, heavy machinery, aerospace | Household fixtures, general hardware |
The choice between zinc and chrome plating for wear resistance largely depends on the specific requirements of the application. Chrome plating is preferred for environments where high wear resistance and durability are critical, while zinc plating is more cost-effective for less demanding applications.
Aesthetic Differences
Visual Appearance of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating features a subdued, matte finish achieved through the electrochemical application of a thin zinc layer onto a metal surface. Zinc’s appearance can be modified through post-treatment processes like passivation, which adds colors such as yellow, blue, or black, providing customization and versatility.
Visual Appearance of Chrome Plating
Chrome plating involves depositing a thin layer of chromium onto a metal surface, resulting in a shiny, reflective finish prized for its aesthetic appeal. This luxurious finish is often associated with high-end products and is valued for its striking appearance.
Aesthetic Considerations in Various Applications
Decorative and Consumer-Facing Products
The shiny, mirror-like finish of chrome plating makes it ideal for decorative applications. It is commonly used in products where appearance is crucial, such as vehicle parts, household appliances, and furniture. The high-gloss finish of chrome plating adds a touch of luxury and sophistication, enhancing the visual appeal of these items.
While zinc plating does not offer the same level of shine, it provides a clean and industrial look that can be appealing in certain contexts. Its matte finish is suitable for architectural elements, storefronts, restaurants, and retail spaces where a less flashy, more understated look is preferred. The ability to apply different colors through passivation also adds to its aesthetic versatility.
Industrial and Functional Applications
Beyond its decorative appeal, chrome plating is also used in industrial applications where both aesthetics and durability are important. The hard, glossy surface not only looks good but also provides excellent wear and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for automotive exteriors, heavy machinery, and aerospace components.
In industrial settings, the aesthetic value of zinc plating is often secondary to its protective qualities, but its clean, professional look suits functional items like fasteners, hardware, and tools. The matte finish of zinc plating gives these items a professional, utilitarian look that is appropriate for their intended use.
Cost Analysis
Cost Factors in Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is known for being cost-effective due to its straightforward process of electrochemically depositing zinc onto a metal surface. This simplicity translates to lower production costs because it uses less energy and fewer specialized materials. Zinc plating’s affordability makes it ideal for large-scale or budget-sensitive projects, and its low cost allows for frequent replacements and maintenance without major expense.
Key Cost Considerations:
- Energy Efficiency: Zinc plating requires less energy compared to chrome plating, which helps reduce – Material Costs: The materials used in zinc plating are usually cheaper and easier to find.
- Process Simplicity: The straightforward nature of zinc plating reduces the need for specialized equipment and labor, further driving down costs.
Cost Factors in Chrome Plating
Chrome plating, while more expensive, offers significant benefits that justify its higher cost for certain applications. The process involves the use of specialized electrolyte solutions and higher energy consumption, contributing to the increased cost. However, chrome plating provides enhanced durability, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal, making it a valuable investment for premium applications.
Key Cost Considerations:
- Specialized Materials: Chrome plating requires costly electrolyte solutions and other specialized chemicals.
- Energy Consumption: The process is more energy-intensive, leading to higher operational costs.
- Labor and Equipment: The need for precise control and specialized equipment adds to the cost of chrome plating.
Comparative Cost Analysis: Zinc vs Chrome Plating
When comparing the costs of zinc and chrome plating, several factors emerge that influence the decision-making process:
- Initial Investment: Zinc plating generally requires a lower initial investment due to its simpler process and lower material costs. Chrome plating, on the other hand, demands a higher initial investment because of the specialized materials and equipment needed.
- Long-Term Costs: Although zinc plating is cheaper initially, chrome plating can provide better long-term value for applications needing high durability and less maintenance. The enhanced wear resistance and corrosion protection offered by chrome plating can result in fewer replacements and lower – Application Suitability: For applications where budget constraints are a major consideration, zinc plating is often the preferred choice. However, for high-performance applications requiring superior durability and aesthetic qualities, the higher cost of chrome plating is justified.
Industry-Specific Cost Reduction Strategies
Different industries employ various strategies to manage and reduce the costs associated with plating:
Automotive Industry
- Zinc Alloys: Utilizing zinc alloys in die-casting reduces production costs by lowering energy consumption and improving mold usage.
- Precision Machining: Optimizing machining processes for zinc-plated components can lead to significant cost savings.
Aerospace and Heavy Machinery
- Selective Plating: Applying chrome plating only to critical areas that require high wear resistance can reduce – Process Optimization: Implementing advanced process controls and energy-efficient technologies can lower the operational costs of chrome plating.
Knowing the costs and benefits of each plating method is key to making smart choices in metal finishing.
Industrial Applications
Common Applications of Zinc Plating
General Hardware and Fasteners
Zinc plating is commonly used in the production of general hardware and fasteners, such as screws, bolts, and nuts. Its primary function in these applications is to provide corrosion resistance, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the hardware over time. The sacrificial nature of the zinc layer ensures that the underlying metal is protected from rust and degradation.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, zinc plating is commonly applied to under-the-hood components like brackets, clamps, and fasteners, where corrosion resistance is crucial. These parts are often exposed to moisture and various chemicals, making corrosion resistance a critical factor. Zinc plating offers an economical solution that ensures the longevity and reliability of these components.
Electrical and Electronics
Zinc plating is also used in electrical and electronic components to enhance conductivity and provide corrosion protection. Items such as connectors, terminals, and switch plates benefit from the conductive properties of zinc, which helps maintain efficient electrical connections and provides corrosion protection.
Common Applications of Chrome Plating
Automotive Exteriors
Chrome plating is highly valued in the automotive industry for its aesthetic appeal and durability. It is commonly used on exterior parts such as bumpers, grilles, and trim to provide a high-gloss, mirror-like finish that enhances the vehicle’s appearance. Additionally, the hard chrome layer offers excellent wear and corrosion resistance, protecting these components from environmental damage.
Heavy Machinery
In heavy machinery, chrome plating is used on parts subjected to significant mechanical stress and abrasion, such as hydraulic cylinders, pistons, and shafts. The hard chrome layer increases surface hardness and wear resistance, ensuring these components can withstand harsh operational conditions and prolonging their service life.
Aerospace Components
The aerospace industry utilizes chrome plating for critical components that require high durability and corrosion resistance. Parts such as landing gear, engine components, and structural elements benefit from the enhanced protection provided by chrome plating, which helps maintain their performance and safety standards.
Sector-Specific Uses: Automotive, Aerospace, Construction
Automotive Sector
Both zinc and chrome plating are extensively used in the automotive sector, but their applications vary based on the required properties. Zinc plating is preferred for internal components and fasteners where cost-effectiveness and moderate corrosion resistance are key. Chrome plating, on the other hand, is used for exterior parts and high-stress components that demand superior aesthetics and durability.
Aerospace Sector
In the aerospace sector, chrome plating is favored for its exceptional wear resistance and ability to withstand extreme conditions. It is used on critical components that require long-lasting protection and minimal maintenance. Zinc plating may be used for less critical parts that need corrosion resistance, but chrome plating is often preferred for its high performance.
Construction Sector
The construction industry benefits from both zinc and chrome plating for different applications. Zinc plating is commonly used for structural fasteners, fittings, and other hardware exposed to the elements, providing essential corrosion protection at a lower cost. Chrome plating is utilized for specialized tools and equipment that require enhanced durability and wear resistance, ensuring they can handle the rigors of construction work.
Advanced Applications in New Industries
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, zinc plating is used for components in wind turbines and solar panel mounts to protect against environmental corrosion. Chrome plating is applied to parts that require high wear resistance and durability, such as hydraulic systems in wind turbines.
Medical Devices
Chrome plating finds applications in the medical device industry for instruments and equipment that need to maintain a high level of cleanliness and resistance to wear. The smooth, hard surface of chrome-plated tools ensures they can be sterilized easily and remain durable through repeated use.
Electronics and Technology
Both zinc and chrome plating are employed in the electronics and technology sectors. Zinc plating is used for connectors and housings to improve conductivity and provide corrosion resistance. Chrome plating is applied to components that require a high level of wear resistance and aesthetic appeal, such as certain consumer electronics and high-end devices.
The choice between zinc and chrome plating in these industries depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the need for corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic considerations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc plating and chrome plating are two common techniques used for protecting metal surfaces. Each has its own environmental impact, sustainability aspects, costs, and applications.
Environmental Impact
Zinc plating is more environmentally friendly than chrome plating due to its use of fewer hazardous chemicals and reduced waste production. Modern techniques focus on minimizing waste, making the process safer for both the environment and workers.
Chrome plating poses significant environmental challenges, especially due to the use of toxic hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen. This requires strict safety measures and advanced wastewater treatments to protect both the environment and workers.
Sustainability
Zinc plating is sustainable because zinc can be recycled, contributing to a circular economy. The cost-effectiveness and simplicity of the process also make it a practical choice for large-scale manufacturing.
While chrome plating offers a long-lasting protective layer that can reduce the need for frequent maintenance, its sustainability is compromised by the environmental impact of the chemicals used. Despite its higher cost, chrome plating’s superior durability can justify its use in specific premium applications.
Cost and Efficiency
Zinc plating is known for its cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for high-volume production. The process is simpler and requires lower energy consumption, reducing overall manufacturing costs.
Although chrome plating is more expensive due to specialized materials and higher energy use, its superior durability and aesthetics can justify the cost for high-end applications. However, the process requires strict environmental controls, reducing its widespread adoption due to the potential release of hazardous chemicals.
Applications and Versatility
Zinc plating is widely used in various industries, including automotive, construction, and electronics, thanks to its corrosion resistance and versatility. It provides reliable protection against harsh environmental conditions, thus extending the lifespan of the products it coats. This versatility makes zinc plating a practical choice for a broad range of applications.
Chrome plating is ideal for applications requiring high surface hardness and wear resistance, such as automotive exteriors and heavy machinery. Its superior protection in harsh conditions makes it suitable for demanding environments, although it requires more stringent environmental controls. The combination of durability and aesthetic appeal ensures that chrome plating remains a valuable option for specific high-performance applications.
Standards Compliance
Zinc plating follows well-established standards to ensure its quality and performance. One of the most prominent standards is ASTM B633, which provides comprehensive guidelines for zinc coatings applied to iron and steel. This standard categorizes zinc plating into six types, each specifying different chromate or passivate treatments, such as colorless or colored chromates. It also outlines Service Conditions (SC1 to SC4) that define the minimum thickness of the zinc coating required for various environmental exposures. These conditions determine the zinc coating thickness needed for various environments, from mild indoor (SC1) to harsh outdoor (SC4).
Zinc plating also aligns with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive, particularly when using trivalent chromates. Trivalent chromates are RoHS compliant as they do not contain hexavalent chromium, which is restricted due to its environmental and health hazards. This compliance makes zinc plating a more environmentally friendly option compared to processes that use hexavalent chromium.
Chrome plating must comply with stringent environmental regulations due to the use of hexavalent chromium, a substance classified as a carcinogen. These regulations are crucial for managing the environmental and health risks associated with chrome plating. Facilities engaged in chrome plating are required to implement strict waste and emission controls, ensuring that hexavalent chromium is properly managed to minimize environmental impact.
Chrome plating lacks a specific ASTM standard like ASTM B633 for zinc plating. However, it follows various process standards to ensure quality, often involving combinations of nickel, copper, and chromium layers to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Facilities must comply with EPA and international regulations to control emissions and treat wastewater from hexavalent chromium.
When comparing the standards compliance of zinc and chrome plating, several key differences arise. Zinc plating, particularly with trivalent chromates, is more environmentally friendly and RoHS compliant. Chrome plating, on the other hand, involves hexavalent chromium, necessitating rigorous environmental controls to manage its carcinogenic risks. Zinc plating benefits from a clear, detailed standard (ASTM B633) that outlines classifications and service conditions. Chrome plating lacks a direct equivalent but follows various guidelines to maintain quality and safety. Both plating methods must adhere to environmental regulations, but chrome plating faces stricter controls due to the hazardous nature of hexavalent chromium.
These differences underscore the importance of considering both environmental impact and regulatory compliance when choosing between zinc and chrome plating for specific applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
What are the differences between zinc and chrome plating?
Zinc and chrome plating differ primarily in their finish, corrosion resistance, durability, cost, and environmental impact. Chrome plating offers a high-gloss, mirror-like finish that is visually appealing for decorative applications. It provides superior corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments, and has excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for high-impact uses like automotive exteriors and aerospace components. However, chrome plating is more expensive and involves environmentally harmful chemicals such as hexavalent chromium.
In contrast, zinc plating has a more subtle, matte finish and acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding before the underlying metal. It is more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, using less hazardous chemicals. Zinc plating is ideal for less aggressive environments and moderate wear conditions, often used in architectural elements and general hardware.
Which is better for corrosion resistance?
For corrosion resistance, chrome plating is generally better than zinc plating. Chrome plating, especially when layered over copper and nickel, provides superior protection in harsh environments such as saltwater and industrial settings. This multilayer approach enhances its anti-corrosion properties, making it highly durable and resistant to wear and tear.
On the other hand, zinc plating offers good corrosion resistance in less aggressive environments. It acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding to protect the underlying metal, which is effective in humid conditions but less durable in more severe environments.
Therefore, for applications exposed to extreme conditions, chrome plating is the preferable choice due to its enhanced durability and superior corrosion resistance. In contrast, zinc plating is more suitable for moderate conditions and is a cost-effective option for general protection needs.
What are the applications of chrome and zinc plating?
Zinc plating is widely utilized in industries such as automotive, construction, aerospace, and electronics due to its excellent corrosion resistance, cost-effectiveness, and ability to enhance wear resistance. In the automotive sector, it is used to protect components like gears, fasteners, and chassis. In construction, it is applied to steel beams and fasteners to withstand environmental conditions. Aerospace and defense industries use zinc plating for components exposed to harsh environments, while in electronics, it improves conductivity and solderability in connectors and circuit boards.
Chrome plating, known for its high durability and aesthetic appeal, is used extensively in automotive exteriors for trim and other visible components due to its shiny finish and high wear resistance. It is also applied in heavy machinery and aerospace for protection against extreme conditions like high friction and harsh chemicals. Additionally, chrome plating is popular in consumer goods for its luxurious appearance and ease of maintenance.
How does electroplating relate to zinc and chrome plating?
Electroplating is a crucial process in zinc and chrome plating, as it involves using electrolysis to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a substrate. In zinc plating, a layer of zinc is electroplated onto the metal surface to provide corrosion protection, acting as a sacrificial anode that corrodes instead of the base metal. This makes it ideal for preventing rust, especially in humid environments. Chrome plating, on the other hand, deposits a layer of chromium, enhancing surface hardness, wear resistance, and providing an aesthetically pleasing shiny finish. While chrome plating is often used in high-impact applications and for decorative purposes, it may require a nickel undercoat to enhance its corrosion protection. Both methods leverage the electroplating process to improve the durability and appearance of metal parts, but they cater to different needs and applications, as discussed earlier.
What are the cost implications of choosing zinc vs chrome plating?
When choosing between zinc and chrome plating, cost considerations encompass several factors such as initial investment, durability, maintenance, and environmental impact.
Zinc plating is generally more cost-effective due to its simpler electroplating process, which requires less specialized equipment and energy. This makes it suitable for large-scale or budget-sensitive projects focused primarily on corrosion protection. However, zinc-plated components may need more frequent replacement compared to chrome-plated ones.
Chrome plating, on the other hand, is more expensive initially but offers superior durability and aesthetic appeal. It’s ideal for premium applications where a high-quality finish is essential. The cost varies based on factors like the thickness of the chrome layer and additional operations such as grinding or polishing. Chrome plating also involves the use of hazardous chemicals, increasing operational costs due to stringent environmental regulations.
Are there any environmental advantages of zinc plating over chrome plating?
Zinc plating offers several environmental advantages over chrome plating. Firstly, zinc plating uses less hazardous chemicals, avoiding toxic substances like hexavalent chromium found in chrome plating, which poses significant health and environmental risks. Secondly, zinc plating produces minimal waste and its coatings are highly recyclable, promoting a circular economy. In contrast, chrome plating generates more hazardous waste due to the chemicals involved.
Additionally, zinc plating is more energy-efficient, reducing operational costs and lowering the carbon footprint. Furthermore, zinc plating generally results in less water and air pollution, requiring less stringent waste management compared to chrome plating. Lastly, zinc plating enhances the durability of metal products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby decreasing waste generation over time. Thus, from an environmental perspective, zinc plating is a more sustainable option compared to chrome plating.
